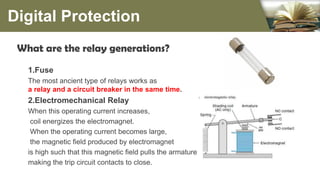
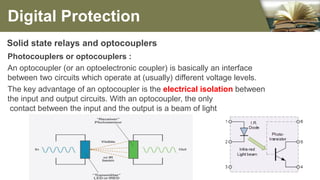
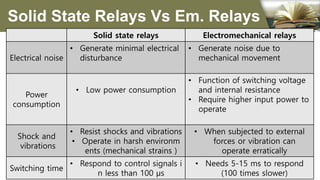
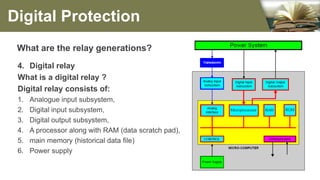
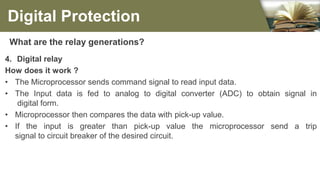
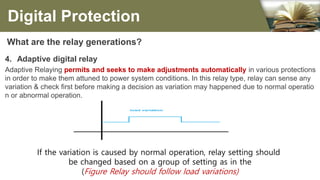
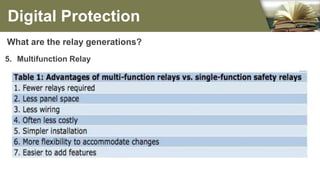
The document summarizes the different generations of electrical relays used in digital protection systems. It discusses fuse relays, electromechanical relays, solid state relays, digital relays, adaptive digital relays, multifunction relays, and intelligent relays. Electromechanical relays were prone to failures over time but newer digital and solid state relays are more reliable with no moving parts. Digital relays allow for more complex functions, self-testing, and communication compared to earlier relay technologies. Adaptive digital relays can automatically adjust settings based on changes in power system conditions. Multifunction relays provide multiple protection functions in a single unit to reduce space and wiring needs. Intelligent relays allow customers to change