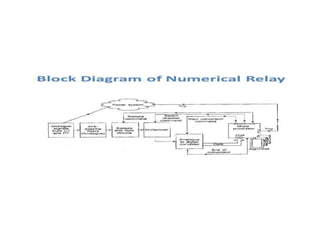
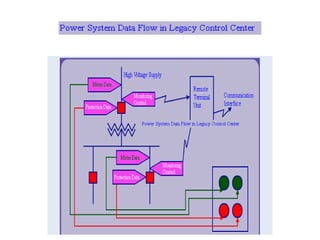
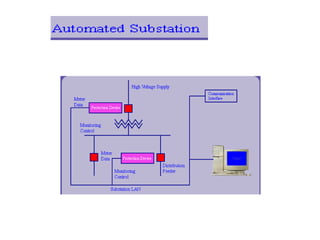
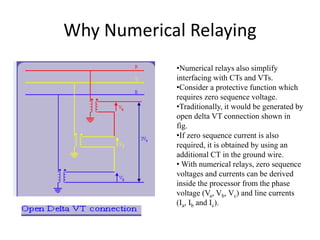
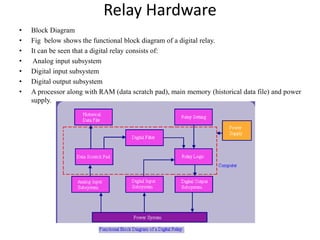
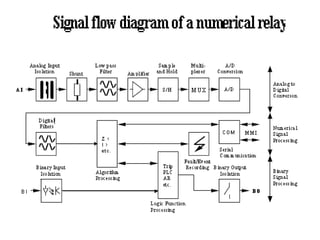
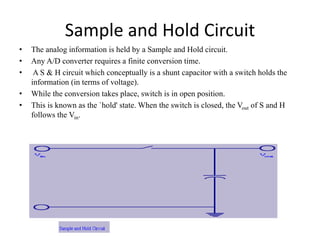
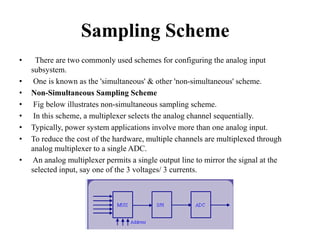
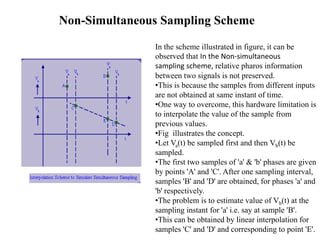
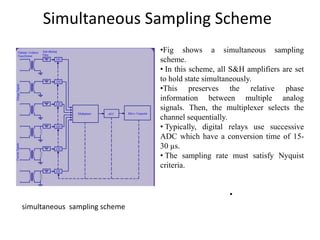
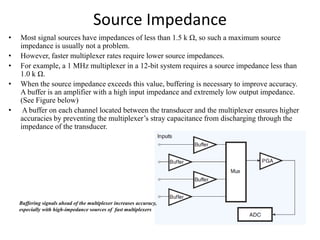
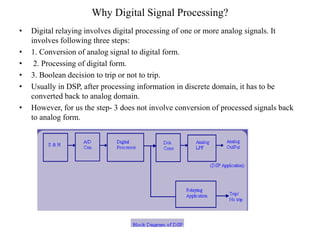
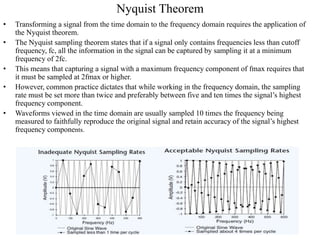
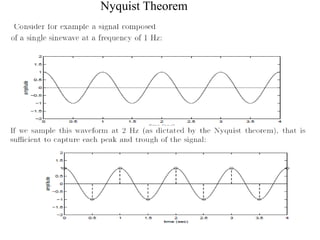
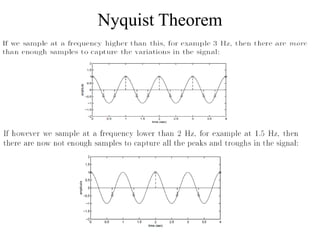
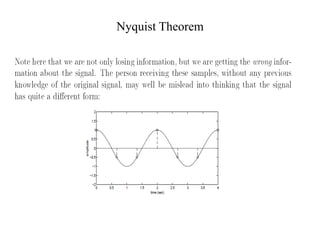
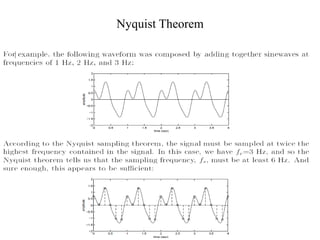
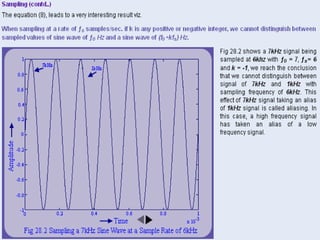
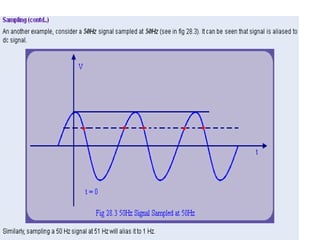
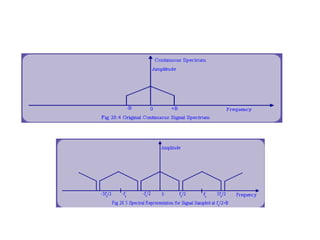
Numerical relays provide several advantages over electromechanical and solid state relays including improved reliability, flexibility, and performance. They allow for advanced protection schemes through programming and use of microprocessors. Numerical relays also simplify interfacing with current and potential transformers, enable advanced functions like phasor measurement, and provide time-stamped fault data for analysis. Their main advantages are reliability, security, dependability, and ability to implement new protection schemes through programming.