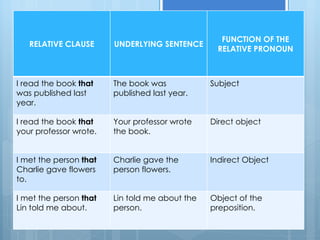
A relative clause is a dependent clause that provides information about a noun or noun phrase in the main clause. There are two types of relative clauses: restrictive and non-restrictive. Restrictive relative clauses are essential to the meaning of the sentence and are not set off by commas, while non-restrictive clauses provide extra information and are set off by commas. Relative pronouns like who, whom, which, and that are used to replace the noun in the relative clause and avoid repetition.


![How can RELATIVE CLAUSES be recognized? It contains a subject and a verb. It will begin with a relative pronoun [who, whom, which or that] It functions as an adjective. Richard kept the gift which I did not accept.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativeclauses-111210203427-phpapp01/85/Relative-clauses-3-320.jpg)