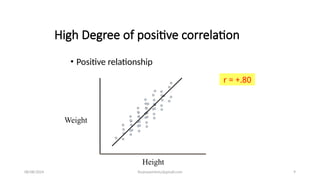
The document discusses correlation and regression analysis, explaining the relationship between variables, correlation coefficients, and methods for studying correlation. It distinguishes between correlation and causation, describes types of correlations, and introduces regression analysis for predicting variable values. Additionally, it covers logistic regression and its application in modeling binary outcomes based on independent variables.