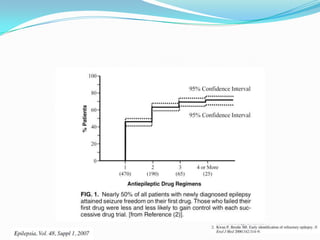
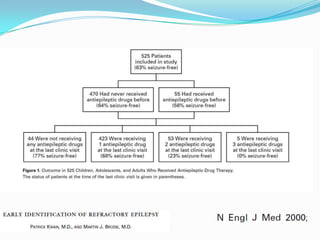
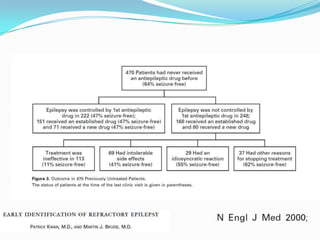
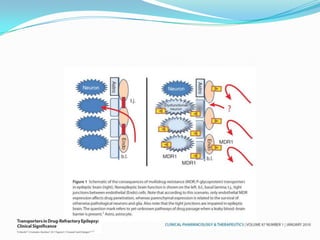
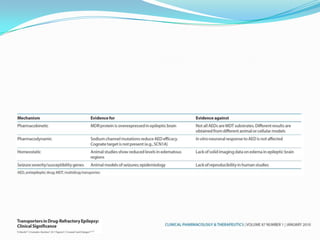
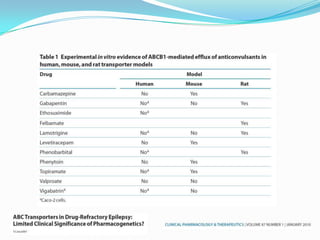
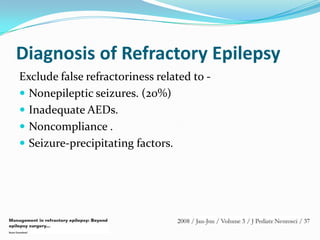
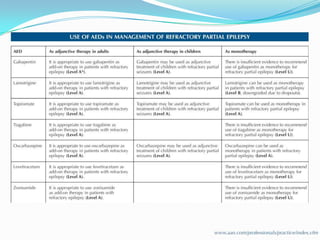
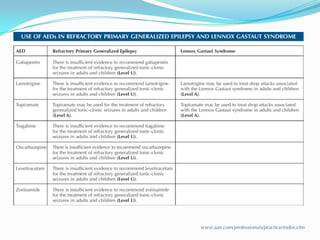
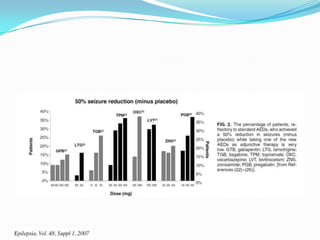
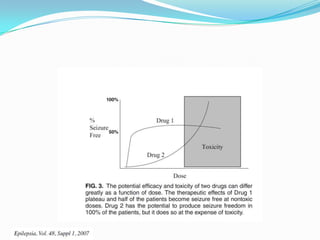
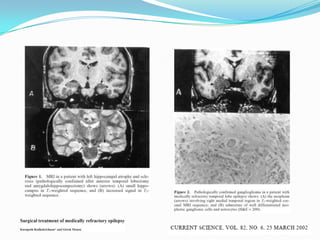
This document discusses refractory epilepsy, including definitions, epidemiology, mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment approaches. It defines refractory epilepsy as the absence of response to two anti-epileptic drugs at reasonable doses, with a minimum seizure frequency of one per month. It estimates that 20% of people with epilepsy have refractory seizures, totaling around 1 million people in India. Causes of refractory epilepsy include drug transporter issues, target resistance, and intrinsic disease severity. Surgical treatment and alternative therapies like the ketogenic diet, vagus nerve stimulation, polymers, and electrical brain stimulation are reviewed as potential treatment options.