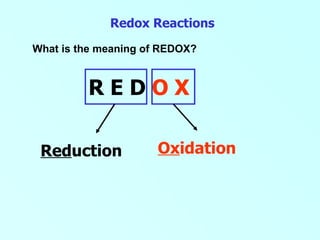
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between reactants, resulting in both oxidation and reduction occurring simultaneously. Oxidation is defined as either the loss of electrons or gain of oxygen. Reduction is defined as either the gain of electrons or loss of oxygen. Common examples of redox reactions in daily life include combustion, corrosion/rusting, photosynthesis, and respiration.