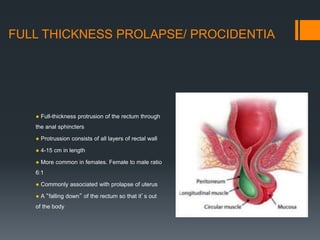
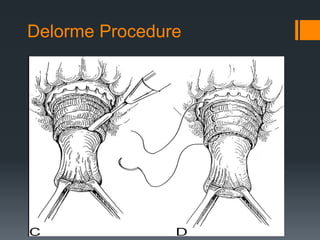
This document discusses rectal prolapse, including different types (full thickness, internal, mucosal), causes, clinical features, and treatment options. It describes full thickness prolapse as a full-thickness protrusion of the rectum through the anal sphincters. Mucosal prolapse involves protrusion of the rectoanal mucosa only. Treatment includes non-operative options like fiber supplements as well as surgical procedures. Perineal surgeries include resection, reefing, and encirclement techniques while abdominal surgeries include anterior and posterior rectopexy to fixate the rectum. Laparoscopic rectopexy is now commonly used with lower morbidity than open abdominal procedures. Surgery aims to correct the