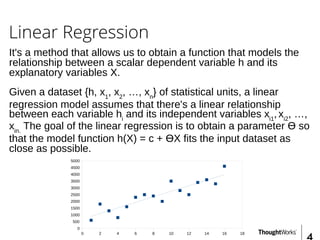
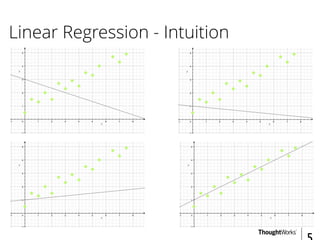
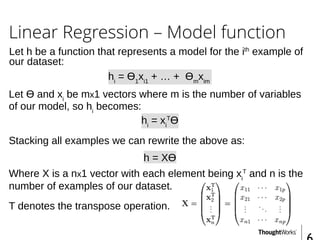
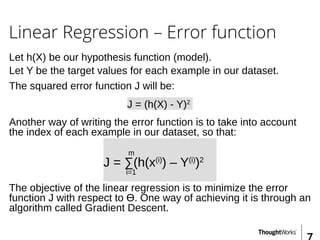
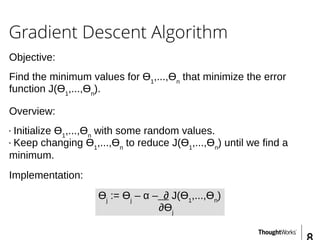
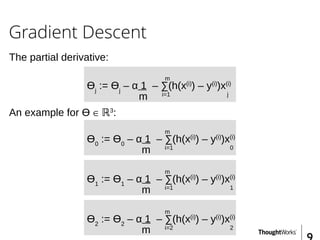
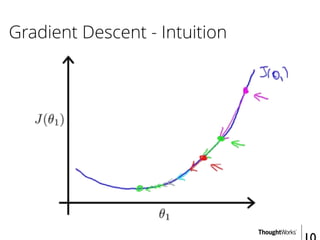
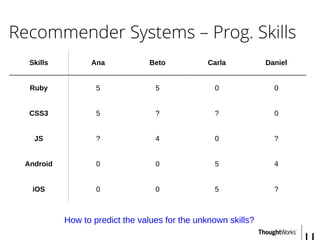
This document provides an overview of recommender systems including background information, implementation details, and a demonstration. It discusses machine learning applications like unsupervised learning, linear regression, and gradient descent algorithms. It covers content-based filtering using known product features and collaborative filtering to identify unknown product features. Examples are given on using linear regression and gradient descent to make predictions for skills data and handle unknown values.



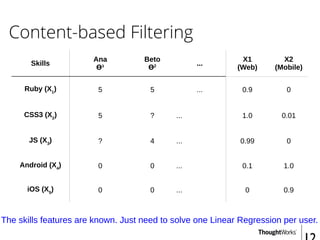
![Content-based Filtering - Predicting
Skills
Ana
Ɵ¹ = [5, 0]
...
X1
(Web)
X2
(Mobile)
Ruby (X1
) 5 ... 0.9 0
CSS3 (X2
) 5 ... 1.0 0.01
JS (X3
) 5 ... 0.99 0
Android (X4
) 0 ... 0.1 1.0
iOS (X5
) 0 ... 0 0.9
Ana(JS) => Ɵ¹ * X3
=> [5, 0] * [0.99, 0] = (5 * 0.99) + (0 * 0) = 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystems-150913090527-lva1-app6892/85/Recommender-Systems-13-320.jpg)
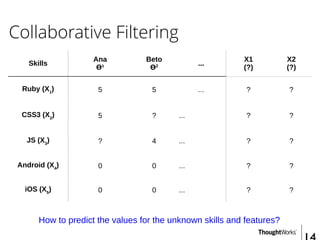

![Collaborative Filtering - Predicting
Skills
Ana
Ɵ¹ = [5, 0]
... X1 X2
Ruby (X1
) 5 ... 0.9 0
CSS3 (X2
) 5 ... 1.0 0.01
JS (X3
) 5 ... 0.99 0
Android (X4
) 0 ... 0.1 1.0
iOS (X5
) 0 ... 0 0.9
Ana(JS) => Ɵ¹ * X3
=> [5, 0] * [0.99, 0] = (5 * 0.99) + (0 * 0) = 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recommendersystems-150913090527-lva1-app6892/85/Recommender-Systems-17-320.jpg)


