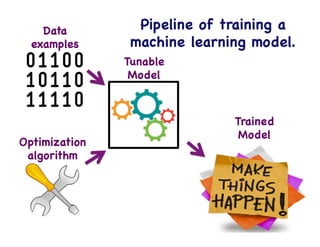
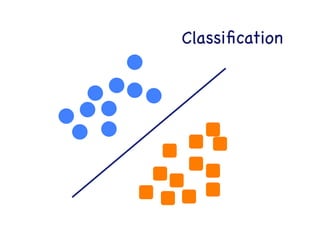
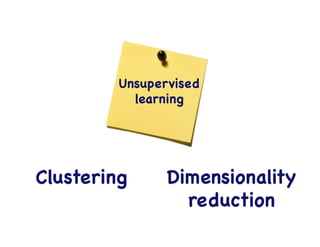
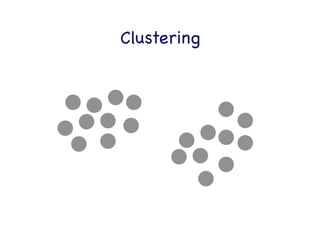
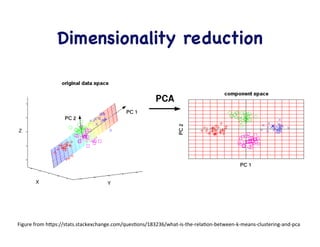
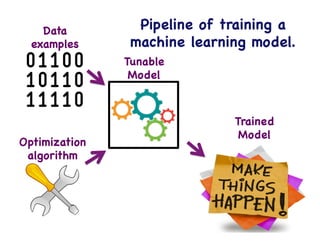
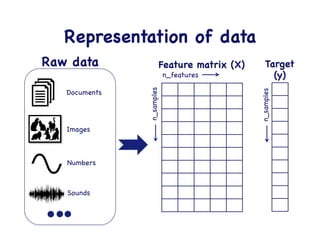
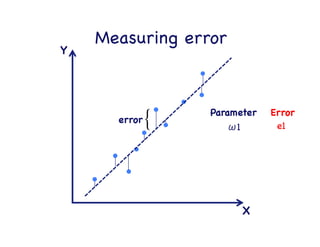
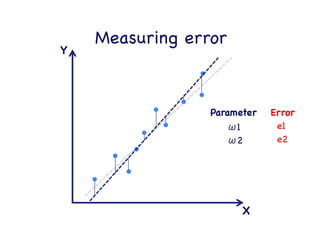
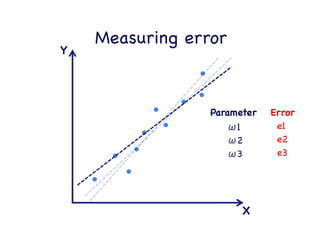
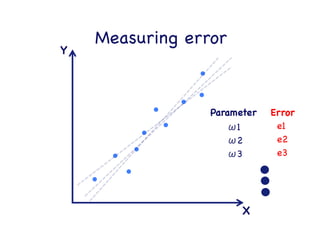
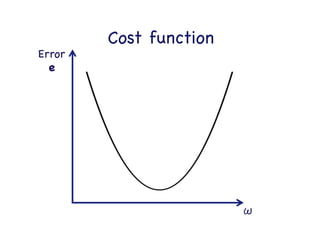
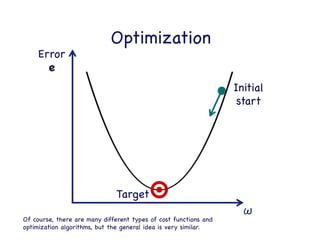
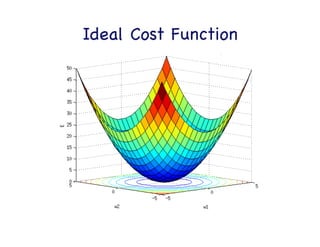
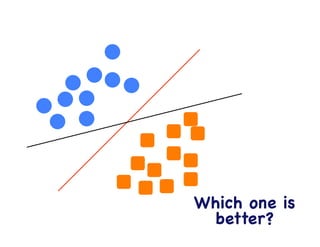
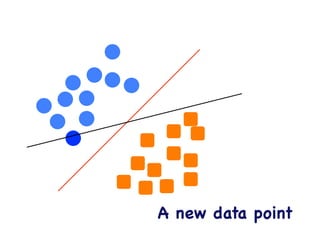
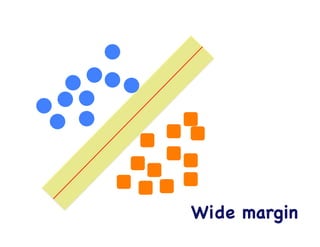
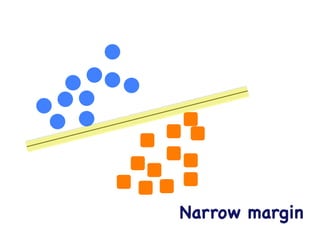
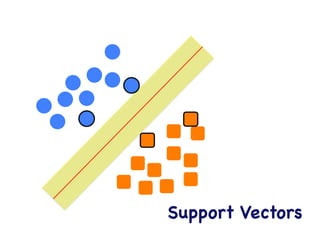
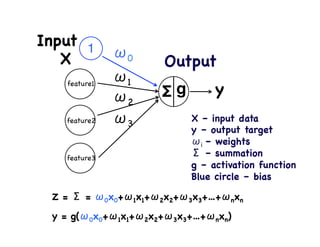
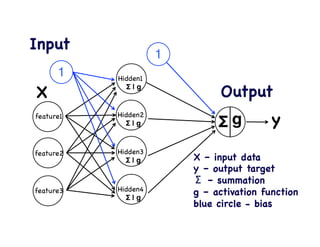
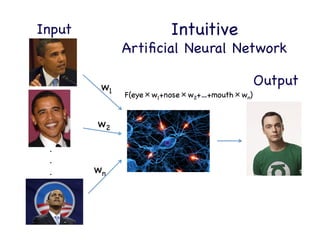
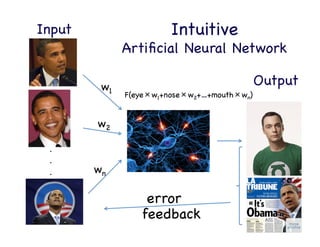
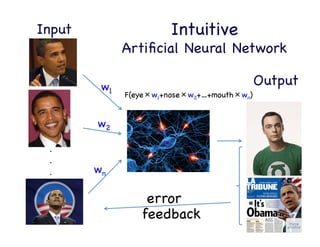
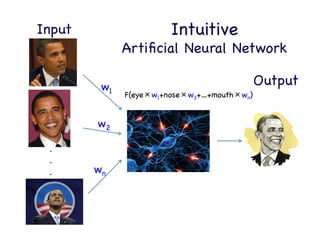
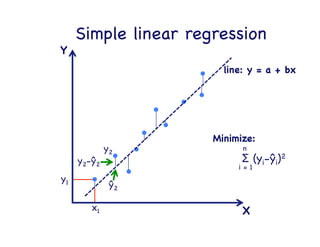
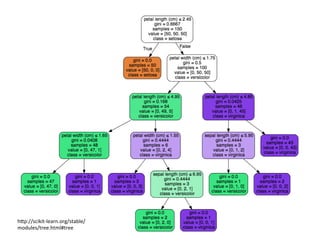
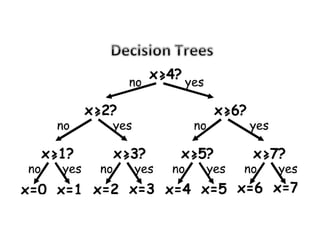
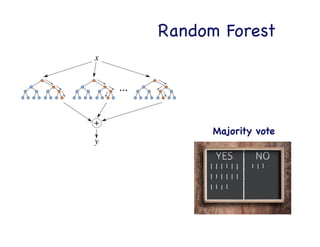
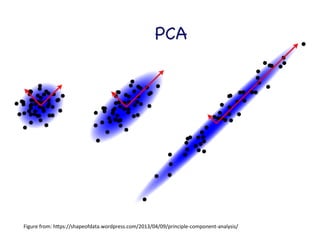
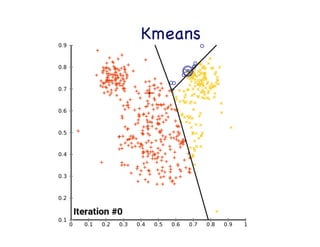
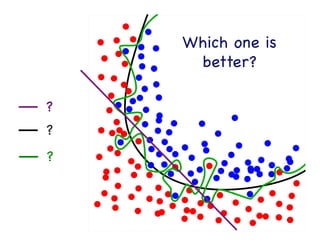
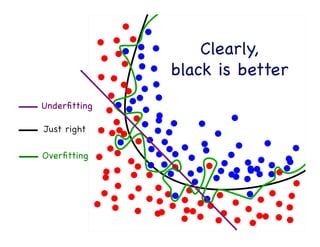
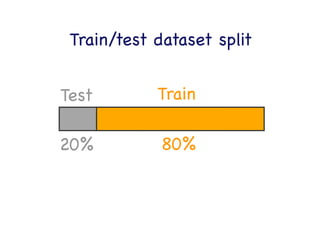
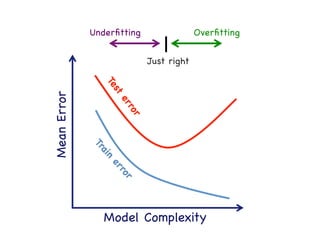
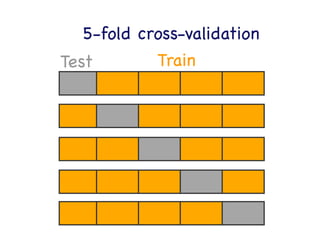
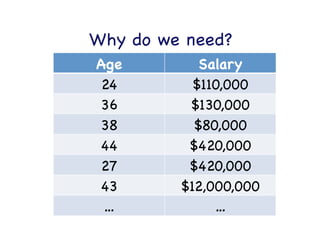
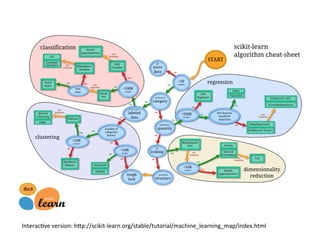
This document provides an overview of machine learning concepts and techniques using the scikit-learn library in Python. It begins with introductions to different types of machine learning problems including supervised learning tasks like classification and regression as well as unsupervised learning problems like clustering and dimensionality reduction. It then discusses common machine learning algorithms such as support vector machines, k-means clustering, random forests, and principal component analysis. The document also covers best practices for developing machine learning models including data preprocessing, evaluating model performance, and tuning hyperparameters.