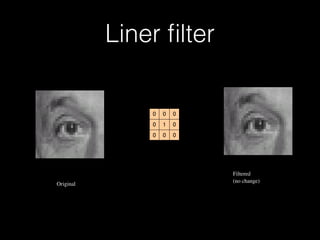
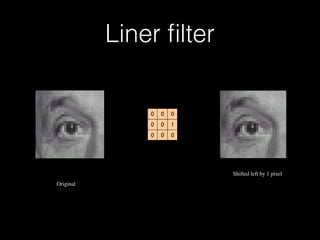
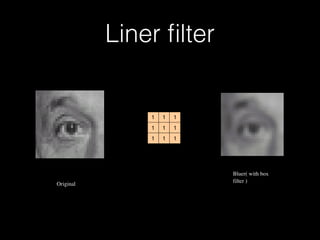
This document provides an introduction and overview of image processing using Matlab. It discusses the basics of Matlab including its environment, syntax, variables, vectors and matrices. It then covers image processing topics such as importing and exporting images, viewing histograms, and applying filters like box filters and linear filters to images. The document is intended to teach the fundamentals of working with images in the Matlab programming language.







![Vectors and Matrices
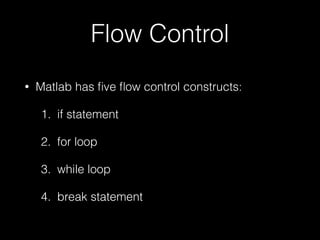
• How to build a matrix?
>> a = [1 5 8]
a =
1 5 8
>> a = [ 1 2 3]'
a =
1
2
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageprocessing-150809150935-lva1-app6891/85/Image-processing-9-320.jpg)
![>> a = [ 0:2:4 ; 8:1:10; 35:5:45]
a =
0 2 4
8 9 10
35 40 45
>> a = [1:3; 4:6; 7:9]
a =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageprocessing-150809150935-lva1-app6891/85/Image-processing-10-320.jpg)

![• Operations ad functions that were defined scalars
in the previous section can also be used on
vectors and matrices, For example.
>> a = [ 1 2 3];
>> b = [ 4 5 6];
>> c = a + b
c =
5 7 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageprocessing-150809150935-lva1-app6891/85/Image-processing-12-320.jpg)




![for i=1:10
x(i) = sin(i * pi / 10);
end;
for i=[ 1, 2, 3, 7]
x(i) = i + 1;
end;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageprocessing-150809150935-lva1-app6891/85/Image-processing-18-320.jpg)



![function
function [ output_args ] = functionName( input_args )
%functionName Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageprocessing-150809150935-lva1-app6891/85/Image-processing-22-320.jpg)




![Images and Matrices
row = 256;
col = 256;
img = zeros(row, col);
img(100:105, :) = 0.5;
img(:, 100:105) = 1;
figure;
imshow(img);
Column 1 to 256
Ro
w 1
to
25
6
o
[0, 0]
o
[256, 256]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageprocessing-150809150935-lva1-app6891/85/Image-processing-28-320.jpg)