1) The document provides recommended safer work practices to prevent sharps injuries for healthcare workers who provide nursing care and perform procedures like venipuncture.
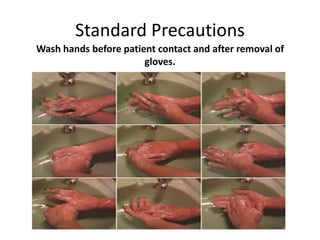
2) It emphasizes standard precautions like hand washing and treating all body fluids as infectious, as well as engineering controls like using safety devices and sharps containers.
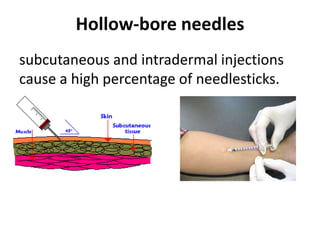
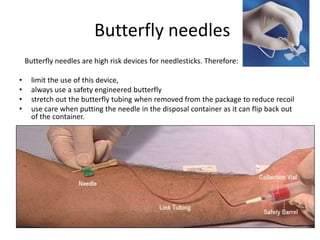
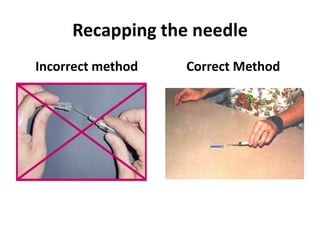
3) Work practice recommendations include always using safety devices, not passing sharps between people, getting assistance for uncooperative patients, and proper disposal techniques.