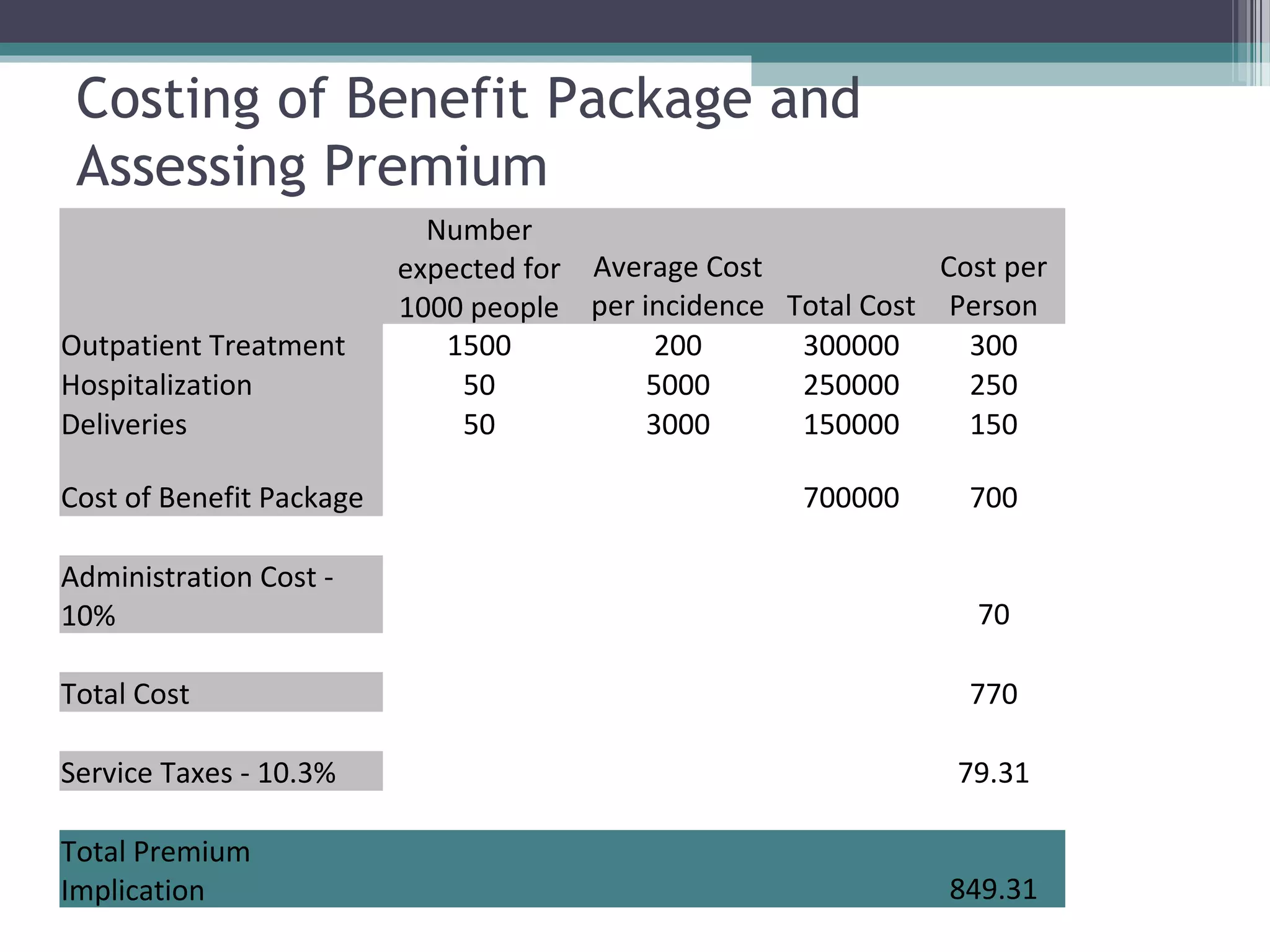
This document discusses methods for assessing health insurance premiums and costing benefit packages. It defines premium as the amount paid by the insured to the insurer for health coverage. It describes four rating methods used by health insurers: community rating, risk rating, income rating, and experience rating. Key factors that influence premium prices are identified as claim costs, administrative costs, marketing costs, contingency margins, and profit margins. Strategies for collecting premiums include payroll deductions, deductions at source, membership payments, and voluntary payments. The document provides a case study example of costing a benefit package for a village community based on population size, expected illness incidence and costs, and factors in premium calculation like administration costs and taxes.