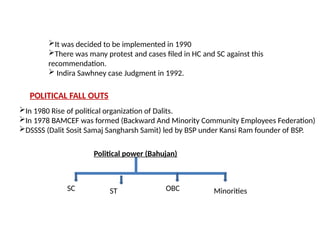
The document examines the evolution of Indian politics from the 1990s, highlighting significant events such as the assassination of Rajiv Gandhi, the rise of coalition politics, and the influence of OBCs following the Mandal Commission's recommendations. It discusses the emergence of Hindutva politics with the BJP's rise and the Babri Masjid demolition, alongside the repercussions these events had on secularism and democracy in India. Additionally, it addresses social movements among marginalized communities like dalits and the political organizations that emerged to represent their interests.