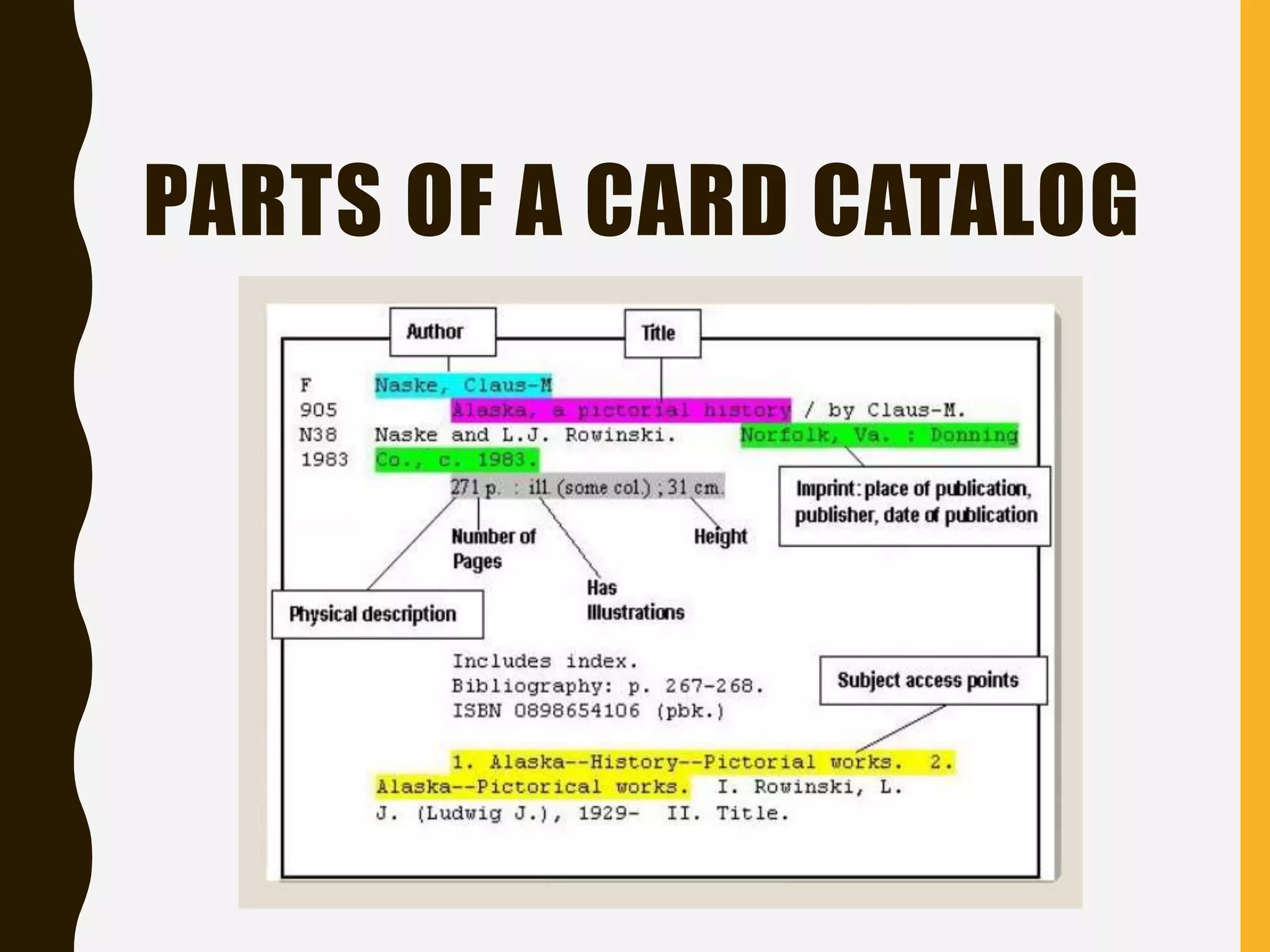
This document provides information on tools and mechanisms for locating resources in the library, including card catalogs, online public access catalogs (OPAC), and other information sources like books, references, newspapers, and databases. It describes how to search these sources by title, author, subject, or keyword and includes examples of activities to demonstrate searching skills. The goal is to teach students how to effectively use library resources to find information for their needs.