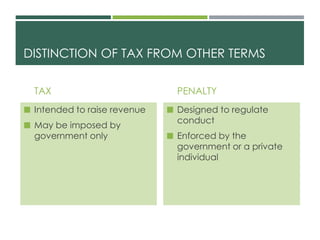
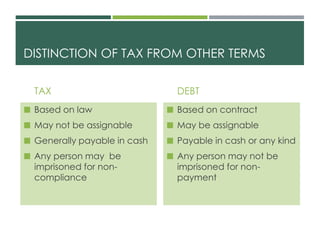
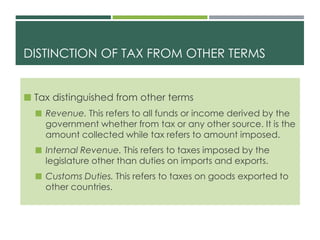
The document defines taxation and income taxation. It discusses the concepts, principles, theories, structures, and significance of taxation. It also covers the classification of taxes, taxpayers, public officers in charge of tax collection, and tax remedies. Key points include that taxation is the process by which governments raise revenue to fund public services and that income tax refers specifically to taxes imposed on a taxpayer's net income within a taxable period.