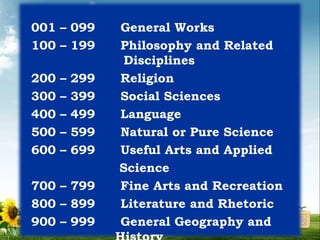
A library is a collection of resources made available to a community for reference or borrowing. A library's collection can include books, periodicals, newspapers, manuscripts, films, maps, documents, CDs, cassettes, videotapes, DVDs, Blu-ray discs, e-books, and audiobooks. Libraries typically have several sections, including general reference, periodicals, general collection/circulation, special collections, children's, and multimedia sections. Libraries use classification systems like the Dewey Decimal System and Library of Congress Classification to organize their collections.