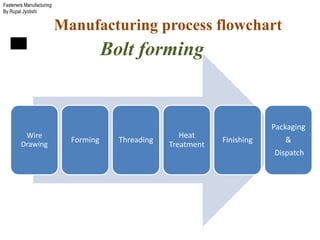
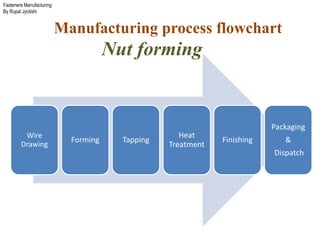
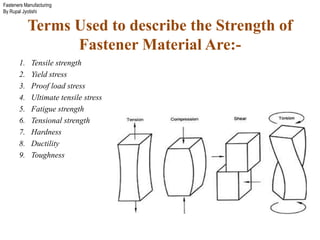
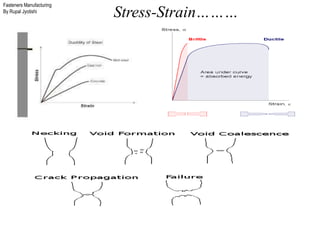
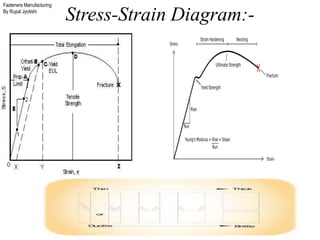
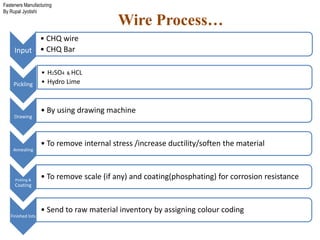
The document outlines the fasteners manufacturing process by Rupal Jyotishi, detailing key aspects such as raw material handling, mechanical properties of various materials, and specific processes like wire drawing and heat treatment. It emphasizes the importance of selecting the right materials for different environments, as well as the mechanical properties that affect fastener performance. Additionally, it provides information on different types of metal used in fasteners, including stainless steel, aluminum, magnesium, and carbon steel.