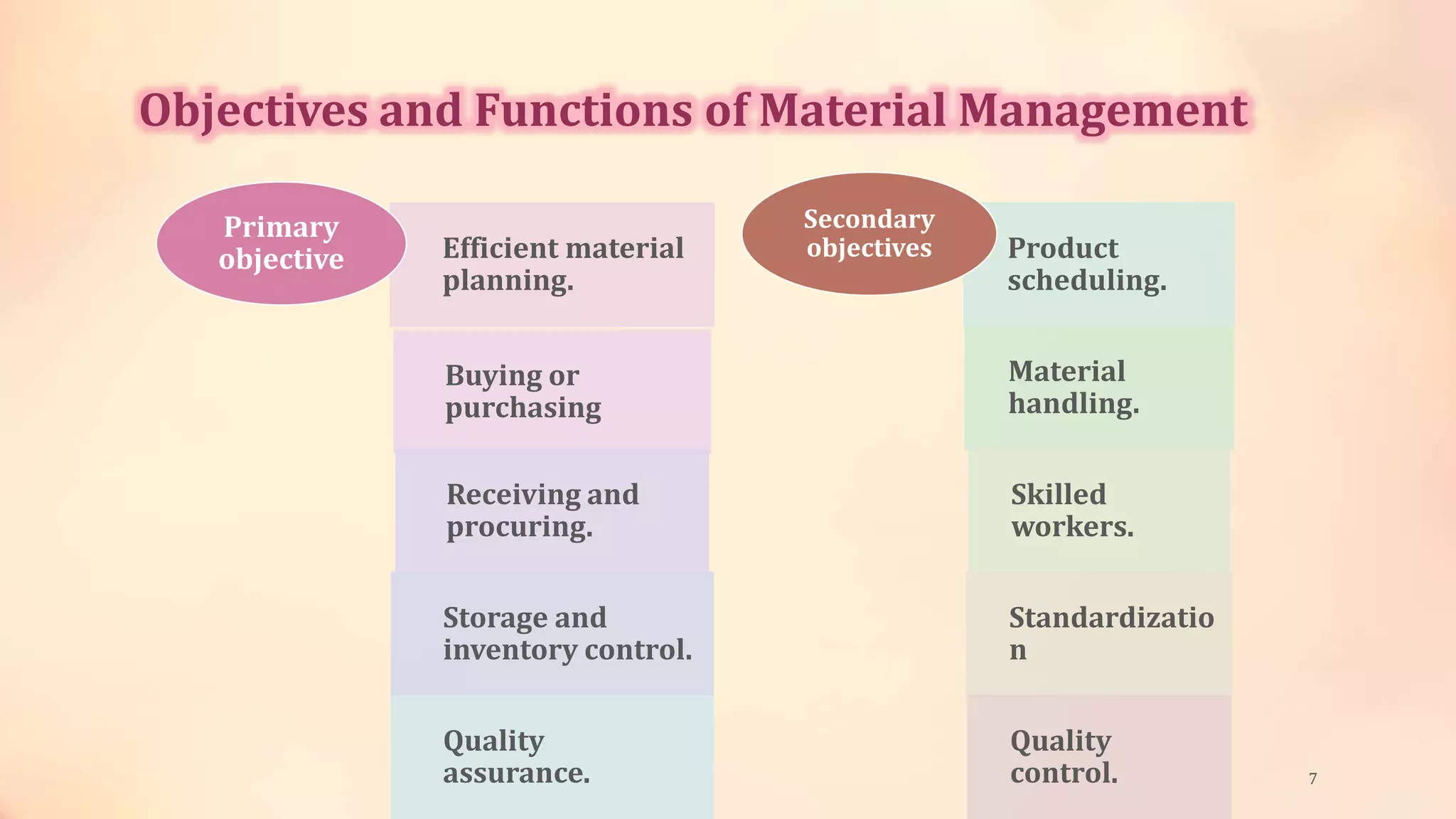
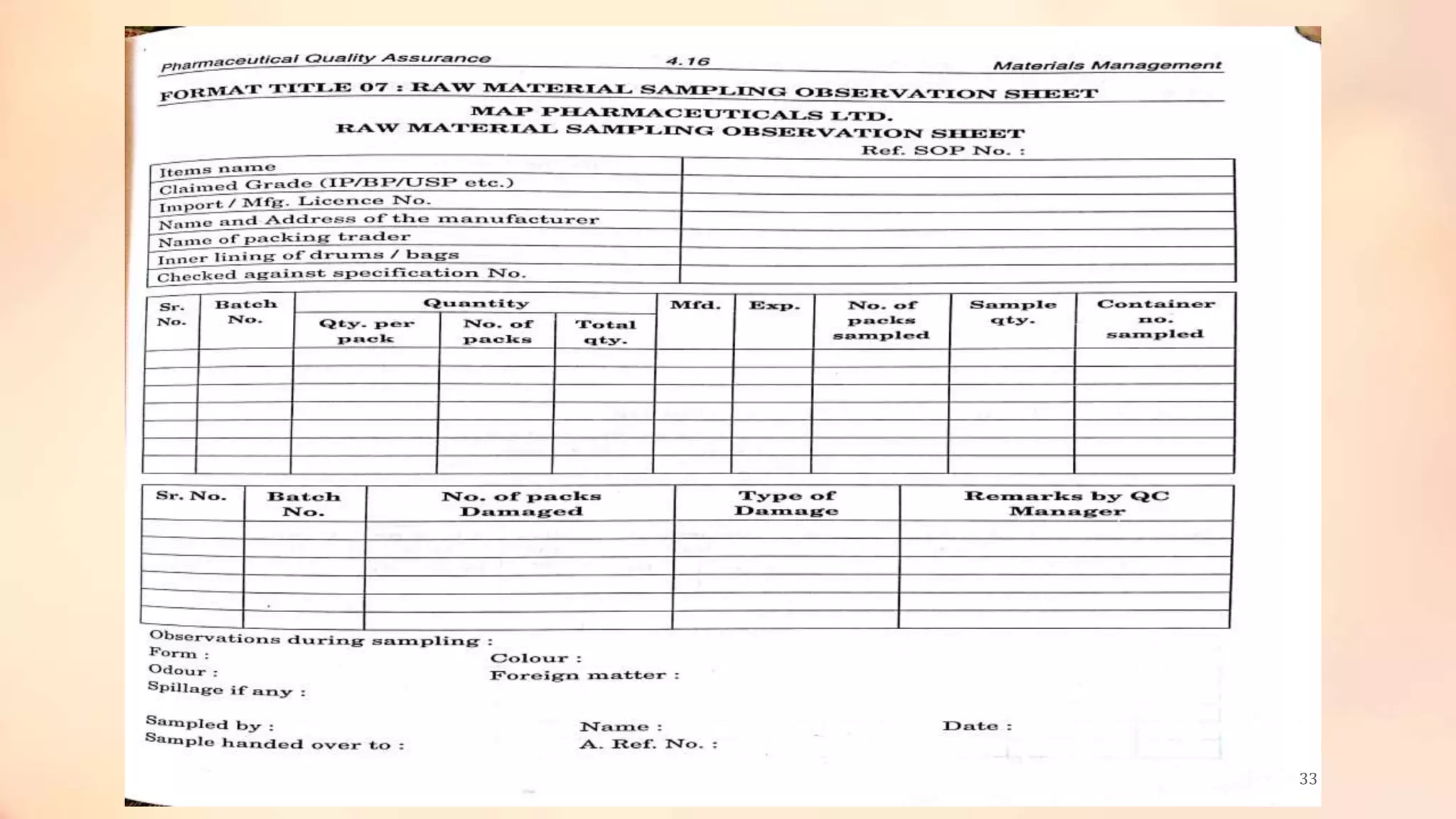
The document discusses material management in the pharmaceutical industry. It covers various topics related to material management including definitions, objectives, purchasing, storage, and handling of raw materials, packaging materials, intermediates, rejected materials, and other item types. Proper documentation, labeling, storage conditions, and quality control are important for ensuring materials are suitable for use in manufacturing pharmaceutical products. The key goal of material management is to source high quality input materials and control their flow through the manufacturing process to deliver quality finished products on time.