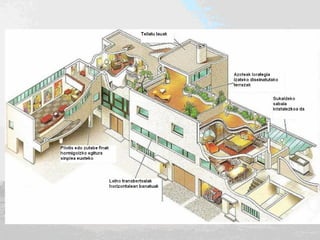
Rationalism was an architectural movement of the 20th century characterized by simplicity of form following function. Rationalist architects used industrial materials like concrete which was cheap, durable, and allowed for prefabrication. They designed with large windows and open floor plans, eliminating decorative elements in favor of proportion and asymmetry. Notable Rationalist architects included Mies van der Rohe, who designed glass skyscrapers with pure forms, and Le Corbusier, who developed the five points of architecture and applied concrete construction and standardization to projects like the Ville Savoye and Unité d'Habitation housing blocks.