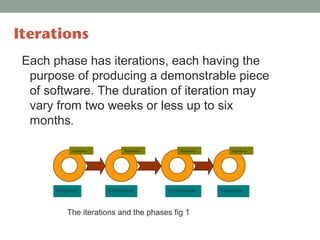
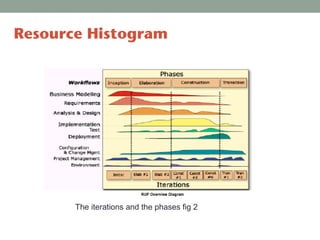
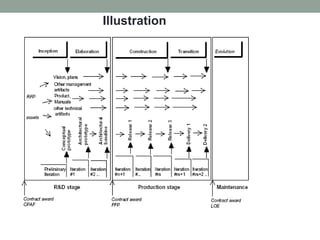
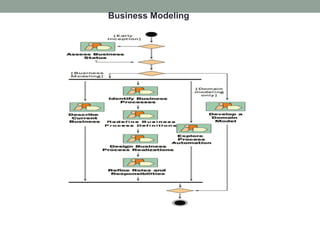
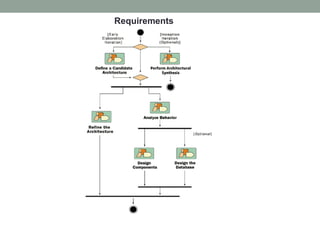
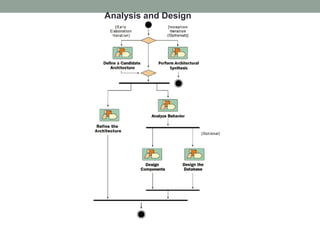
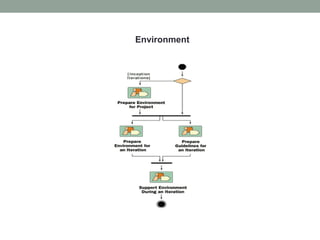
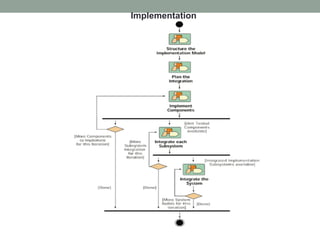
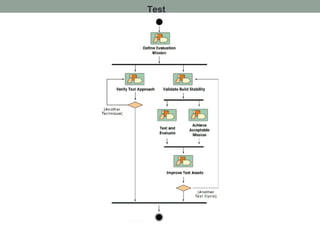
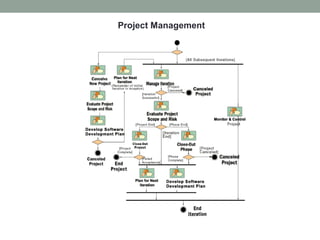
The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development framework that includes four phases: Inception, Elaboration, Construction, and Transition. Each phase contains iterative cycles where requirements, design, and code are developed and tested. RUP emphasizes iterative development, managing requirements and risk, visual modeling, early testing, and architecture-centric design. It is a flexible framework that can be tailored for different project sizes and domains.