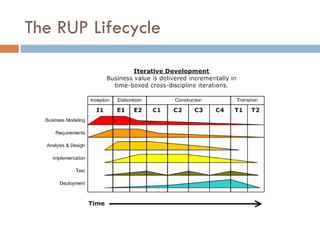
The document provides an overview of the Rational Unified Process (RUP), a software development process originally developed by Rational Software. It describes RUP as an iterative process with four phases (inception, elaboration, construction, transition) and six disciplines (business modeling, requirements, analysis and design, implementation, test, deployment). The document outlines some advantages of RUP like regular feedback, efficient use of resources, and improved risk management compared to traditional waterfall approaches. It also notes some potential disadvantages like complexity and needing expertise to fully adopt RUP.