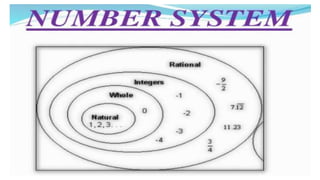
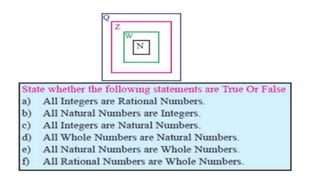
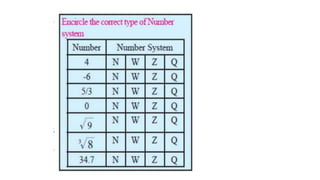
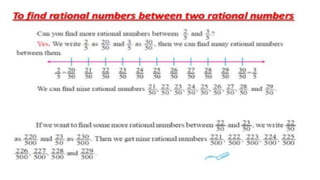
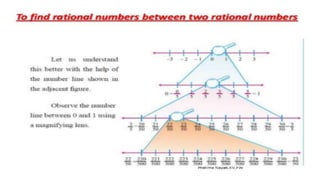
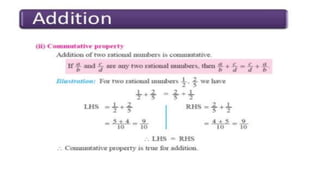
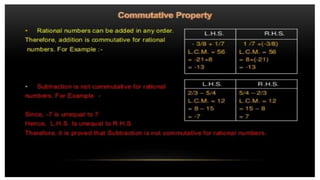
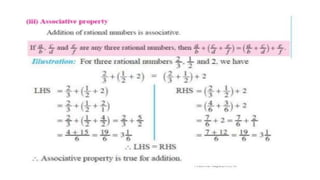
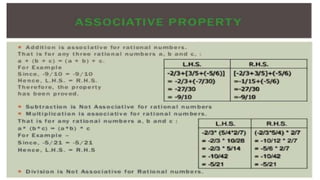
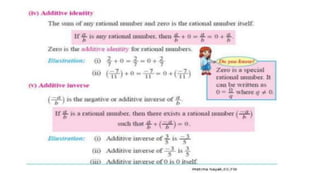
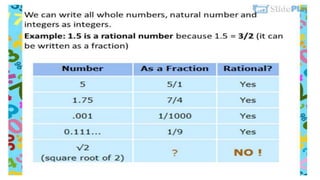
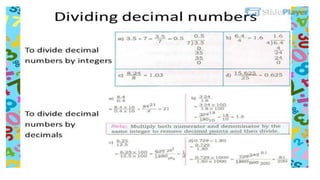
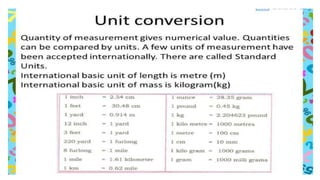
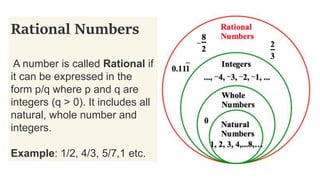
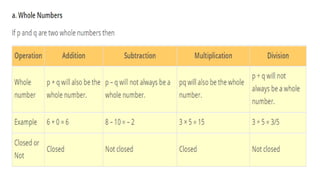
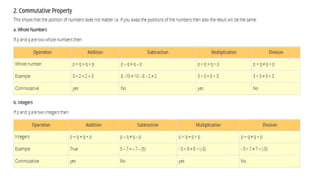
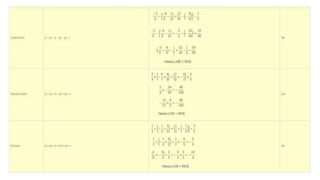
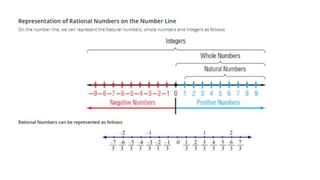
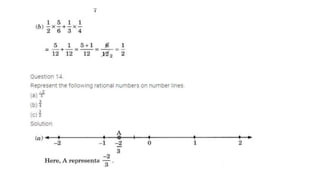
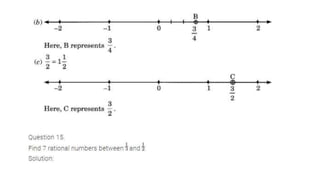
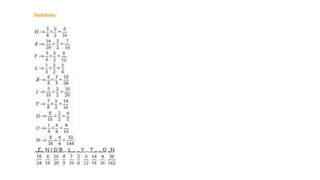
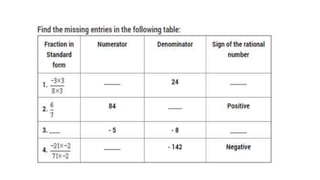
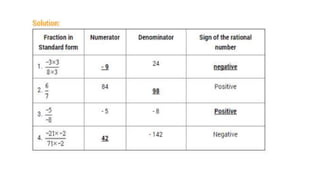
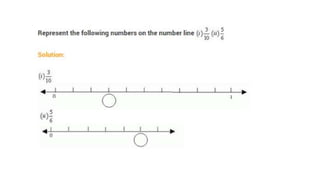
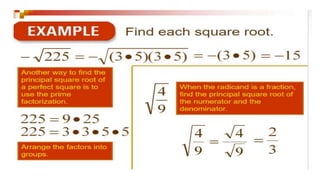
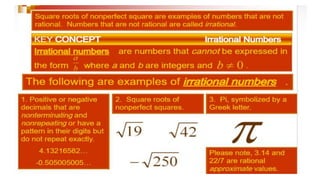
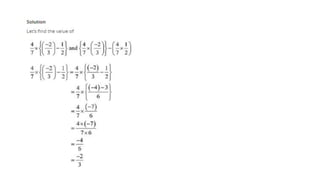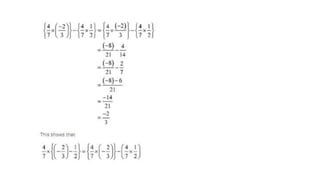The document discusses rational numbers and their properties. Rational numbers can be expressed as quotients of integers (p/q where p and q are integers and q is not zero). They include natural numbers, whole numbers, and integers. Key properties of rational numbers are that they are closed under addition and multiplication, these operations are commutative and associative, and they have additive and multiplicative identities. Rational numbers can also be represented on a number line and there are always rational numbers between any two given rational numbers.