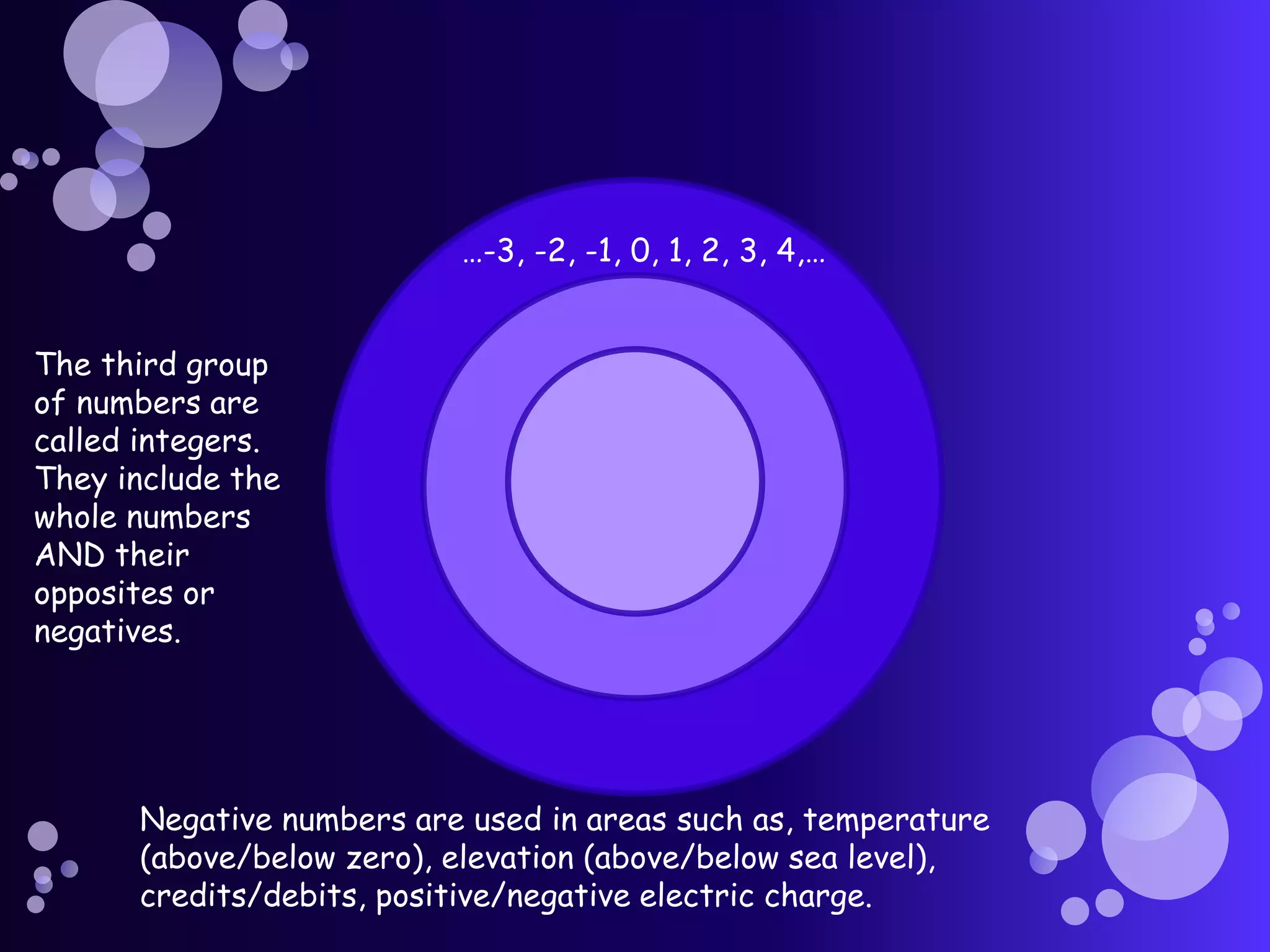
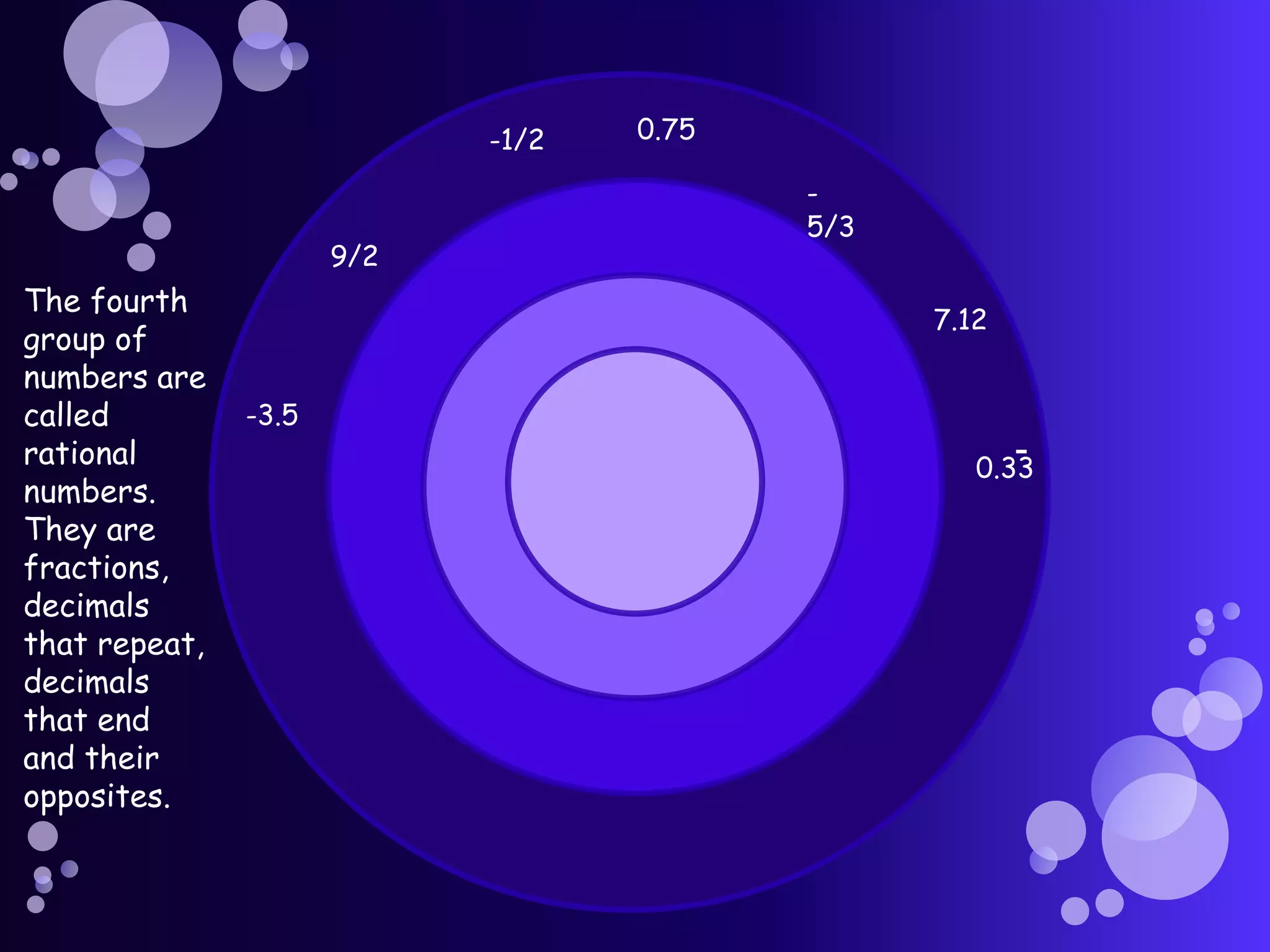
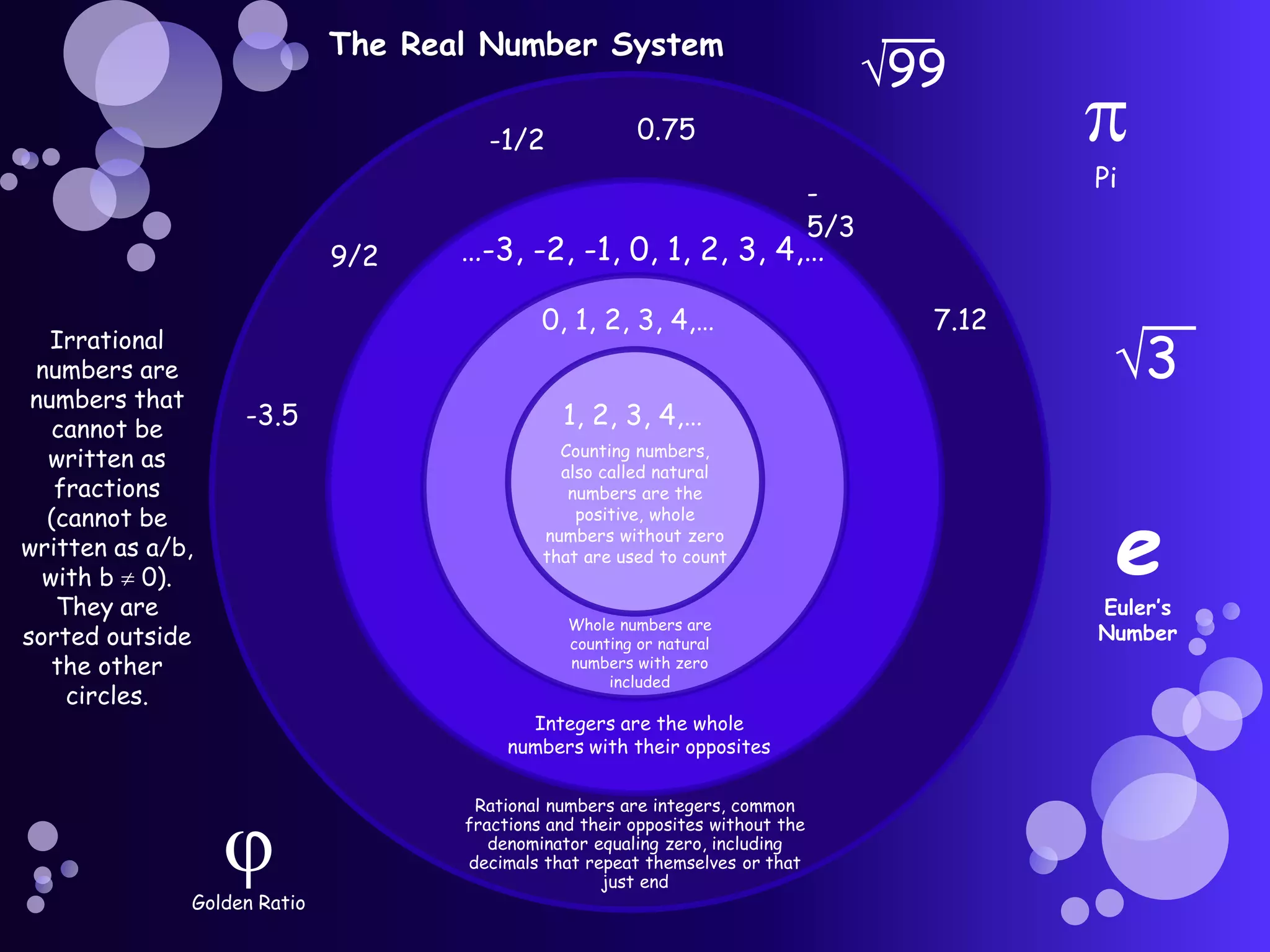
Real numbers include decimals, fractions, integers, rational numbers like fractions and repeating decimals, and irrational numbers like pi. They can be positive or negative, and are organized on a number line that extends infinitely in both directions. Real numbers are grouped into categories including counting numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers.