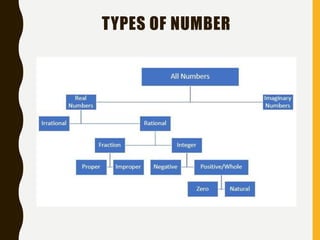
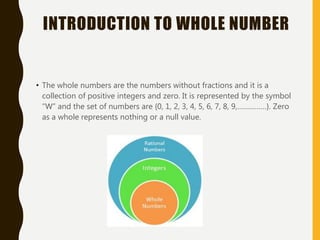
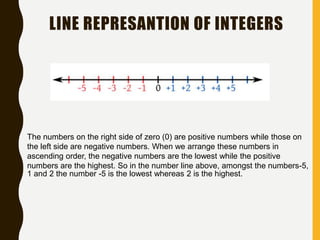
The document provides an introduction to number systems, focusing on whole numbers and integers. It discusses key properties such as the commutative, associative, and distributive properties, which govern mathematical operations. The document also highlights how integers are represented on a number line, distinguishing between positive and negative numbers.