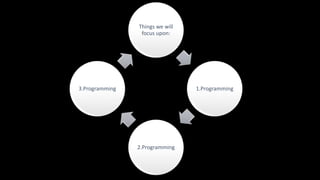
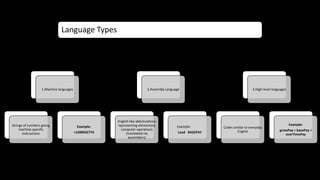
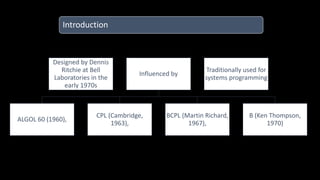
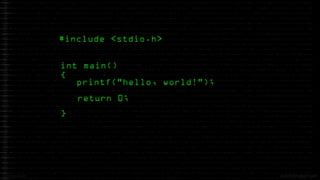
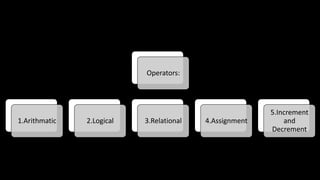
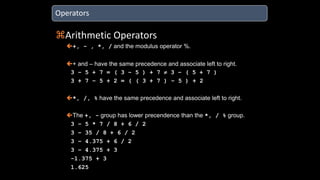
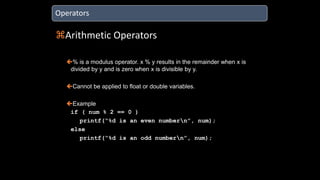
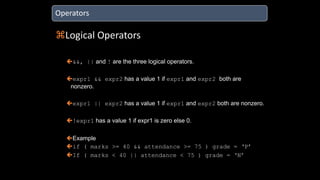
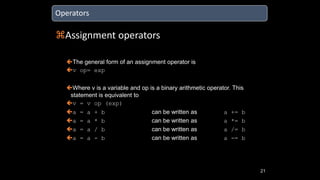
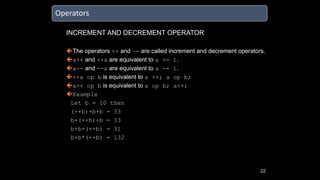
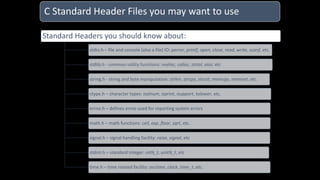
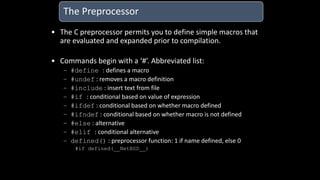
The document discusses an upcoming C programming study group. It provides an overview of topics that will be covered, including programming languages (C, C++, Java), language types (machine, assembly, high-level), tools (Git, GitHub), C standards (C89, C99, C11), operators, and common C header files. The study group aims to help participants learn C programming, and transition from outdated compilers like Turbo C to modern tools like GCC.