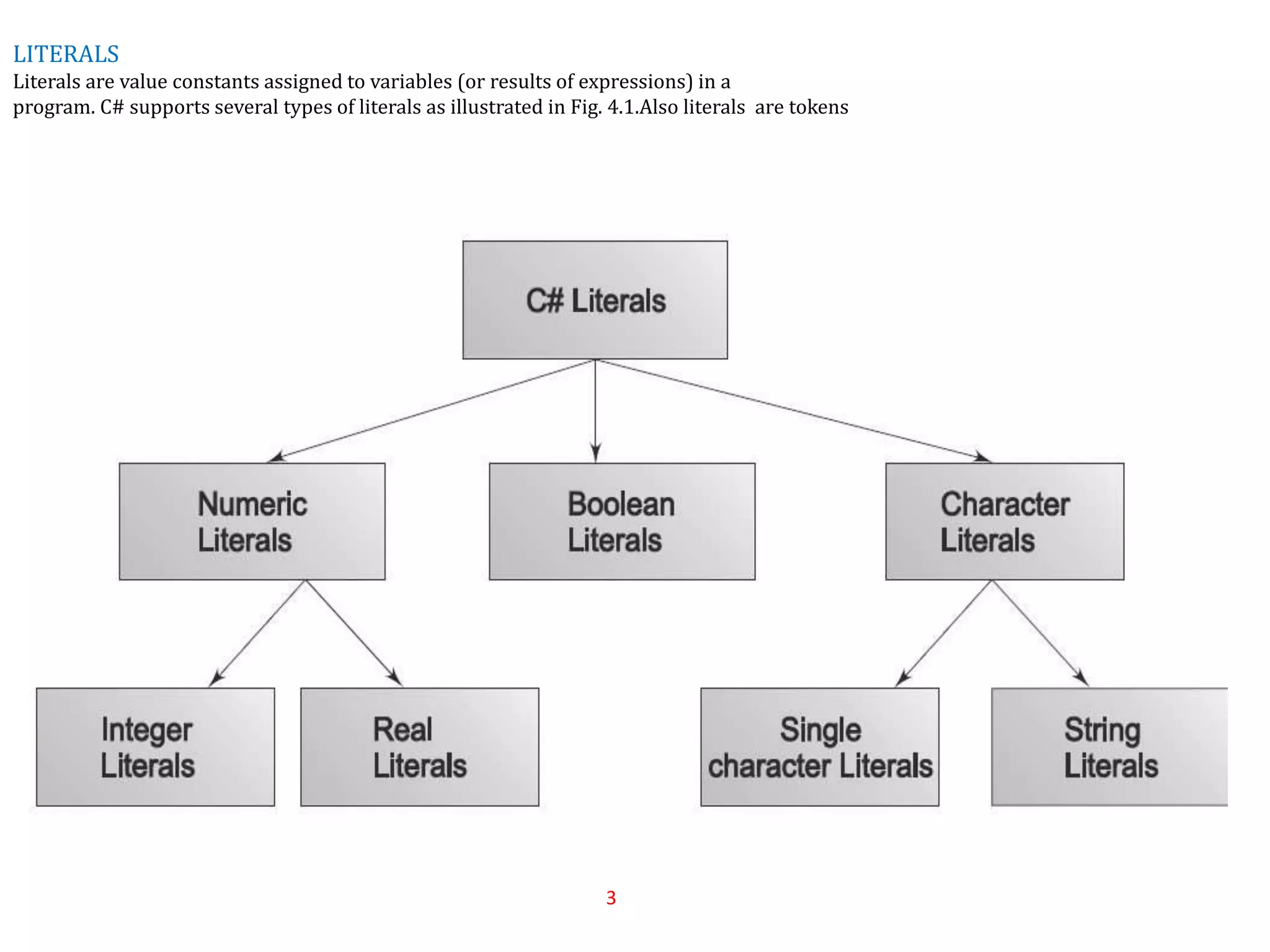
This document discusses different types of literals in C#, including numeric, boolean, character, and string literals. Numeric literals include integer literals like 123 and -321, as well as real/floating point literals like 17.548 and 435.36. Boolean literals are either true or false. Character literals represent a single character within single quotes, while string literals are sequences of characters within double quotes. The document provides examples of each type of literal and their proper formatting in C#.