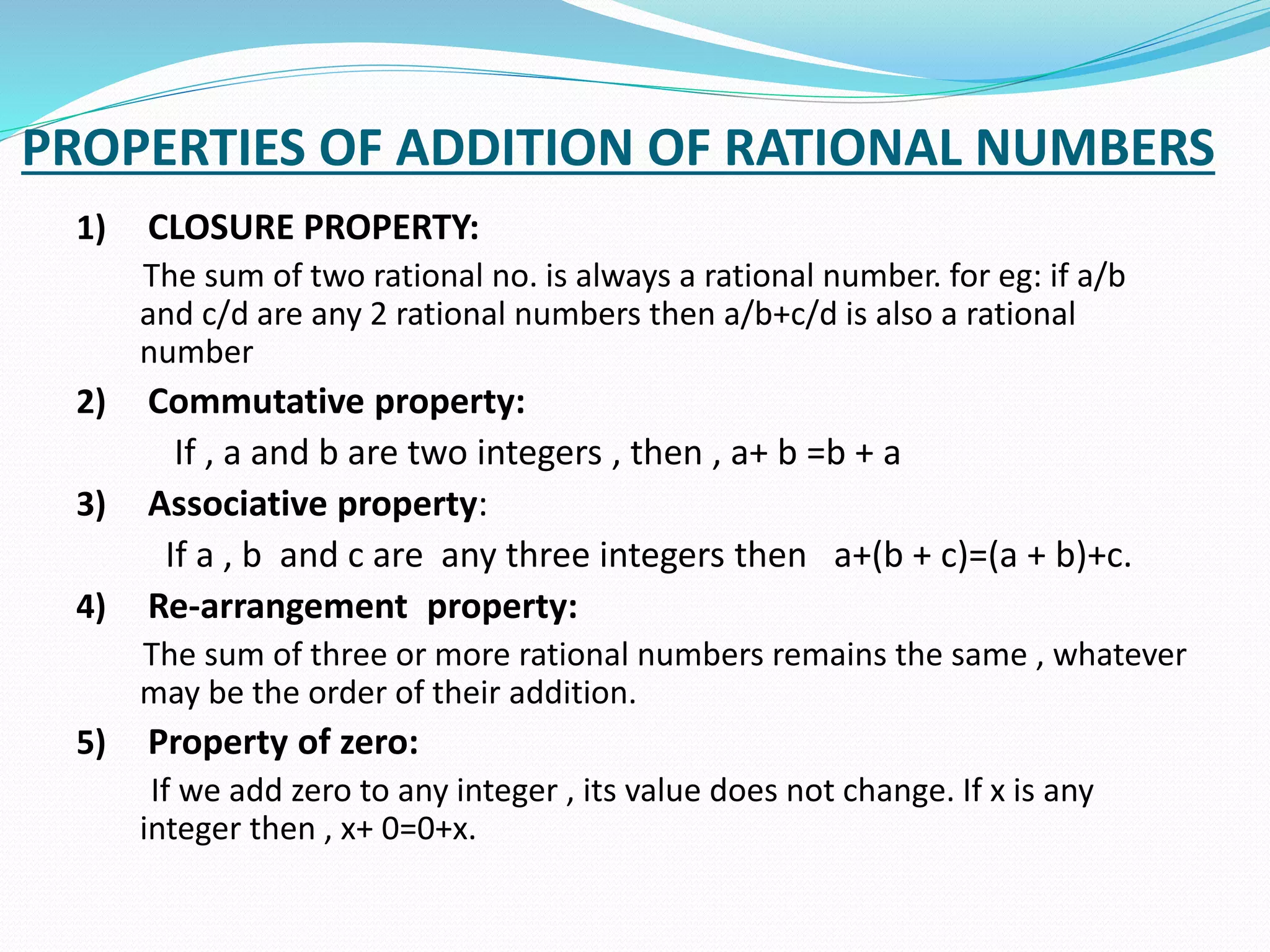
Rational numbers can be written as a ratio of two integers. They can be expressed as decimals that either terminate or repeat. Examples of rational numbers include integers like 16, 1/2, 8, and decimals like 1.33. Rational numbers have properties when added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided, such as closure, commutativity, associativity, and others. Every rational number has a reciprocal, and the reciprocal of a rational number a/b is b/a.