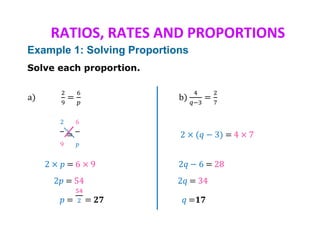
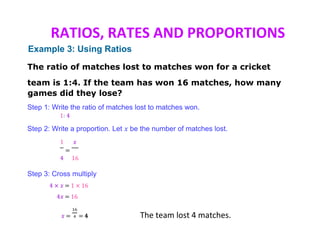
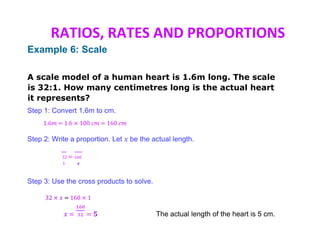
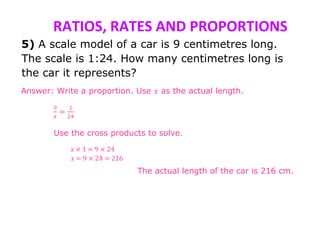
This document discusses ratios, rates, proportions, and scales. It defines ratios as comparisons using division, proportions as equivalent ratios, and rates as ratios with different units. It provides examples of solving proportions, finding unit rates, using ratios and scales, and scale drawings. Examples show setting up and solving proportions to find missing values, converting between ratios and rates, and determining actual measurements based on scale models.