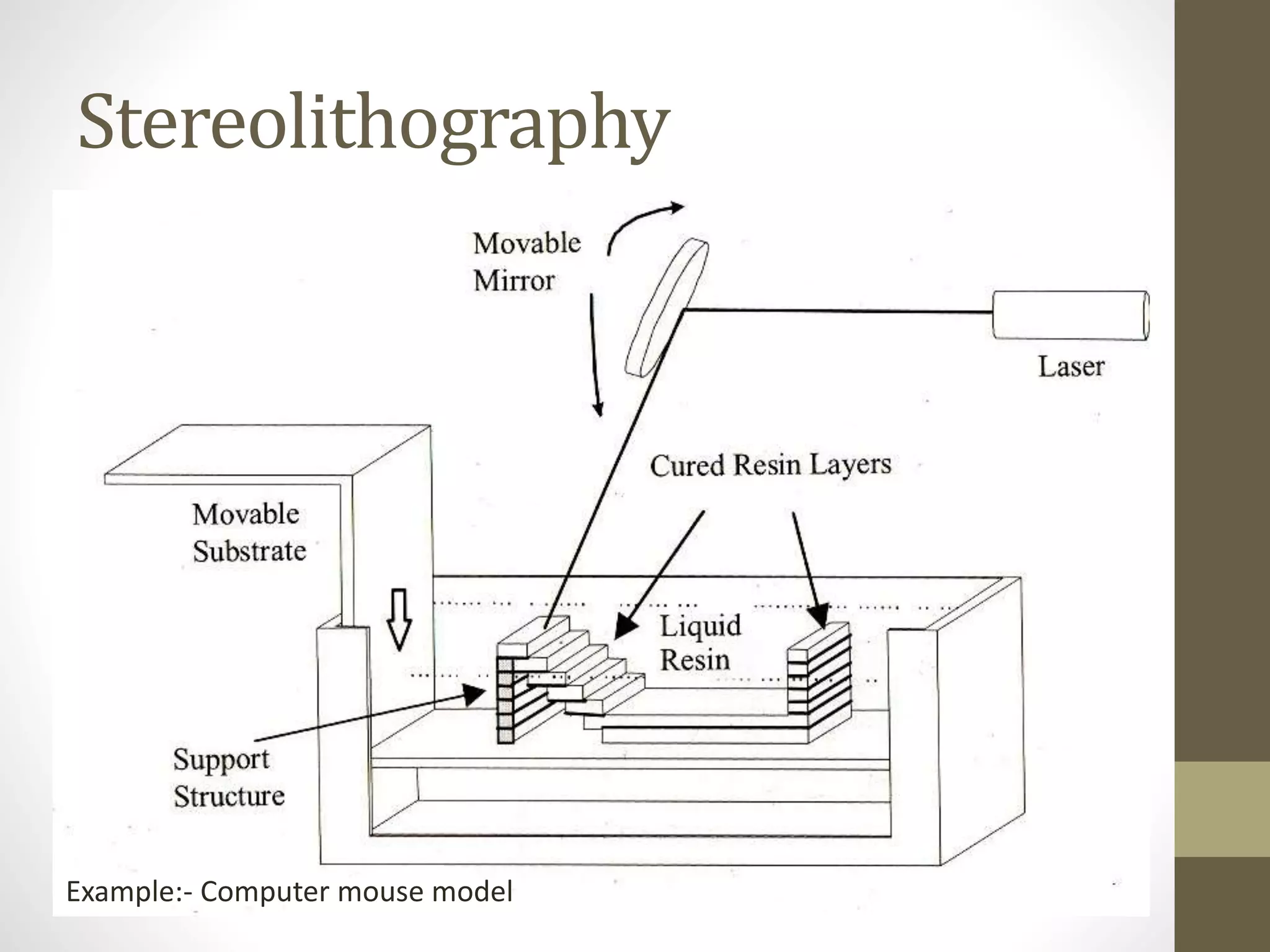
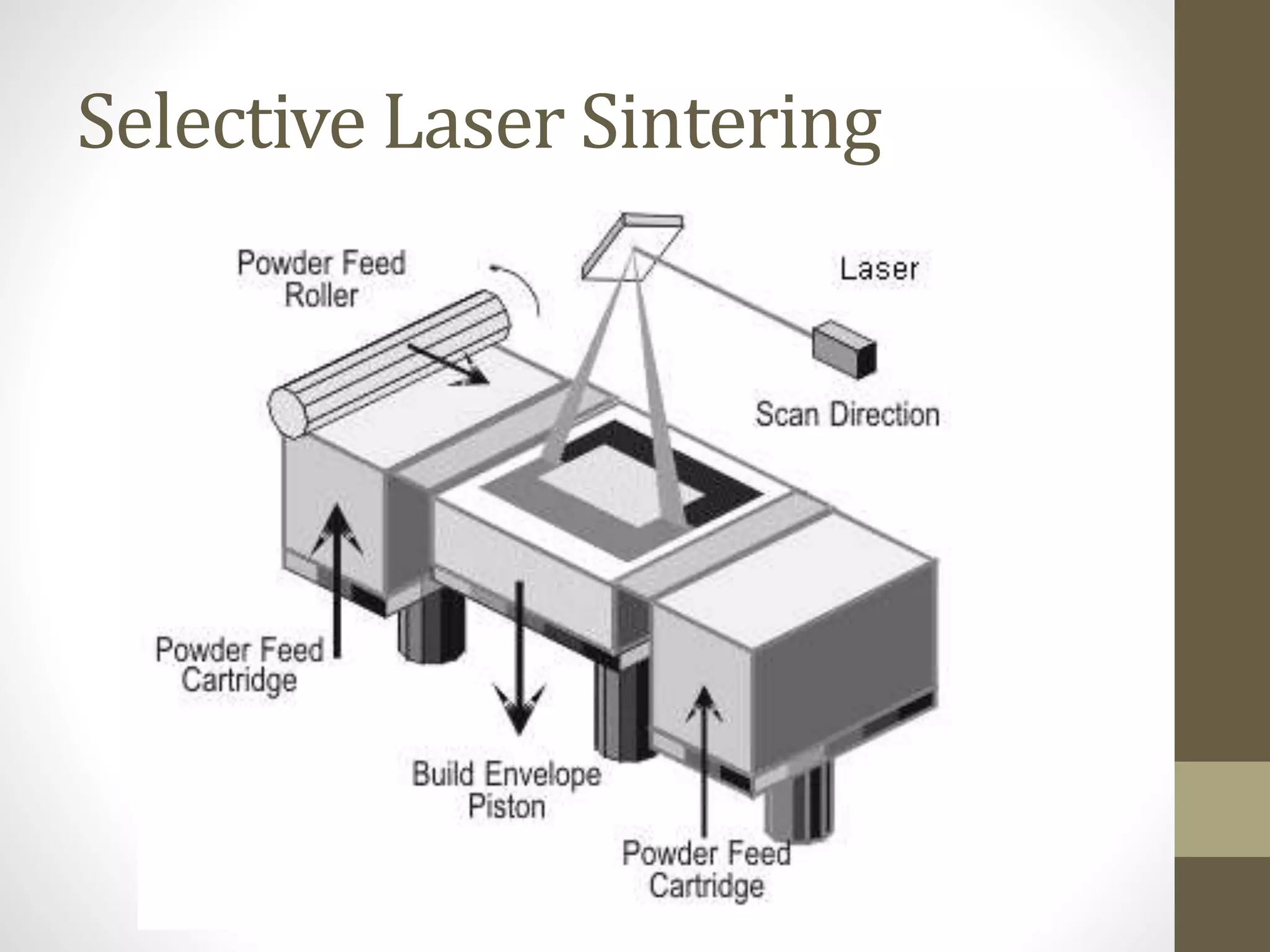
This document discusses rapid prototyping processes. It classifies rapid prototyping into three categories: subtractive, additive, and virtual. Additive processes build parts in layers using techniques like stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and fused deposition modeling. Rapid prototyping allows for faster and more economical manufacturing of prototypes than traditional methods. It has applications in manufacturing, tooling, and casting.