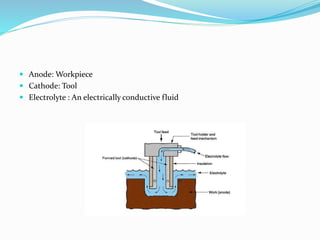
Electrochemical Machining (ECM) is a non-conventional machining process that removes metal using an electrochemical reaction, characterized as 'reverse electroplating'. It relies on Faraday's laws of electrolysis and involves a tool (cathode) and workpiece (anode) with a conductive electrolyte, allowing for high precision and surface quality in machining hard materials. The process has advantages such as no tool wear and high accuracy, but also drawbacks, including high costs and environmental concerns.