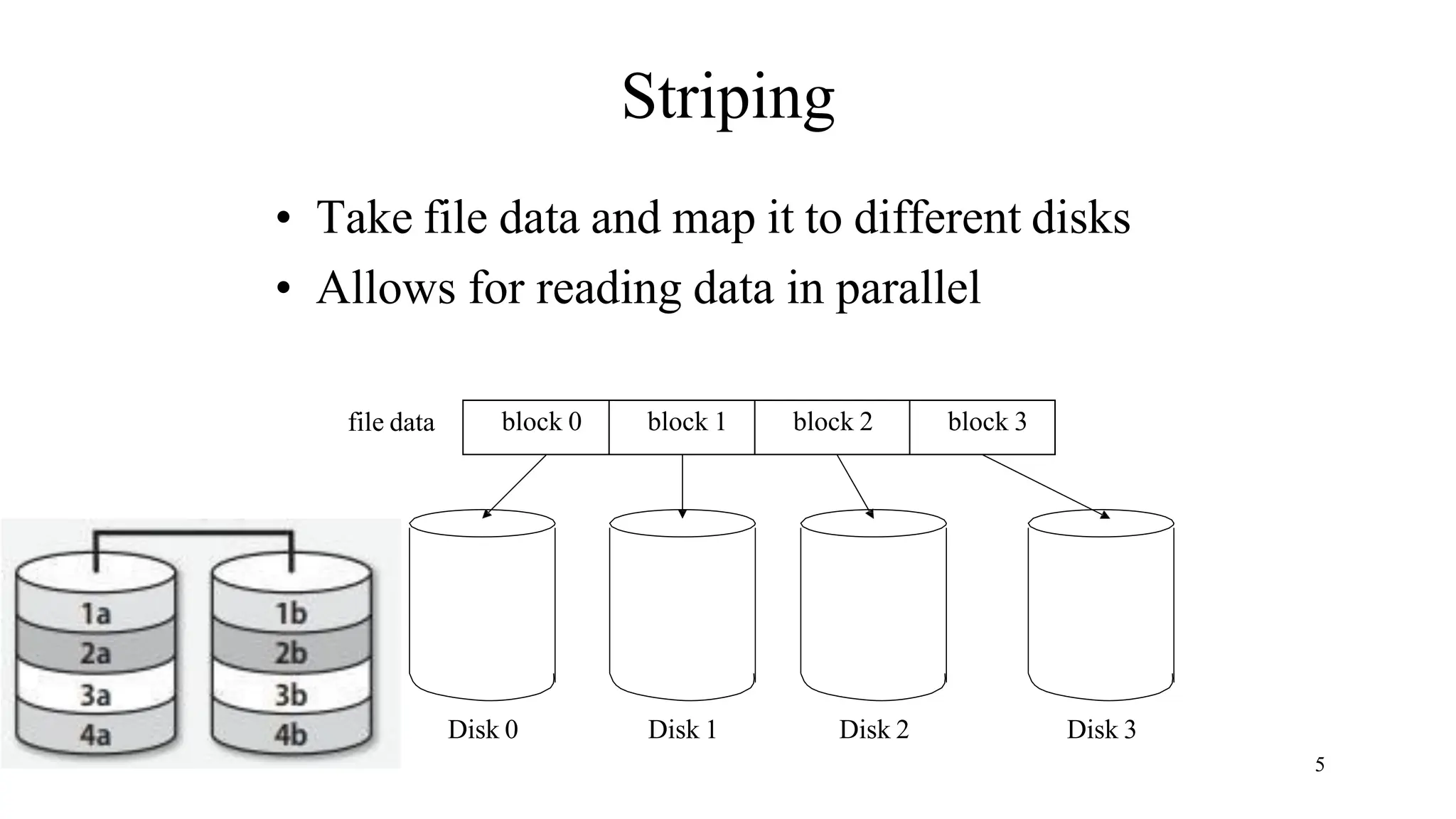
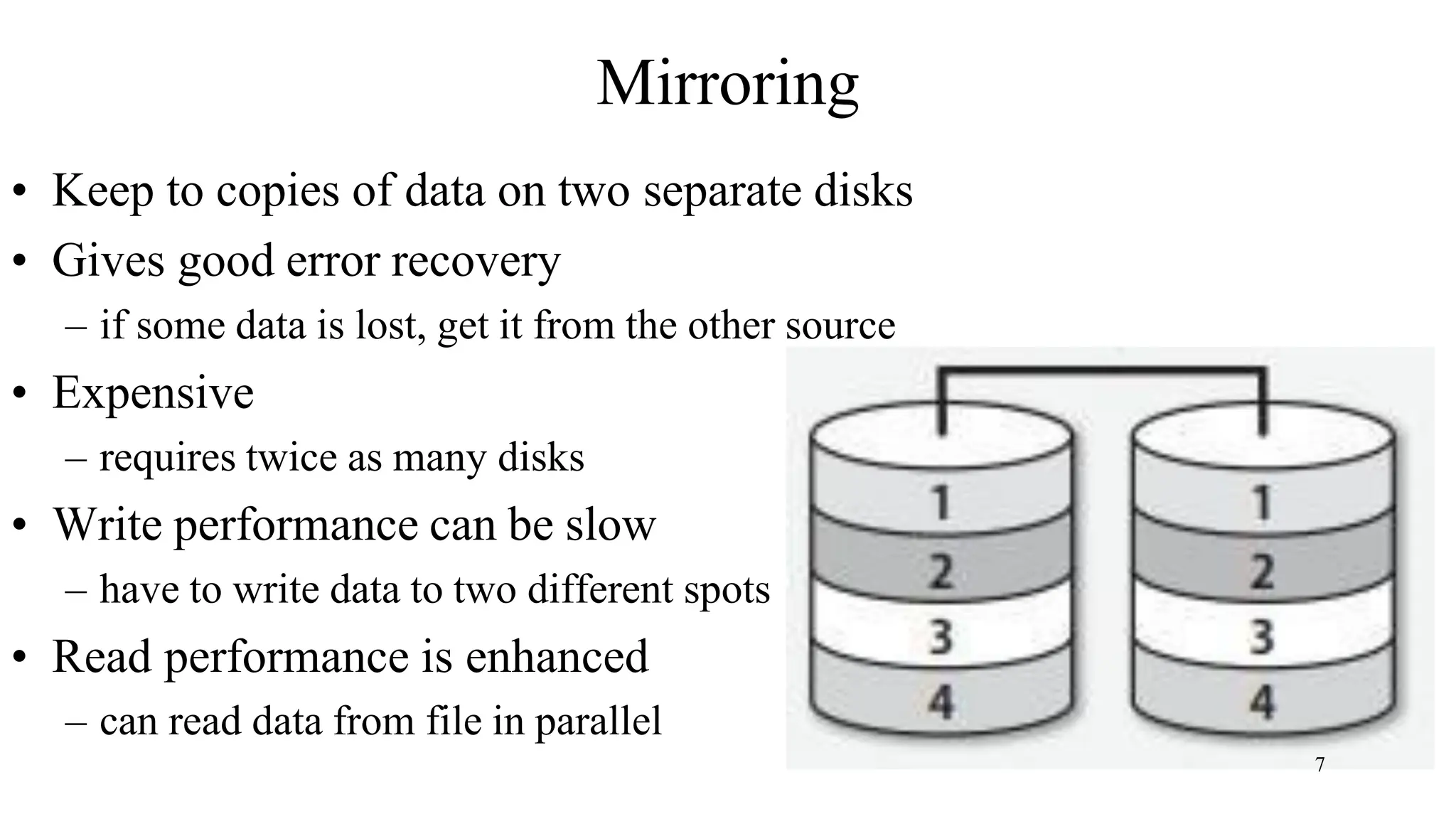
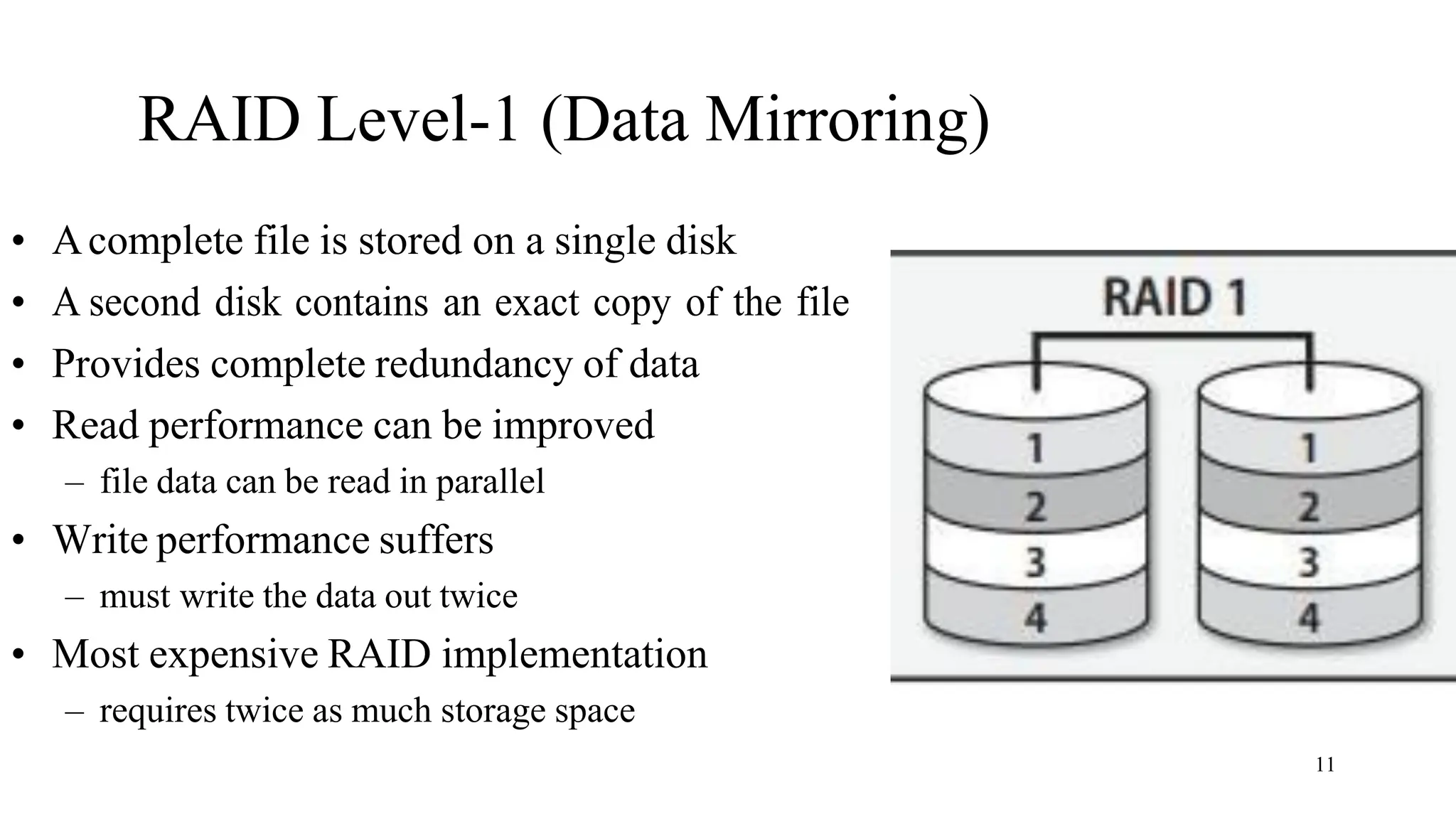
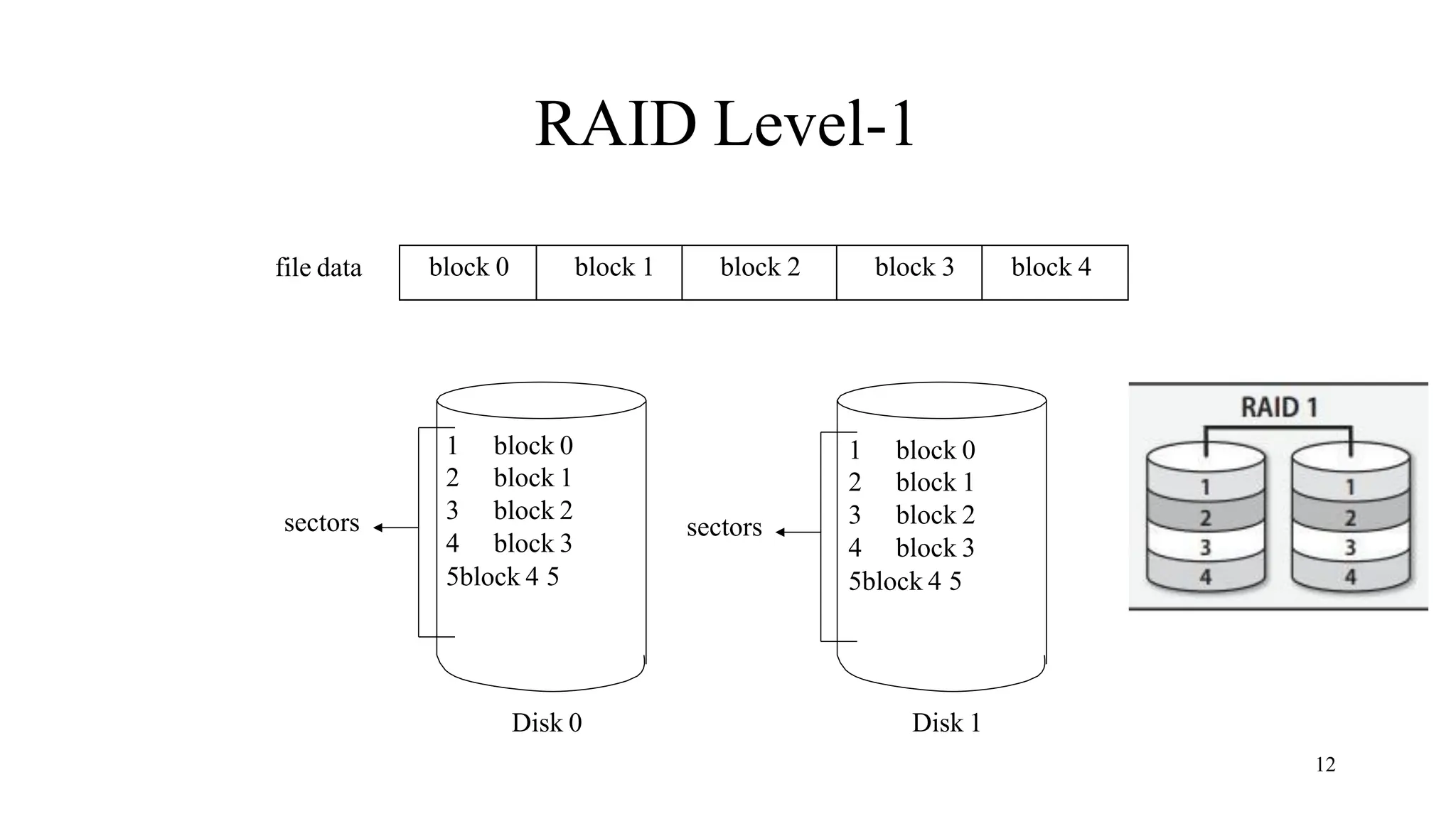
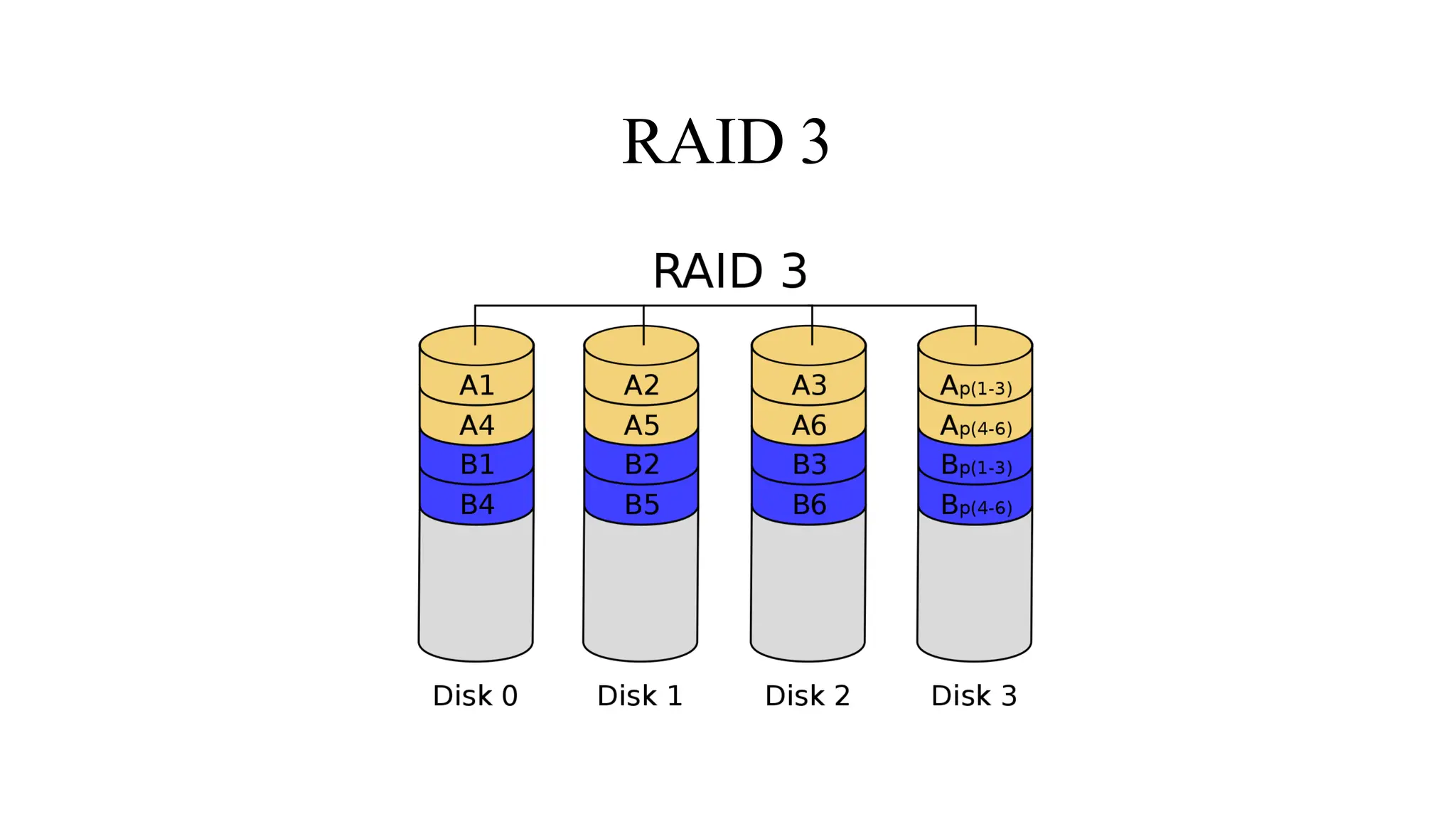
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. The main types are hardware RAID, which uses a RAID controller card, and software RAID, which relies on the operating system. Common RAID levels include RAID 0 (striping for performance), RAID 1 (mirroring for redundancy), RAID 5 (striping with parity for redundancy and performance), and RAID 6 (enhanced RAID 5 with double parity).