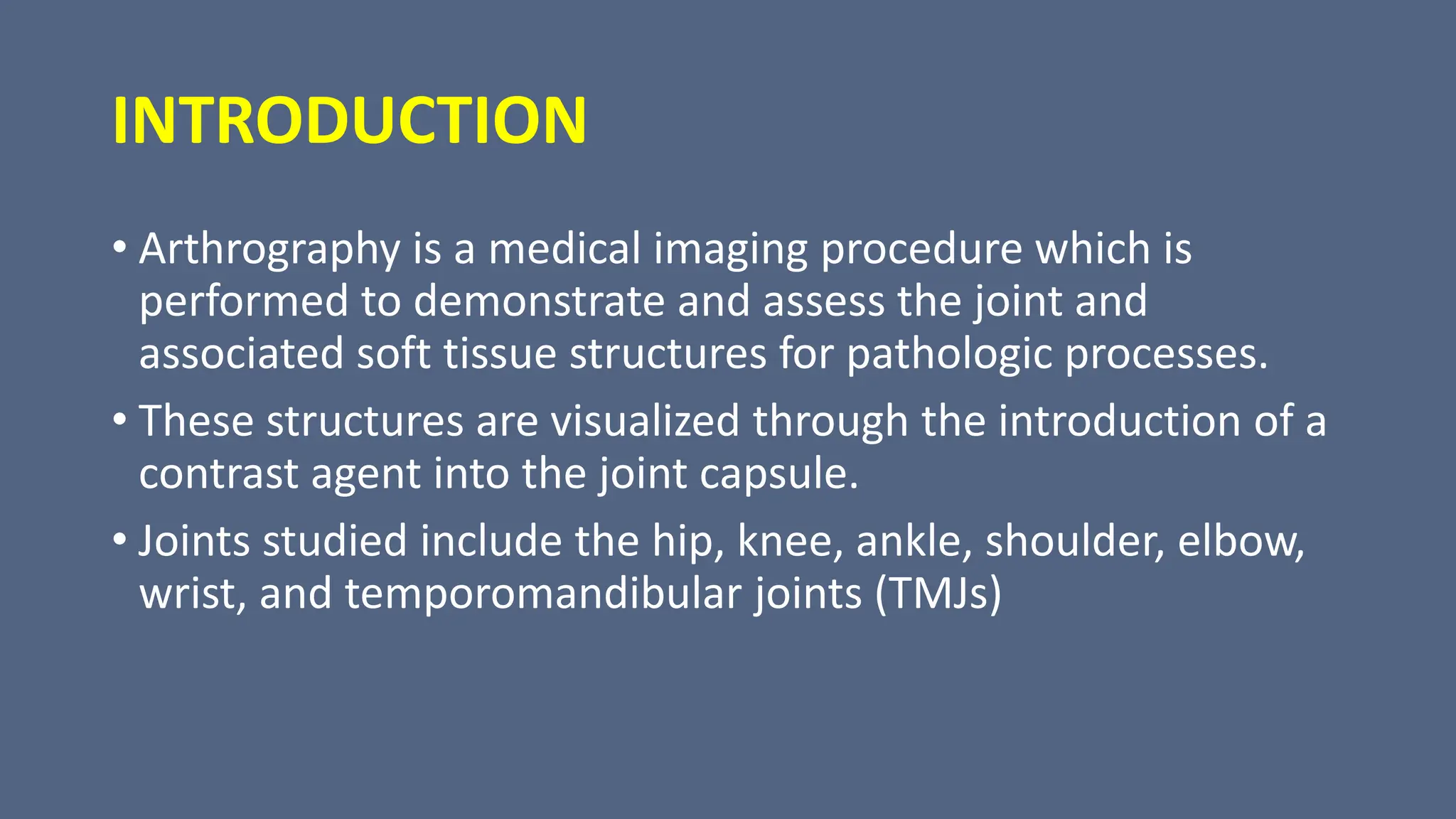
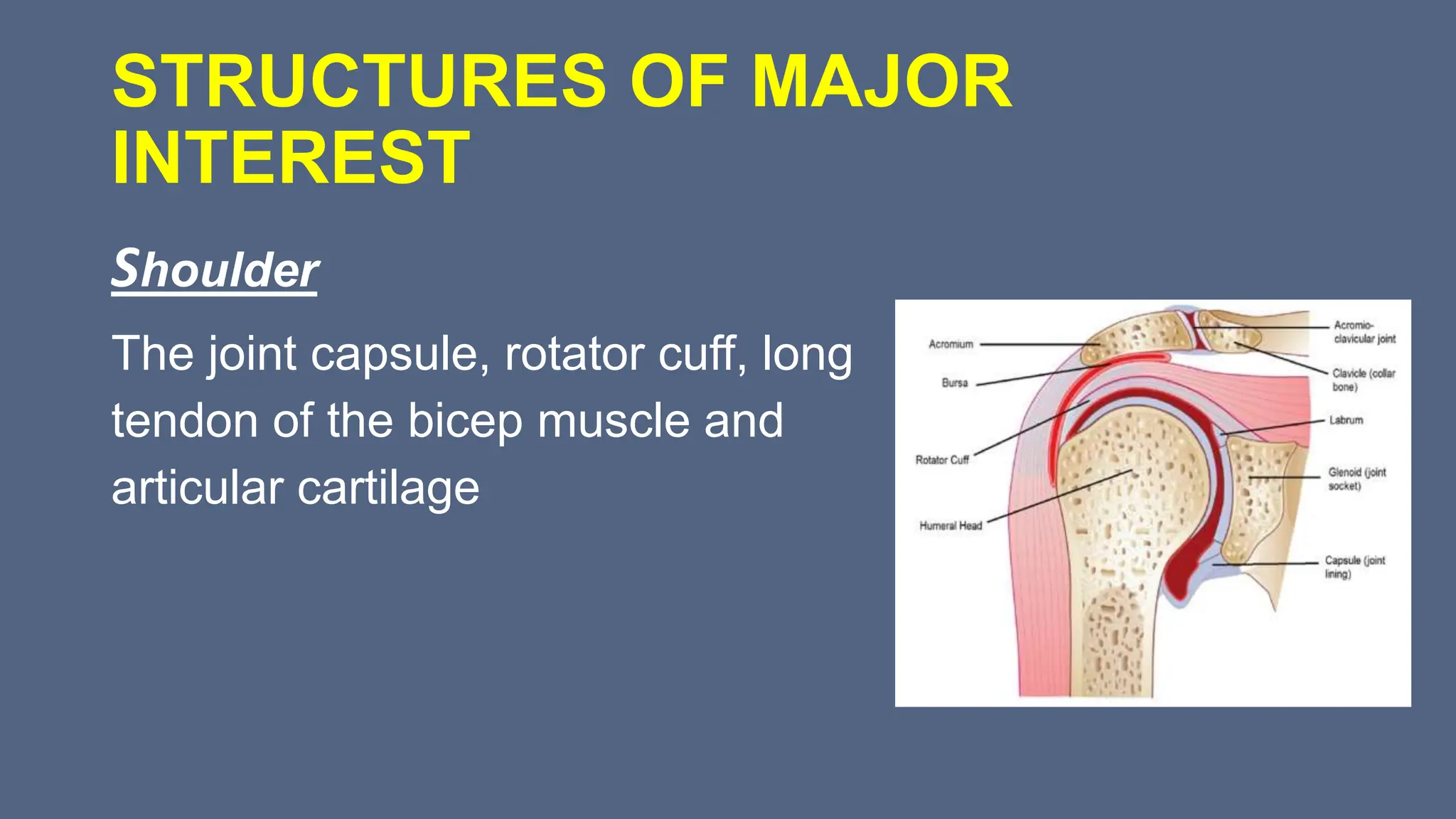
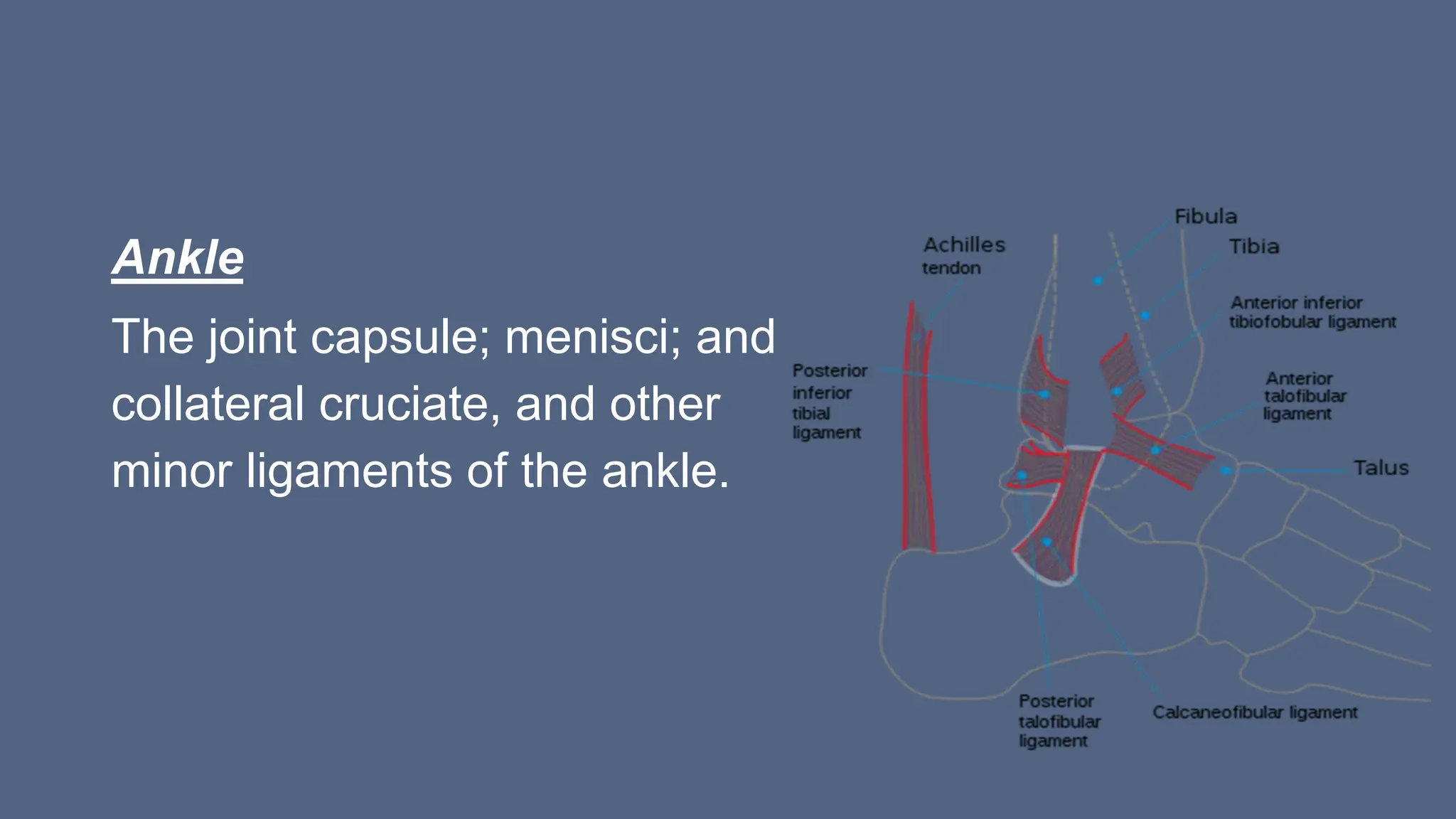
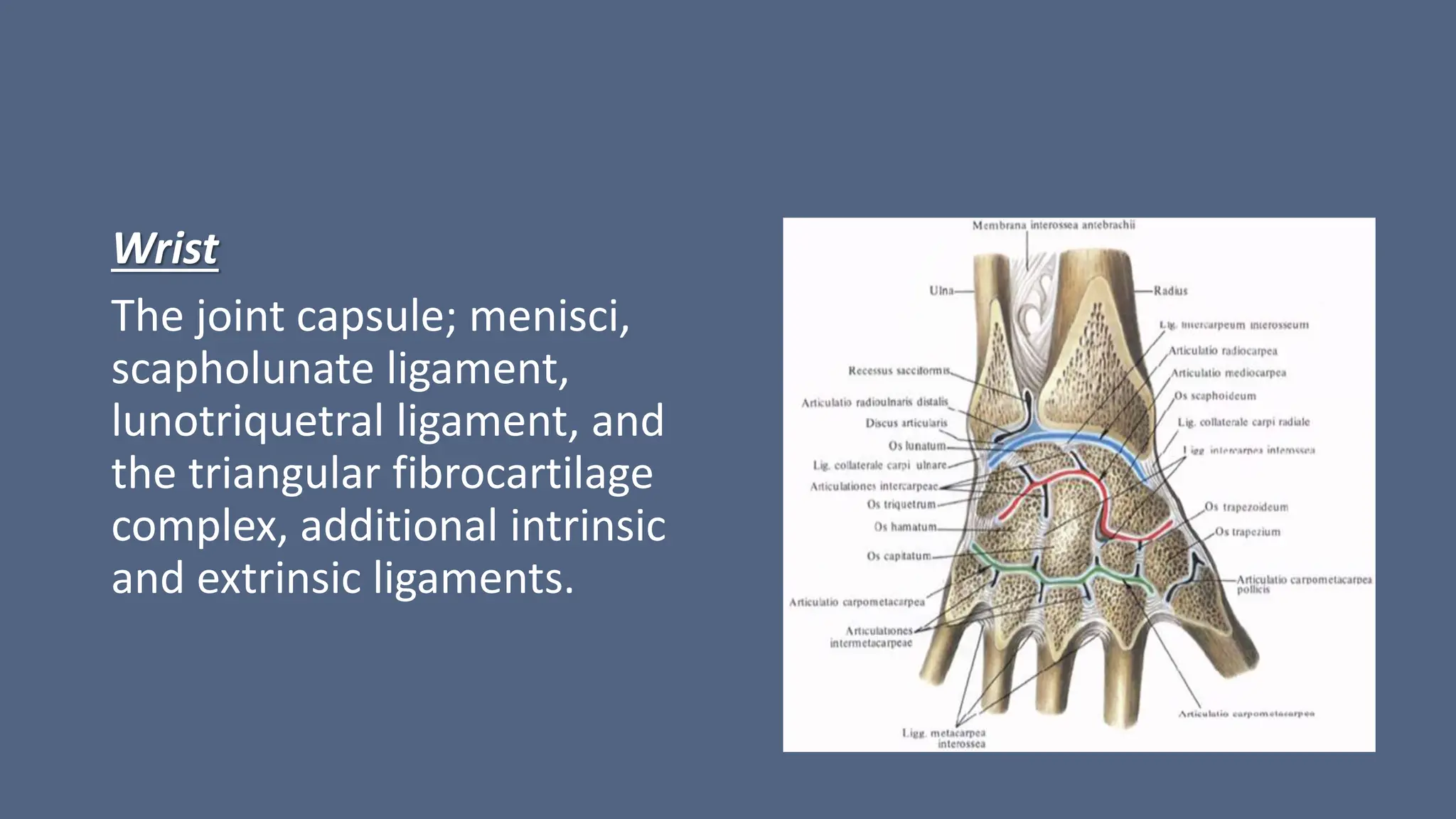
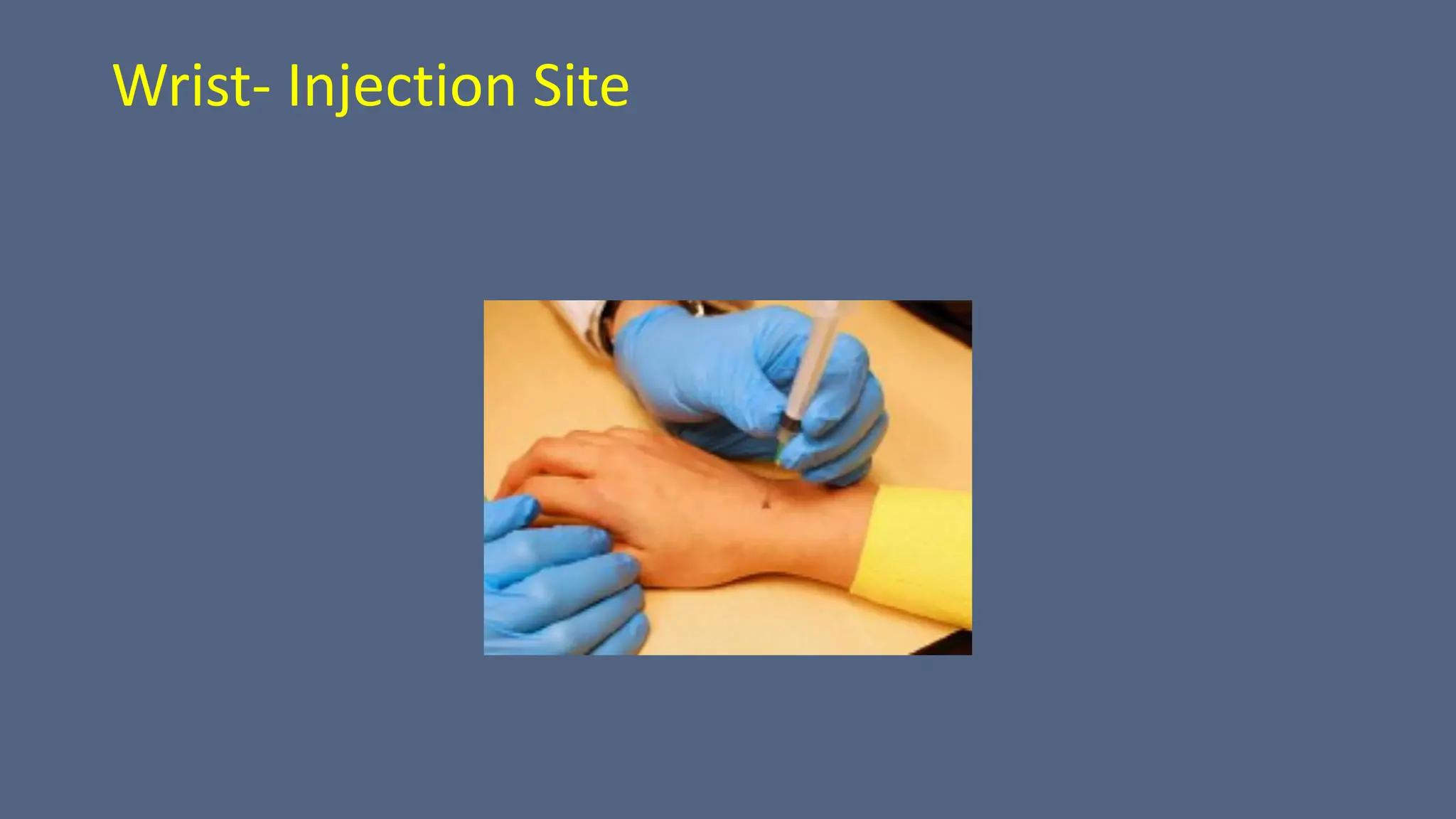
Arthrography is a medical imaging procedure used to evaluate joints and associated soft tissues by introducing a contrast agent into the joint capsule. Common indications for this procedure include trauma, persistent pain, and motion limitations, with imaging typically performed using fluoroscopy, CT, or MRI. Patient preparation involves thorough explanation, informed consent, and monitoring for complications, while aftercare includes rest and managing potential pain or swelling.