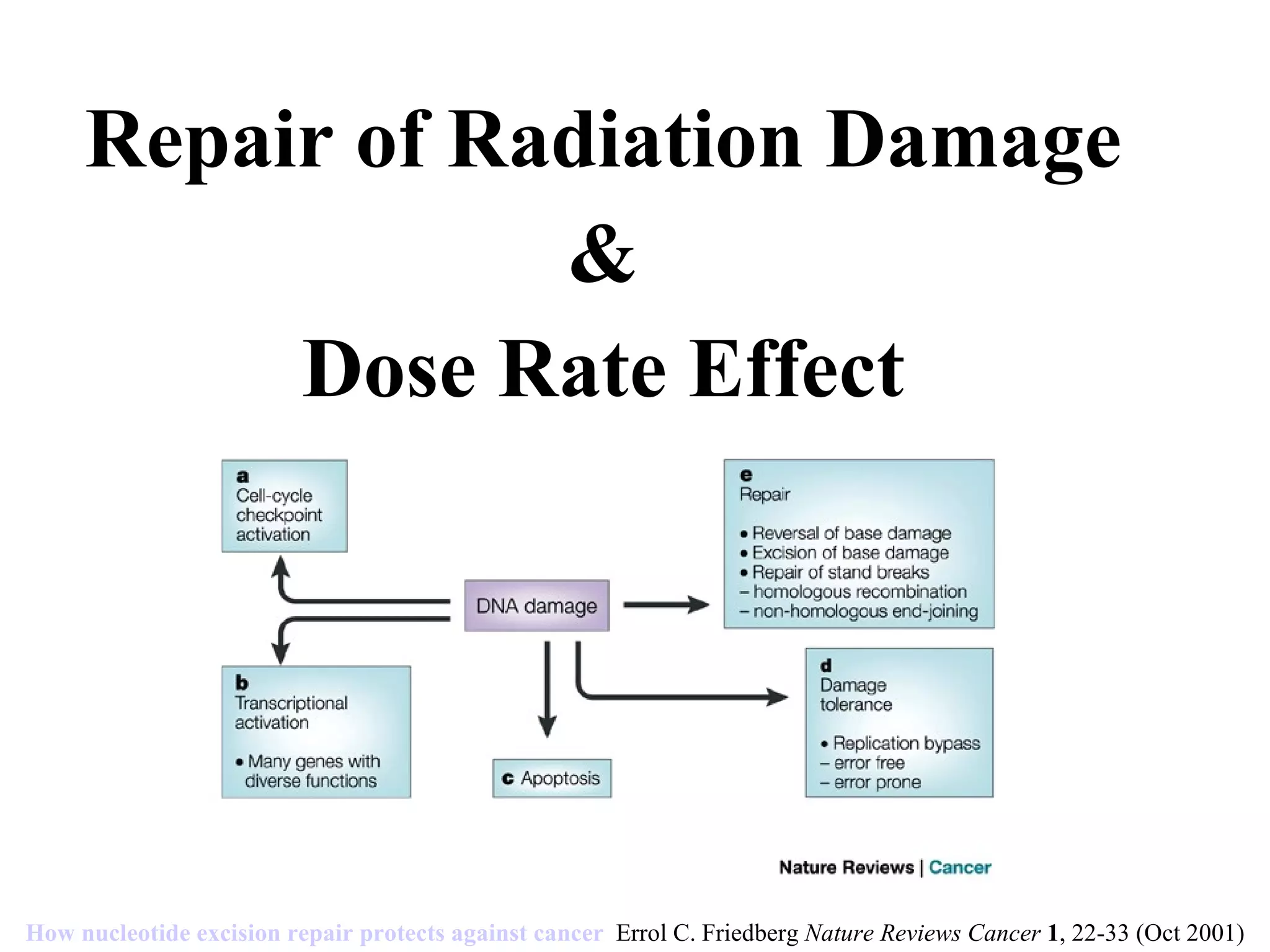
The document summarizes various pathways for repairing DNA damage from radiation: base excision repair removes inappropriate bases; nucleotide excision repair removes bulky adducts like pyrimidine dimers. Mismatch repair fixes base-base mismatches. Non-homologous end joining and homologous recombination repair double-strand breaks, with the former being error-prone and active in G1, and the latter being error-free using a sister chromatid template and most active in G2 phase. Certain syndromes like ataxia-telangiectasia and LIG4 syndrome result from defects in these pathways and cause radiation sensitivity.