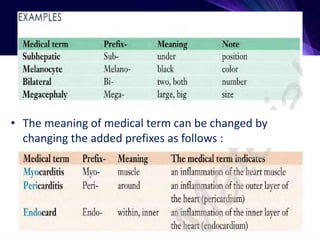
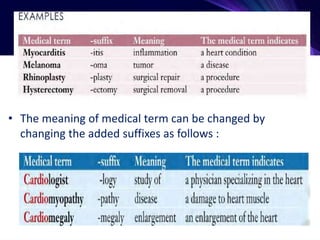
This document provides an introduction to medical terminology. It discusses how medical terminology uses precise terms from Greek and Latin roots to describe concepts in health and medicine. It also outlines some key concepts for understanding medical terminology, including roots, prefixes, and suffixes. Roots convey the essential meaning and often indicate a body part. Prefixes and suffixes are added to roots to modify or further specify a term's meaning by indicating elements like location, size, or a procedure. Understanding the components of terms helps in analyzing and defining their meanings.