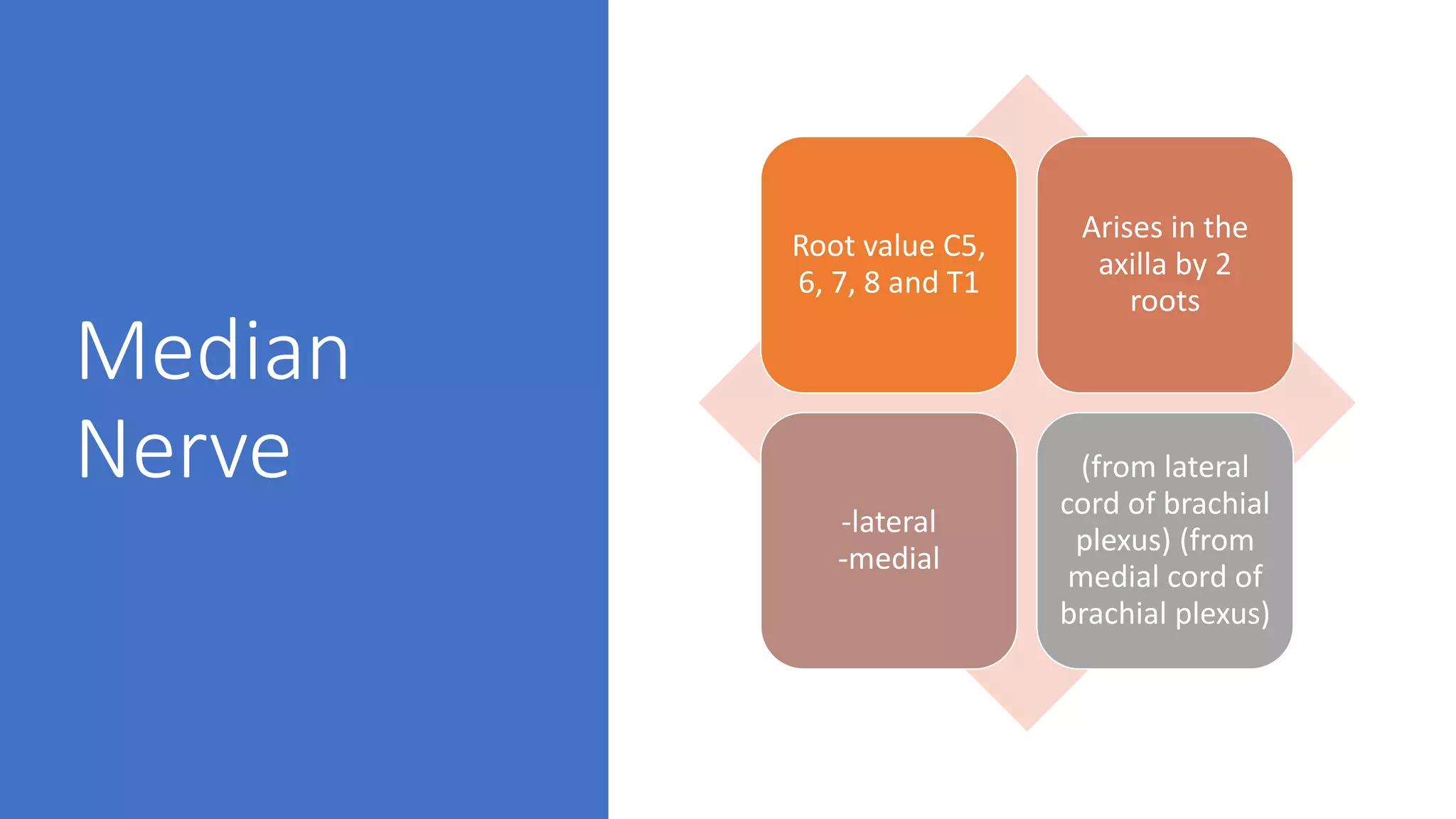
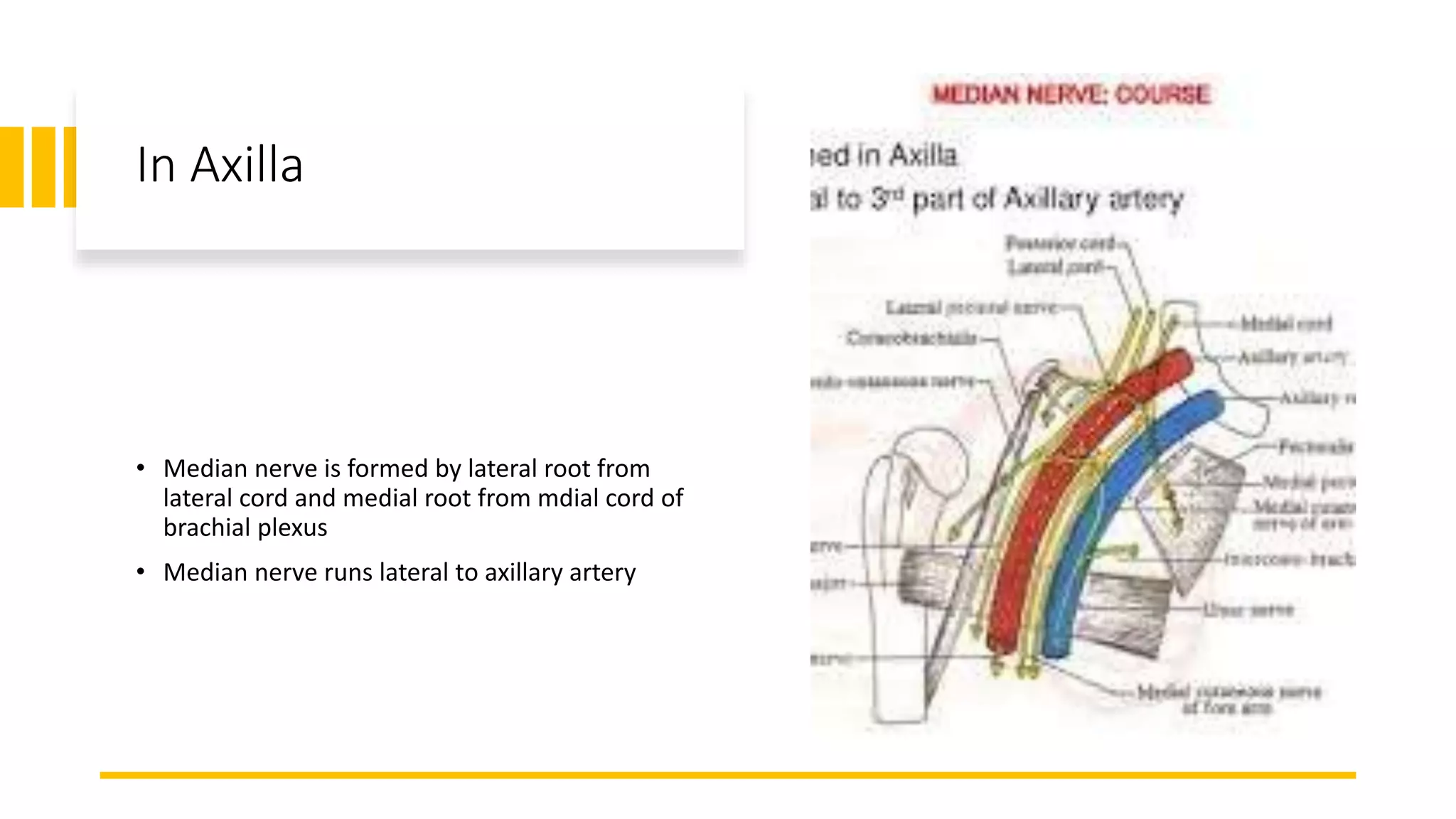
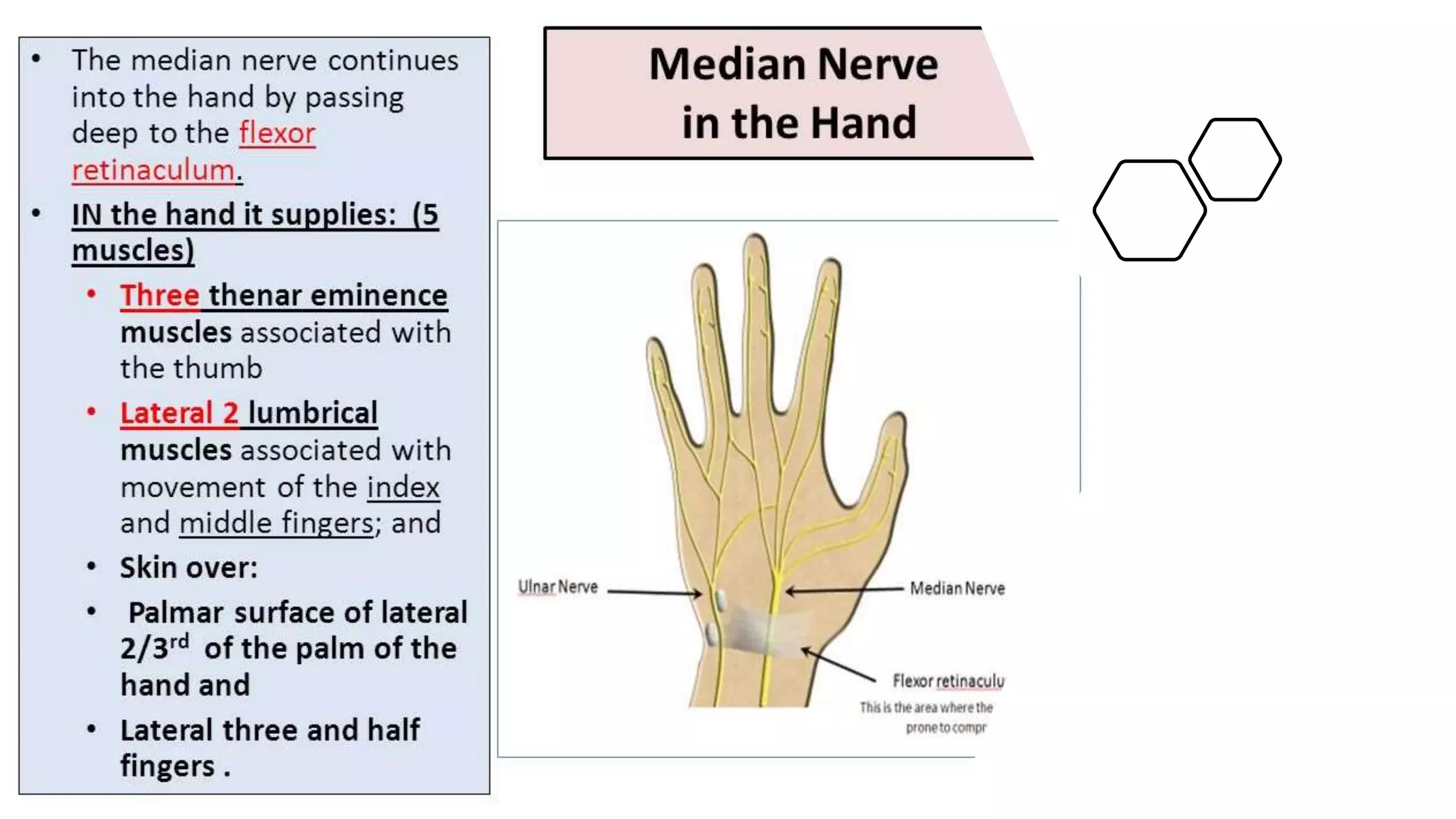
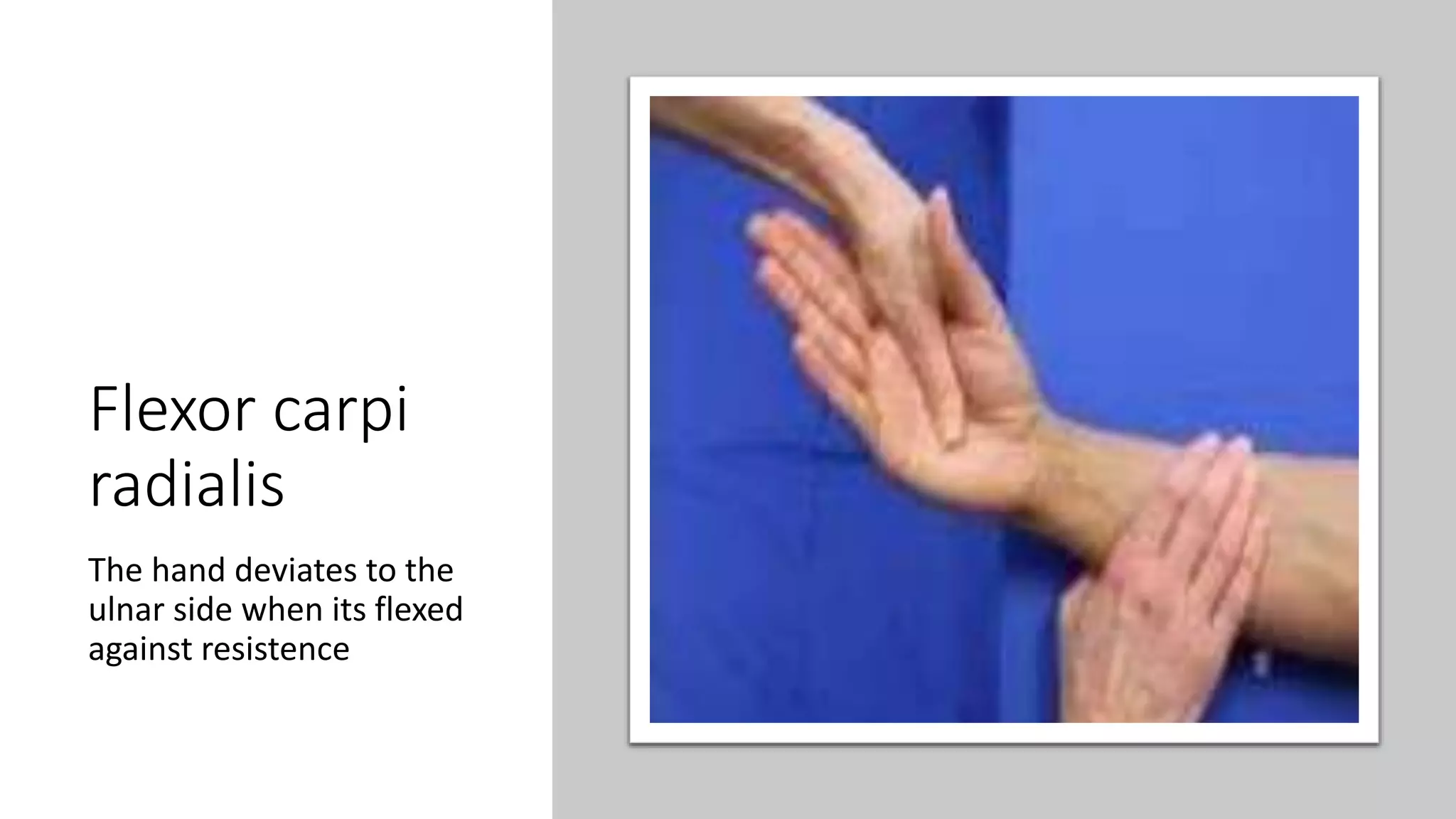
The median nerve forms from two roots in the axilla and runs along the lateral side of the brachial artery in the arm. In the forearm, it passes between muscles and becomes more superficial near the wrist. It supplies muscles in the forearm and hand including those responsible for thumb abduction and opposition. Injuries can occur proximally or distally, causing varying degrees of paralysis in the forearm and hand muscles. Physical exams like Tinel's sign and carpal compression tests help diagnose conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome affecting the median nerve.