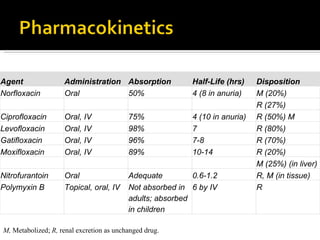
Quinolones are a class of antibiotics that are classified into generations based on their antimicrobial activity and spectrum of coverage. First generation quinolones are active against gram-negative bacteria while later generations have increased activity against gram-positive pathogens and mycobacteria. Quinolones work by inhibiting bacterial type 2 DNA topoisomerases, trapping the enzyme-DNA complex and blocking DNA synthesis. Resistance can develop via mutations in bacterial genes or active drug transport out of cells. Common quinolones available include ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, norfloxacin and more.