The document explains Lagrange's Mean Value Theorem (LMVT), outlining its conditions and providing geometrical interpretation as well as verification examples using different functions. It includes solutions to multiple problems verifying LMVT for specific mathematical functions, demonstrating how to find points where the tangent is parallel to the chord connecting endpoints. Additionally, it notes the applicability of LMVT and identifies when it is not applicable.


![Here, I will only be stating Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorem and not discussing the proof
LAGRANGE’S MEAN VALUE THEOREM states that
If a function f is
i). Continuous on [a,b]
ii) f is derivable on (a,b)
Then there exists at least one real number c ∈ 𝑎, 𝑏 𝑠𝑢𝑐ℎ 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑡 𝑓′
𝑐 =
𝑓 𝑏 −𝑓(𝑎)
𝑏−𝑎](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lagrangesmeanvaluetheorem-180509164717/85/QUICK-METHOD-OF-LEARNING-LAGRANGE-S-MEAN-VALUE-THEOREM-3-320.jpg)


![Question 1 (GRADE XII MATH)
VERIFY Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorem for the function f(x) = 𝑥3
− 5𝑥2
− 3𝑥 𝑖𝑛 [1,3]
i)f being a polynomial function is continuous in [1,3]
ii) 𝑓′
𝑥 = 3 𝑥2
− 10 𝑥 − 3
f is derivable on (1, 3 )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lagrangesmeanvaluetheorem-180509164717/85/QUICK-METHOD-OF-LEARNING-LAGRANGE-S-MEAN-VALUE-THEOREM-6-320.jpg)
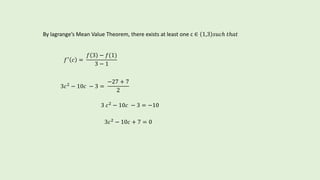
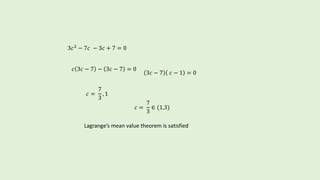
![Question 2
Verify lagrange’s Mean Value Theorem for the function f(x) = sinx – sin 2x on [ 0,𝜋]
i) f being a trigonometric function is continuous on[ 0,𝜋]
ii) 𝑓′ 𝑥 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 − 2 𝑐𝑜𝑠2𝑥
f is derivable on ( 0, 𝜋)
By lagrange’s theorem ∃ 𝑎𝑡 𝑙𝑒𝑎𝑠𝑡 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑐 ∈ 0, 𝜋 𝑠𝑢𝑐ℎ 𝑡ℎ𝑎𝑡](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lagrangesmeanvaluetheorem-180509164717/85/QUICK-METHOD-OF-LEARNING-LAGRANGE-S-MEAN-VALUE-THEOREM-9-320.jpg)
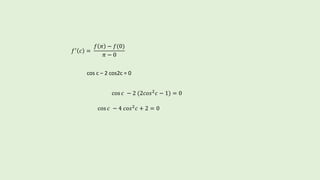

![Question 3
Grade 12 math
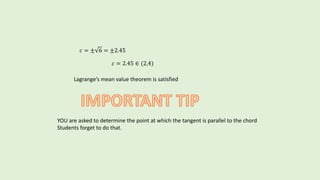
Use lagrange’s mean value theorem to determine a point on the curve
𝑦 = 𝑥2 − 4 defined in [2,4], where the tangent is parallel to the chord joining
the endpoints of the curve
𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2 − 4
i) f is continuous on [2,4] being a polynomial function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lagrangesmeanvaluetheorem-180509164717/85/QUICK-METHOD-OF-LEARNING-LAGRANGE-S-MEAN-VALUE-THEOREM-12-320.jpg)
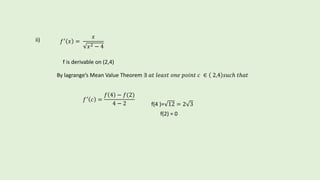

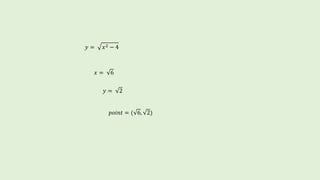
![Question 4
Is lagrange’s Mean Value Theorem applicable for the function f(x) = 𝑥 𝑖𝑛 [−2,3]
𝑥 𝑖𝑠 𝑛𝑜𝑡 𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑣𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑎𝑡 𝑥 = 0
lagrange’s mean value theorem is not applicable
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RNAdeCD1ncw&list=PL26
R7TjUyi8zDE3-OcadJuTKlXApnFJG6
GRADE 12 MATH : DIFFERENTIATION PLAYLIST VIDEOS FOR ISC, CBSE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lagrangesmeanvaluetheorem-180509164717/85/QUICK-METHOD-OF-LEARNING-LAGRANGE-S-MEAN-VALUE-THEOREM-17-320.jpg)
