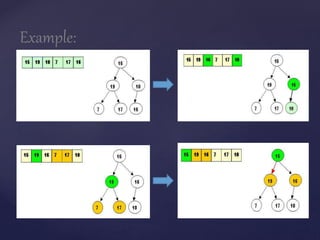
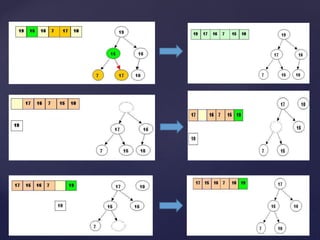
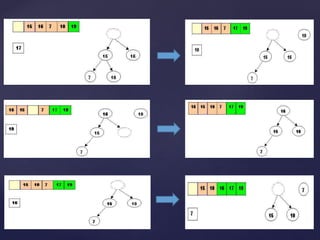
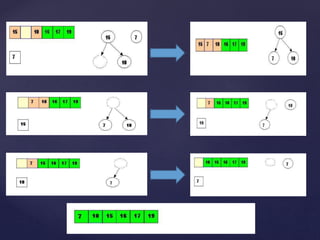
The document describes two sorting algorithms: quicksort and heapsort. Quicksort is a divide and conquer algorithm that works by selecting a pivot element and partitioning the array around it, recursively sorting the subarrays. The performance depends on how well balanced the partitions are. Heapsort uses a binary heap data structure to sort an array in-place. It works by building a max heap from the array and then removing elements from the heap one by one.









![Types Of Heap:
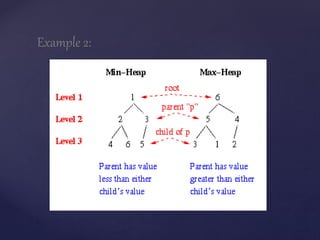
Min Heap :-
If the value at the node N, is less than or equal to
the value at each of the children of N, then Heap is
called a MIN-HEAP.
In General, a Heap represents a table of N
elements or records satisfying the following
property;
Nj Ni for i j n & i = [j/2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst1-141113180046-conversion-gate02/85/Quick-and-Heap-Sort-with-examples-10-320.jpg)
![ Max Heap:-
If the value at the node N, is greater than or equal
to the value at each of the children of N, then Heap
is called a MAX-HEAP.
In General, a Heap represents a table of N
elements or records satisfying the following
property;
Nj Ni for i j n & i = [j/2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bst1-141113180046-conversion-gate02/85/Quick-and-Heap-Sort-with-examples-11-320.jpg)