Data structures notes
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
0 likes•89 views
The document discusses different data structures and their properties. It defines data structures as the logical organization of data and describes several common primitive and non-primitive data structures including arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, trees, graphs, and binary search trees. It provides examples of operations that can be performed on different data structures like insertion, deletion, searching, and sorting.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
linked list in Data Structure, Simple and Easy Tutorial

linked list in Data Structure, Simple and Easy Tutorial
Similar to Data structures notes
Similar to Data structures notes (20)
1.Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms.pptx

1.Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms.pptx
More from Upasana Talukdar
More from Upasana Talukdar (20)
Recently uploaded
Process of Integration the Laser Scan Data into FEA Model and Level 3 Fitness-for-Service Assessment of Critical Assets in Refinery & Process IndustriesFEA Based Level 3 Assessment of Deformed Tanks with Fluid Induced Loads

FEA Based Level 3 Assessment of Deformed Tanks with Fluid Induced LoadsArindam Chakraborty, Ph.D., P.E. (CA, TX)
Model Call Girl Services in Delhi reach out to us at 🔝 9953056974🔝✔️✔️ Our agency presents a selection of young, charming call girls available for bookings at Oyo Hotels. Experience high-class escort services at pocket-friendly rates, with our female escorts exuding both beauty and a delightful personality, ready to meet your desires. Whether it's Housewives, College girls, Russian girls, Muslim girls, or any other preference, we offer a diverse range of options to cater to your tastes. We provide both in- call and out-call services for your convenience. Our in-call location in Delhi ensures cleanliness, hygiene, and 100% safety, while our out-call services offer doorstep delivery for added ease. We value your time and money, hence we kindly request pic collectors, time-passers, and bargain hunters to refrain from contacting us. Our services feature various packages at competitive rates: One shot: ₹2000/in-call, ₹5000/out-call Two shots with one girl: ₹3500 /in-call, ₱6000/out-call Body to body massage with sex: ₱3000/in-call Full night for one person: ₱7000/in-call, ₱10000/out-call Full night for more than 1 person : Contact us at 🔝 9953056974🔝. for details Operating 24/7, we serve various locations in Delhi, including Green Park, Lajpat Nagar, Saket, and Hauz Khas near metro stations. For premium call girl services in Delhi 🔝 9953056974🔝. Thank you for considering us Call Girls in South Ex (delhi) call me [🔝9953056974🔝] escort service 24X7![Call Girls in South Ex (delhi) call me [🔝9953056974🔝] escort service 24X7](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Call Girls in South Ex (delhi) call me [🔝9953056974🔝] escort service 24X7](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Call Girls in South Ex (delhi) call me [🔝9953056974🔝] escort service 24X79953056974 Low Rate Call Girls In Saket, Delhi NCR
Recently uploaded (20)
FEA Based Level 3 Assessment of Deformed Tanks with Fluid Induced Loads

FEA Based Level 3 Assessment of Deformed Tanks with Fluid Induced Loads
Bhubaneswar🌹Call Girls Bhubaneswar ❤Komal 9777949614 💟 Full Trusted CALL GIRL...

Bhubaneswar🌹Call Girls Bhubaneswar ❤Komal 9777949614 💟 Full Trusted CALL GIRL...
Double Revolving field theory-how the rotor develops torque

Double Revolving field theory-how the rotor develops torque
Design For Accessibility: Getting it right from the start

Design For Accessibility: Getting it right from the start
Orlando’s Arnold Palmer Hospital Layout Strategy-1.pptx

Orlando’s Arnold Palmer Hospital Layout Strategy-1.pptx
S1S2 B.Arch MGU - HOA1&2 Module 3 -Temple Architecture of Kerala.pptx

S1S2 B.Arch MGU - HOA1&2 Module 3 -Temple Architecture of Kerala.pptx
DC MACHINE-Motoring and generation, Armature circuit equation

DC MACHINE-Motoring and generation, Armature circuit equation
"Lesotho Leaps Forward: A Chronicle of Transformative Developments"

"Lesotho Leaps Forward: A Chronicle of Transformative Developments"
Call Girls in South Ex (delhi) call me [🔝9953056974🔝] escort service 24X7![Call Girls in South Ex (delhi) call me [🔝9953056974🔝] escort service 24X7](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Call Girls in South Ex (delhi) call me [🔝9953056974🔝] escort service 24X7](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Call Girls in South Ex (delhi) call me [🔝9953056974🔝] escort service 24X7
1_Introduction + EAM Vocabulary + how to navigate in EAM.pdf

1_Introduction + EAM Vocabulary + how to navigate in EAM.pdf
PE 459 LECTURE 2- natural gas basic concepts and properties

PE 459 LECTURE 2- natural gas basic concepts and properties
Data structures notes
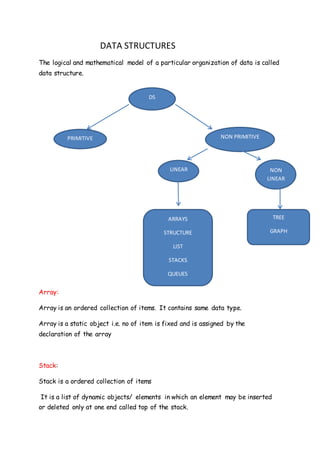
- 1. DATA STRUCTURES The logical and mathematical model of a particular organization of data is called data structure. PRIMITIVE Array: Array is an ordered collection of items. It contains same data type. Array is a static object i.e. no of item is fixed and is assigned by the declaration of the array Stack: Stack is a ordered collection of items It is a list of dynamic objects/ elements in which an element may be inserted or deleted only at one end called top of the stack. DS PRIMITIVE NON PRIMITIVE LINEAR NON LINEAR ARRAYS STRUCTURE LIST STACKS QUEUES TREE GRAPH
- 2. Elements are removed from a stack in the reverse order of that in which they are inserted in the stack. “Push”- to insert into the stack “pop”- to delete an element from a stack. Stacks are used to indicate the order of processing of data when certain steps of the processing must be postponed until other conditions are fulfilled. Follows LIFO Elements are removed from a stack (pop) in the reverse order of that in which they were inserted into the stack (push). It may contain different data types Integer to indicate the current stack top within the array. Operations: push, pop. Queue: An ordered collection of items from which items may be deleted at one end (front end) & items inserted at the other end (rear end). It follows FIFO. Priority Queue: priority queue is a data structure in which the intrinsic ordering of the elements (numeric or alphabetic) Linked list: A linked list is a linear collection of data elements, called nodes, where the linear order is given by pointers. Each node has two parts 1st part contain the information of the element 2nd part contains the address of the next node in the list. double linked list: It is a collection of data elements called nodes, where each node is divided into three parts i) An info field that contains the information stored in the node
- 3. ii) Left field that contain pointer to node on left side iii) Right field that contain pointer to node on right side Tree: It is used to represent data which has a hierarical relationship. It can have any no. of children per node. Binary tree: it can have max. 2 children per node. LEFT SUCCESSOR RIGHT SUCCESSOR A spanning tree is a tree associated with a network. All the nodes of the graph appear on the tree once. A minimum spanning tree is a spanning tree organized so that the total edge weight between nodes is minimized Binary search tree: The values in all nodes in the right subtree of a node are greater than the node values. AVL tree: An empty binary tree, is an AVL tree, a non empty binary T tree is a AVL tree. If given, TL & TR to be the left & right subtrees of T & H(TL) & H(TR) to be the height of the subtrees TL & TR respectively. TL & TR are AVL trees & | H(TL)- H(TR)| <=1 where { H(TL)- H(TR } is known as the balance factor. The balance factor of a node can be either 0,1, or -1 B=-1 B=0 B=-1 50 40 60 () 70 R T1 T2
- 4. B=0 Graph: A+B ::: INFIX +AB ::: PREFIX AB+ ::: POSTFIX Precedence order: 1. Exponential 2. Multiplication 3. Divison 4. Addition 5. Substraction
- 5. Operations done: 1. Insertion 2. Deletion 3. Display/traversing 4. Searching 5. Sorting Bubble sort: Compare 2 adjacent elements, adjust by swapping & compare next 2 elements. Insertion sort: 1st element will be considered as a total array & the rest would be considered as a 2nd array & the adjustment is made by swapping. 2nd step: take 1st 2 elements as the 1st array & rest as 2nd array. Continue till the 2nd array becomes null. Selection sort: Take the smallest element & place it in the 1st position. Then start from the 2nd block & take the 2nd smallest element In each pass we store 2 variables. Binary search: Last index will be in high. 1st index will be in low. Middle index will be stored in mid=(low + high)/2 for low<=high Merge sort: Last index will be in high. 1st index will be in low. Middle index will be stored in mid=(low + high)/2 for low<=high Quick sort: Mid= a[(high +low)/2] =p0 We will start checking from the left side & we will compare with p0 element. Towers of Hanoi
- 6. A B C Moving the blocks, from peg A to peg C, the condition is that only one block can be moved at a time. TREE: It is used in networking. Binary tree: A set of elements that is either empty or is portioned into 3 disjoint subset. The 1st subset contains a single element called “root of the tree”. Each element is called “node of the tree” ROOT LEFT SUB TREE A B C RIGHT SUB TREE D F PREDEESSOR SIBBLINGS S E
- 7. D,E,F – LEAVE NODE, because they don’t have successor. Different type of binary tree: 1. Strictly binary tree: A non leave node has non empty left & right sub tree. A node can contain max. 2 child. 2. Complete binary tree: Each node will contain maximum no. of child. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O MAX. 1 2 3 4 LEVEL 0 1 2 3
- 8. 3. Almost binary tree: All nodes are at its max. level except possibly the last level & all nodes at the last level appear as far left as possible A B C E F G