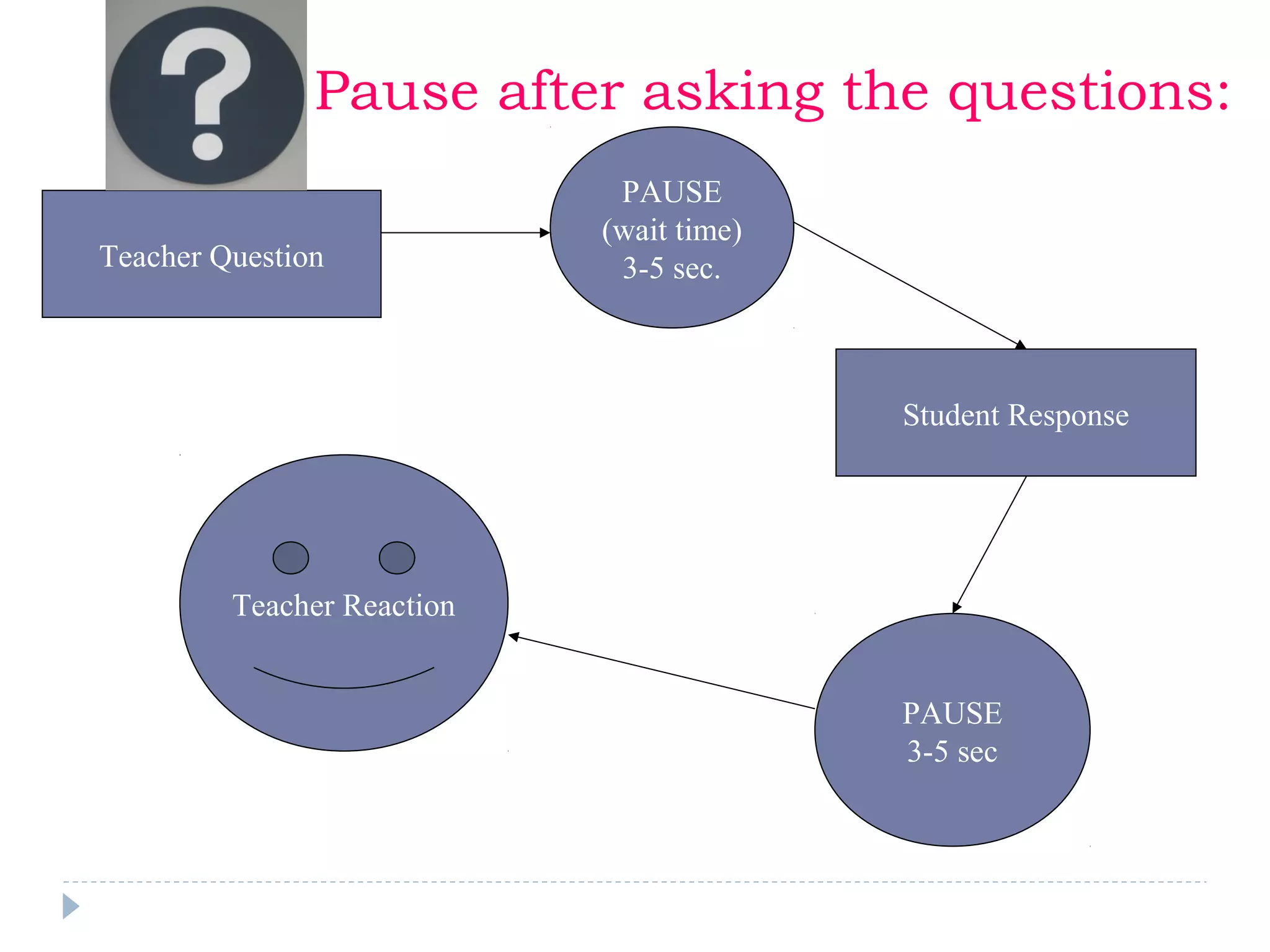
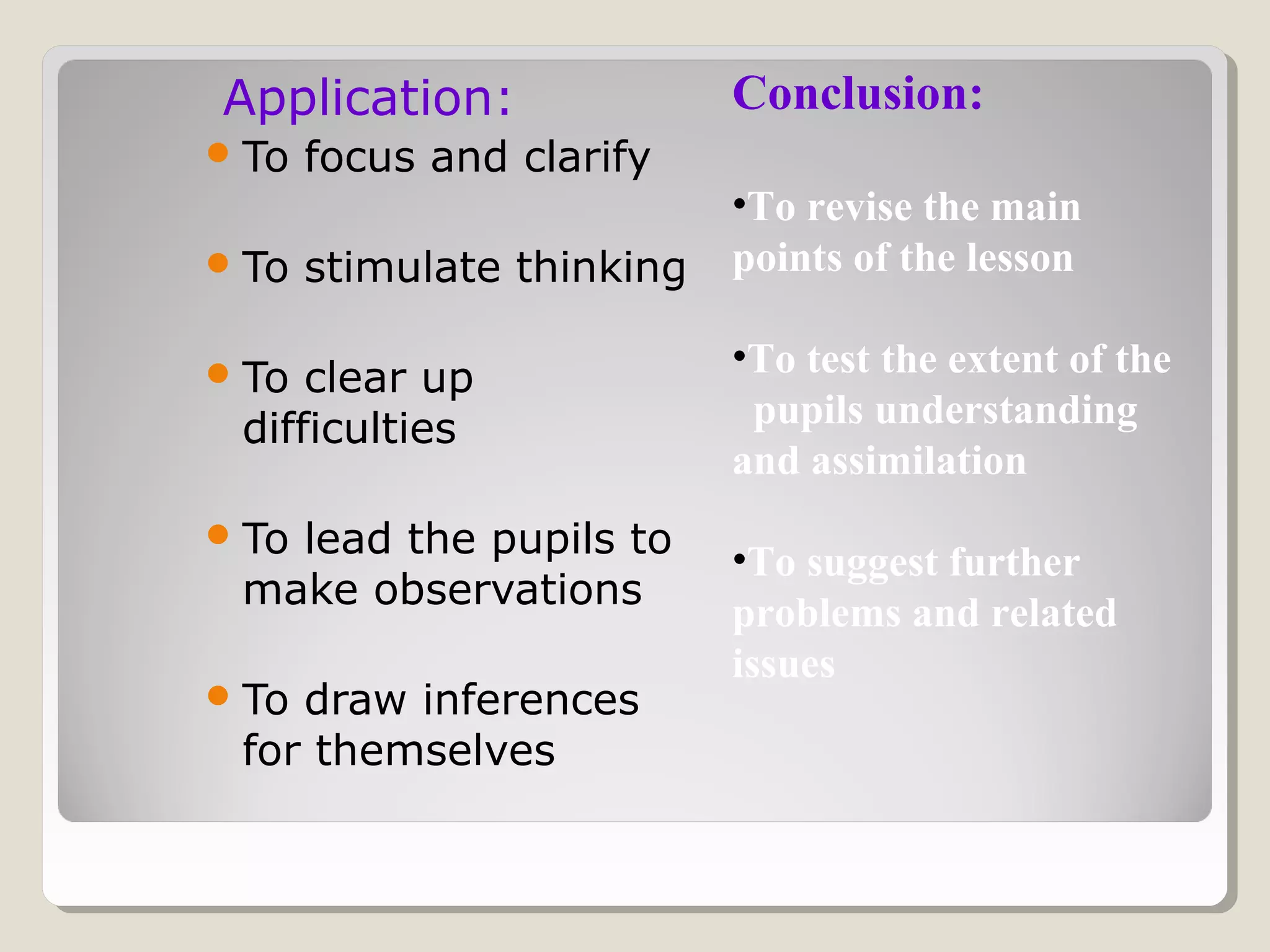
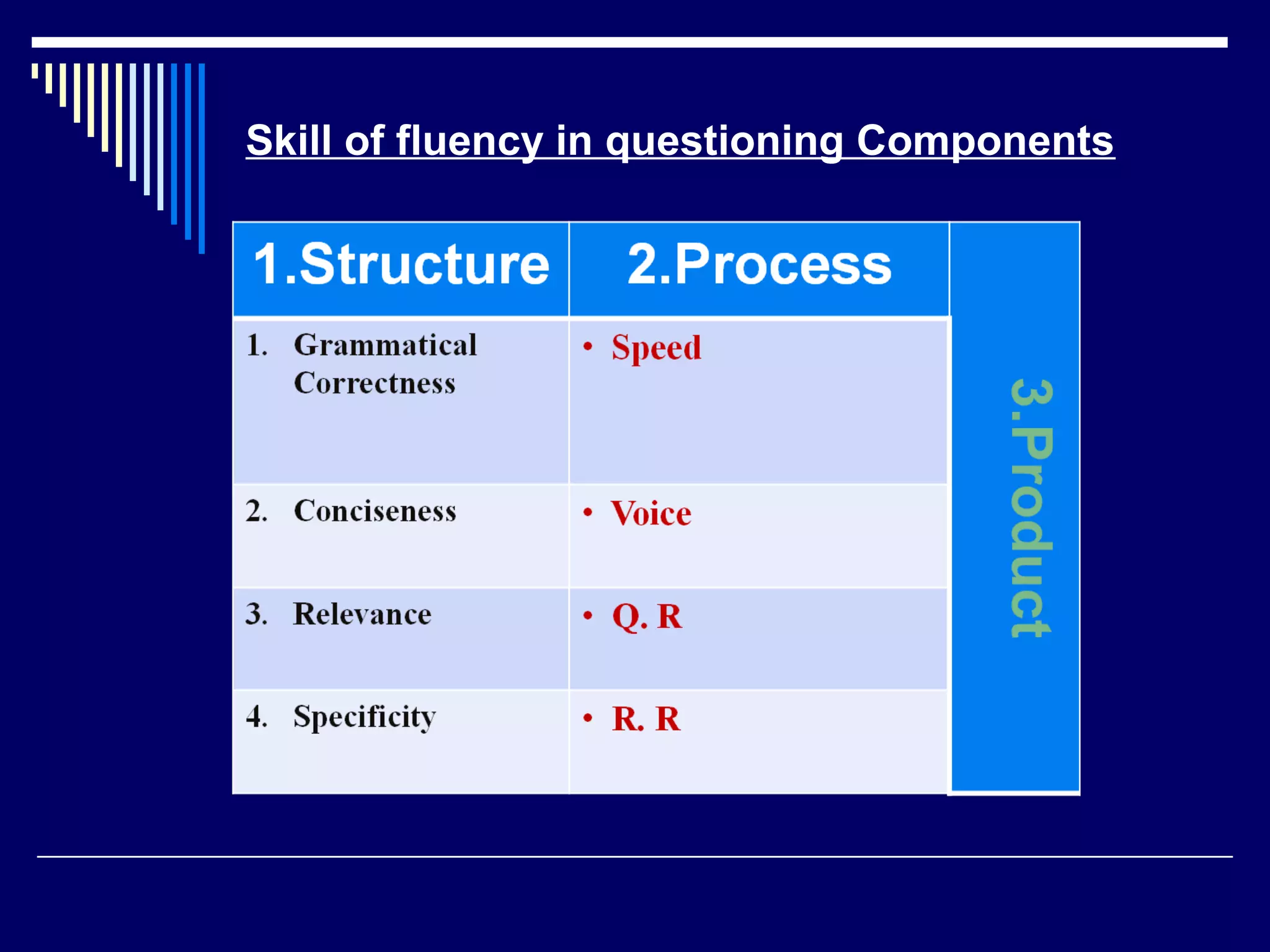
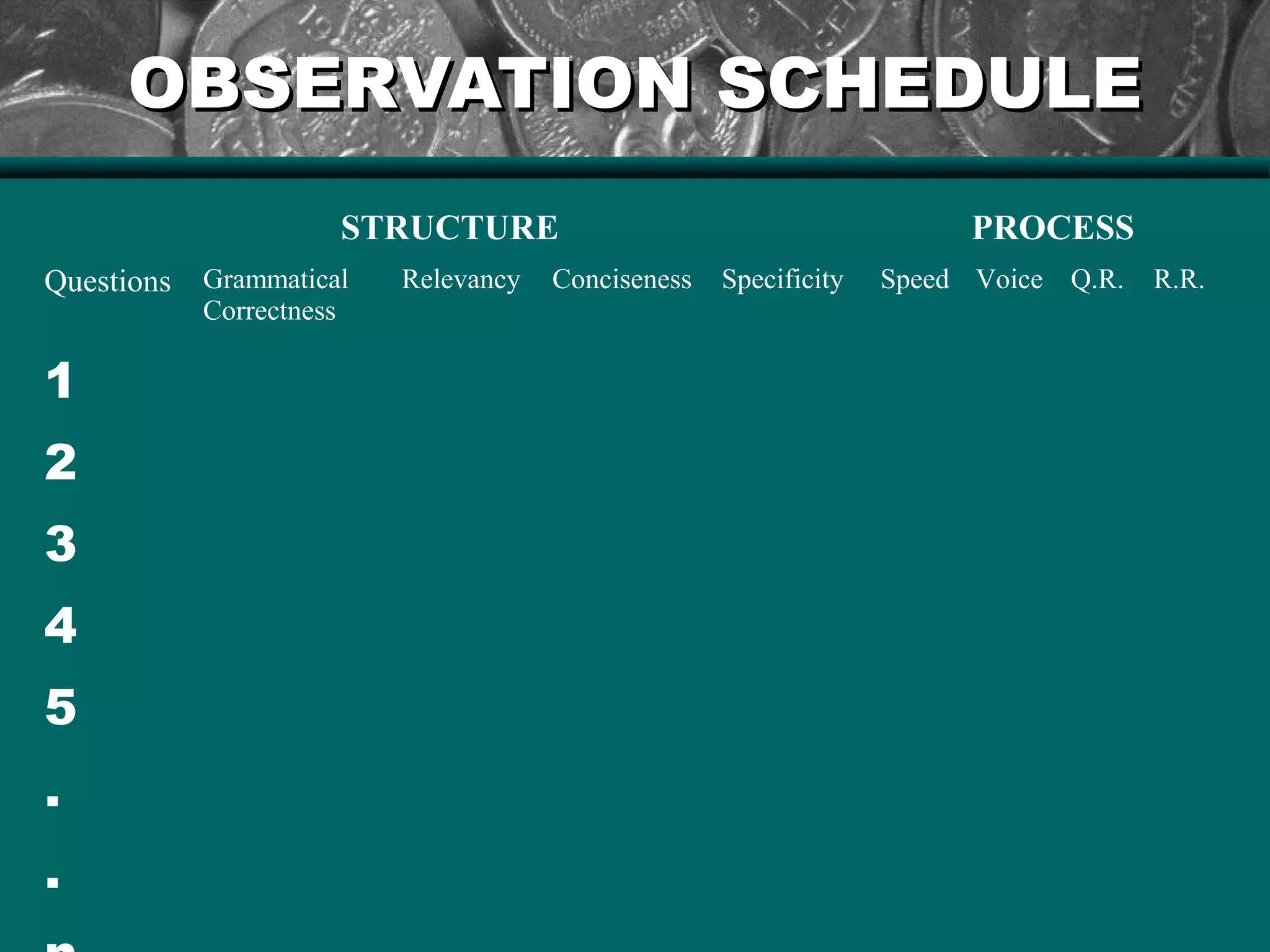
The document discusses the importance of questioning as a key component of effective teaching, emphasizing the need for high-quality questions that motivate and engage students. It outlines various types of questions, techniques for effective questioning, and the impact of questioning on student learning and classroom dynamics. The author stresses that mastery of questioning techniques is essential for teachers to enhance learning outcomes and foster a positive classroom environment.