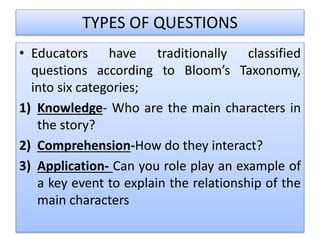
This document discusses effective questioning techniques for teachers. It begins by defining questions and explaining why they are important teaching tools for engaging students and assessing understanding. It then categorizes questions according to Bloom's Taxonomy from basic recall questions to higher-order evaluation questions. Additional questioning strategies are presented, including convergent, divergent, reflective, and evaluative questions. Specific questioning techniques are outlined such as "no hands" and "question of the day." The document concludes by discussing how to properly frame questions using interrogative words.