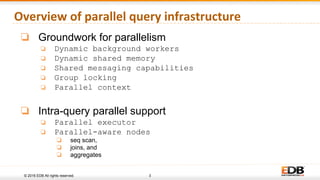
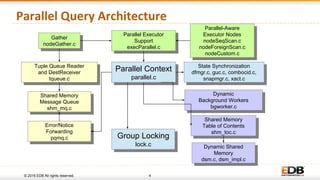
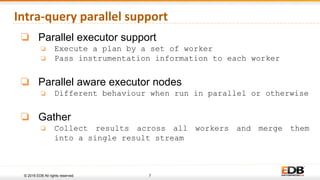
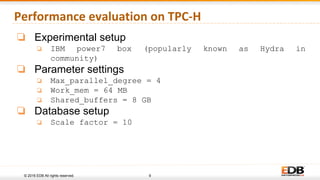
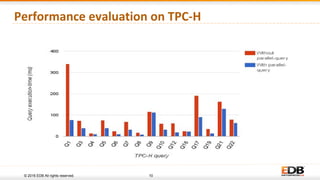
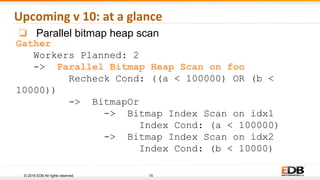
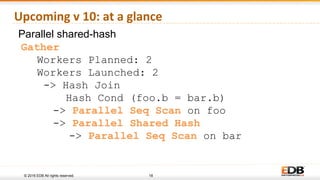
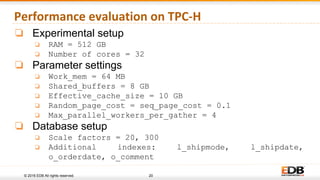
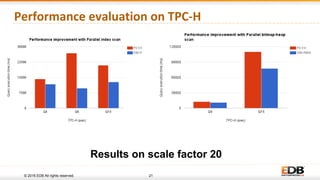
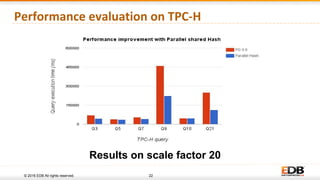
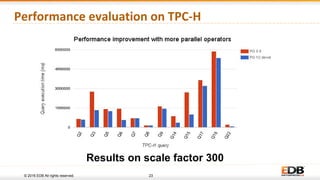
The document discusses advancements in query parallelism within PostgreSQL, specifically highlighting features introduced in versions 9.6 and 10. Key enhancements include dynamic background workers, shared memory capabilities, and various parallel execution strategies for joins, sorting, and aggregates. The overall aim is to improve performance, with significant speed increases observed in multiple TPC-H queries through the new parallel execution features.















![27
Output: Thank You
Gather
Workers Planned: 2
Workers Launched: 2
-> Parallel Index Scan on Common_phrases
Index Cond: ( value = ‘Thank You’ )
Filter: Language = ‘English’
Slide credits:
[1] https://www.pgcon.org/2016/schedule/events/913.en.html
[2] https://www.postgresql.eu/events/schedule/pgconfeu2016/session/1360-parallel-query-in-postgresql/
[3] http://pgconf.in/schedule/query-parallelism-in-postgresql-expectations-and-opportunities/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parallelqueypgdayasia-170318140234/85/Query-Parallelism-in-PostgreSQL-What-s-coming-next-27-320.jpg)