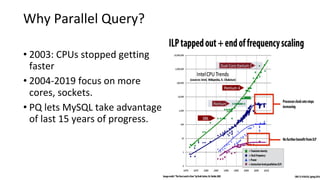
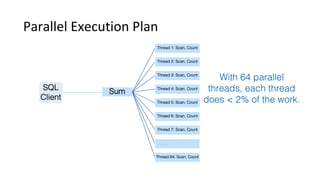
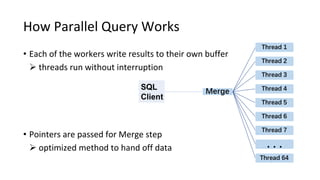
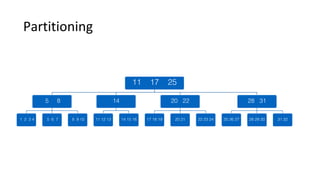
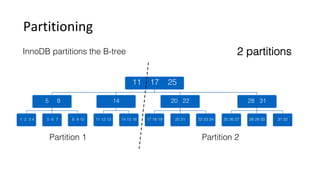
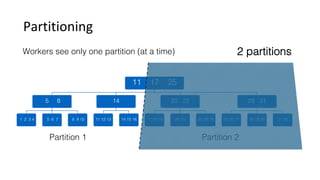
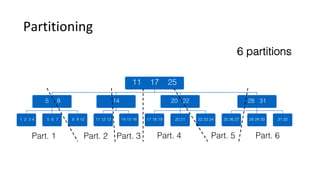
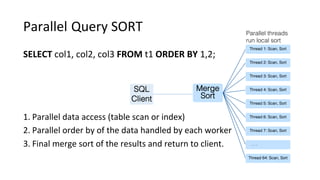
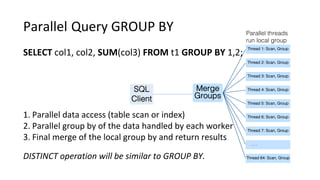
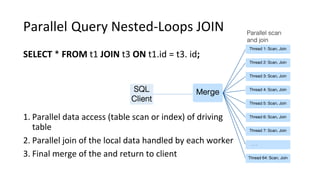
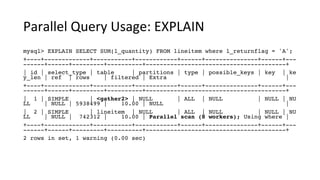
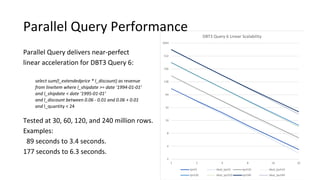
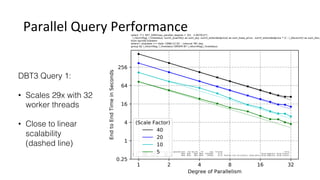
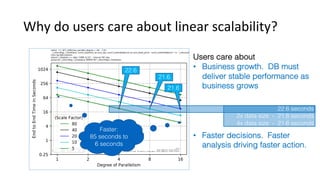
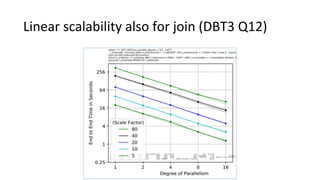
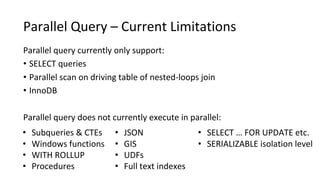
This document discusses Parallel Query, a feature of POLARDB for MySQL that allows queries to run in parallel across multiple CPU cores for improved performance. It begins with an introduction to Parallel Query and how it works, then discusses how to use Parallel Query, how it is implemented internally, examples of performance improvements seen, and some current limitations and plans for future work.