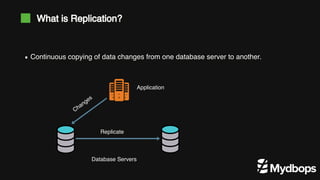
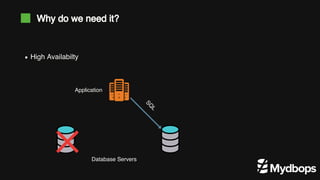
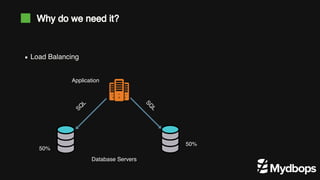
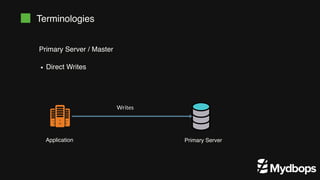
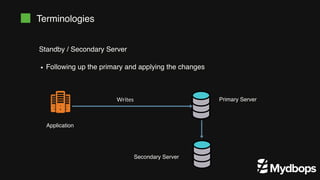
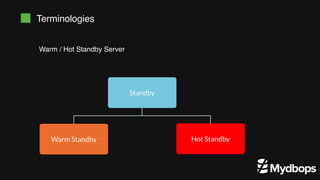
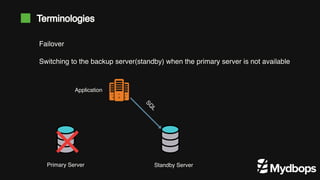
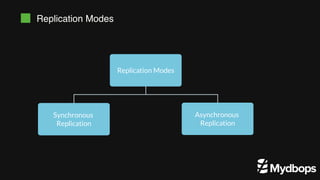
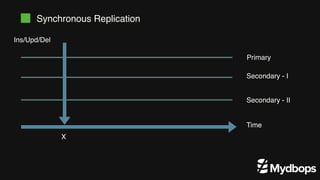
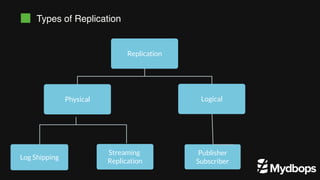
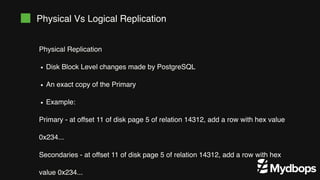
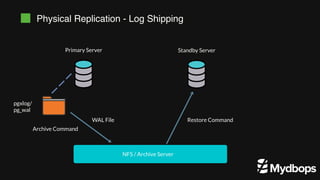
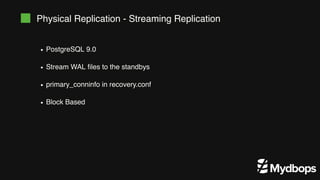
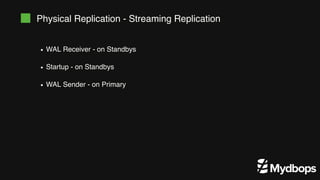
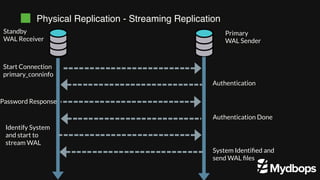
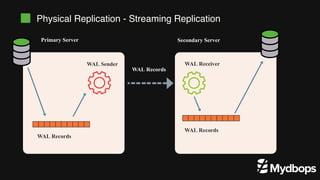
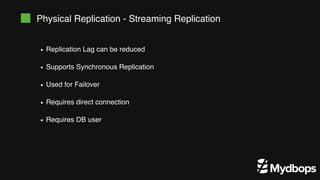
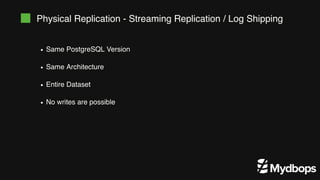
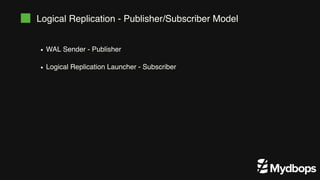
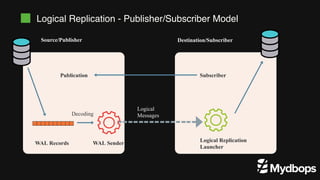
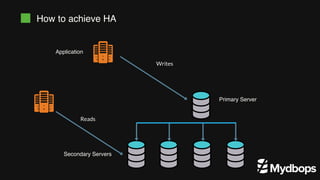
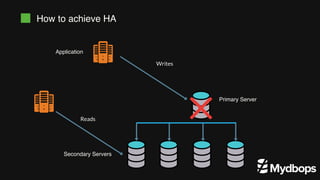
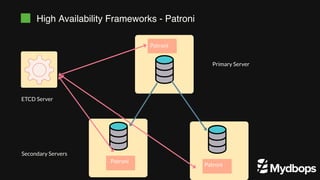
The document discusses PostgreSQL replication and high availability (HA) methods, including types like synchronous and asynchronous replication, as well as physical and logical replication. It outlines the importance of replication in maintaining database availability and performance, detailing various architectures and tools such as Patroni and repmgr for effective management. Additionally, it covers essential terminologies and practices related to replication and HA frameworks.