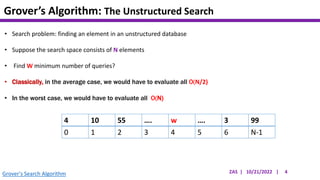
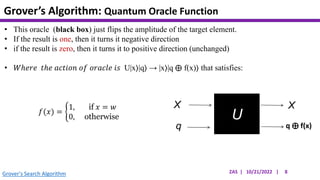
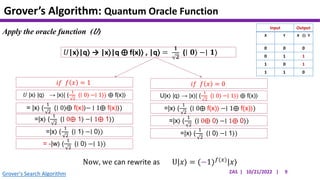
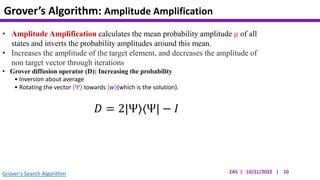
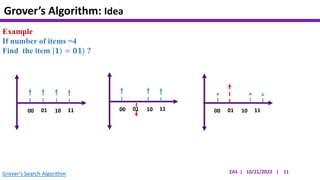
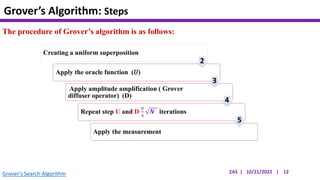
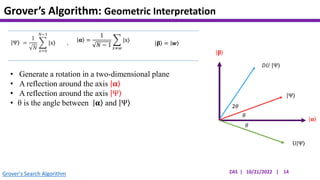
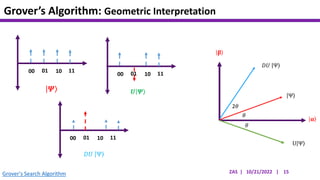
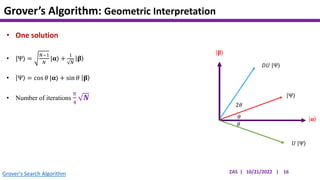
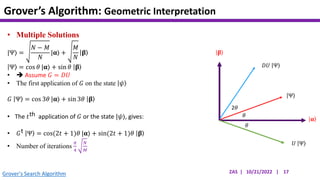
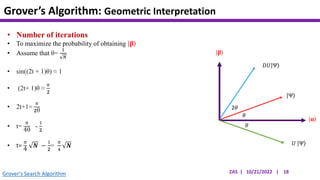
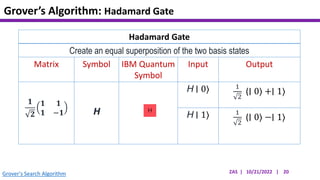
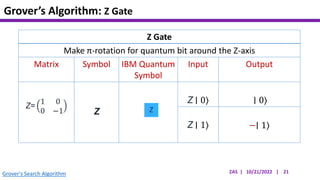
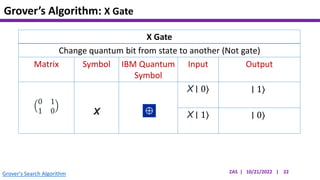
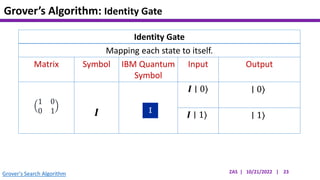
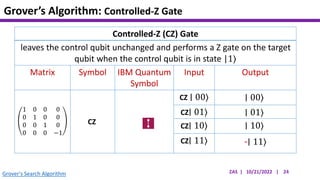
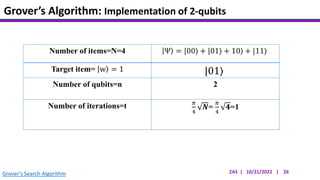
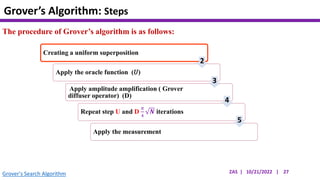
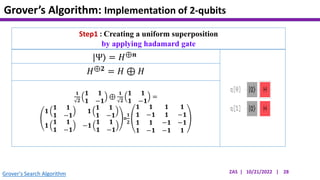
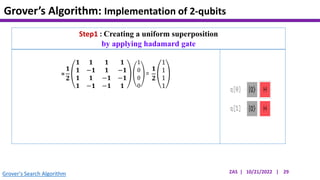
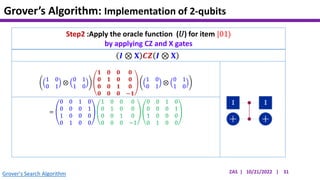
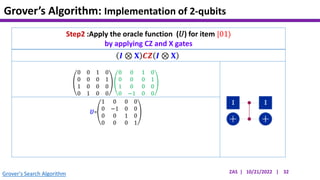
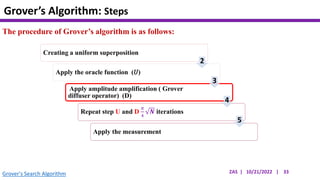
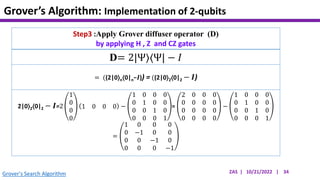
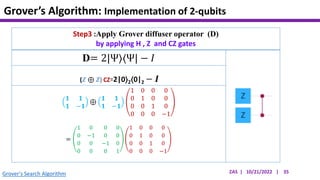
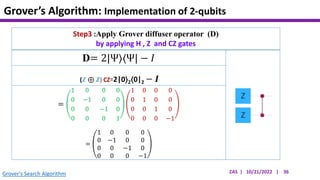
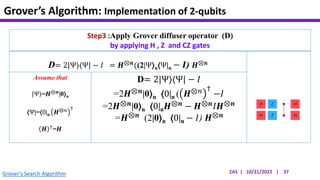
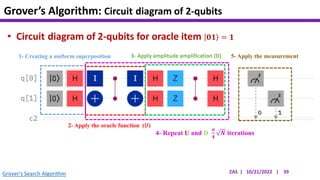
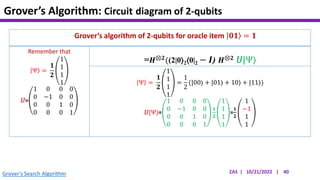
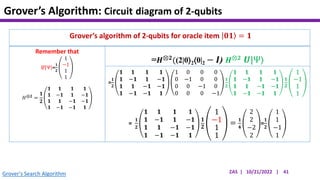
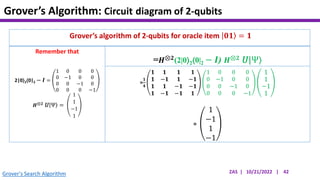
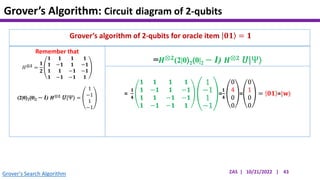
This document presents an implementation of Grover's quantum search algorithm using two qubits. Grover's algorithm allows searching an unstructured database with N elements using O(√N) iterations, compared to O(N) classically. The implementation first creates a uniform superposition of all states using Hadamard gates. It then applies an oracle function that inverts the amplitude of the target state. Amplitude amplification is performed using Grover's diffusion operator to increase the target state's probability. The process is repeated once, as the number of iterations is π√N/4 for this two-qubit example. Measurement then returns the target state with high probability.