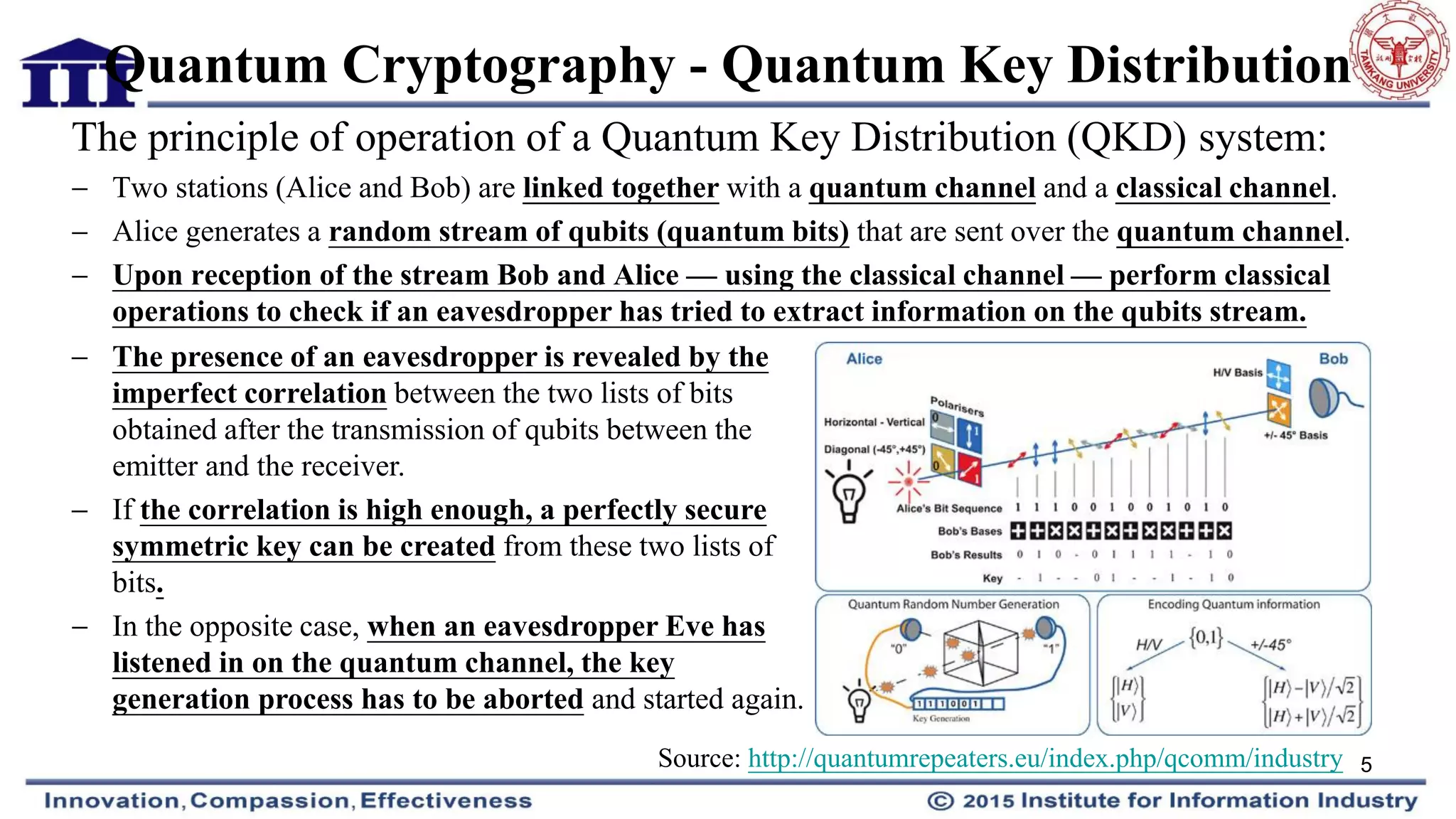
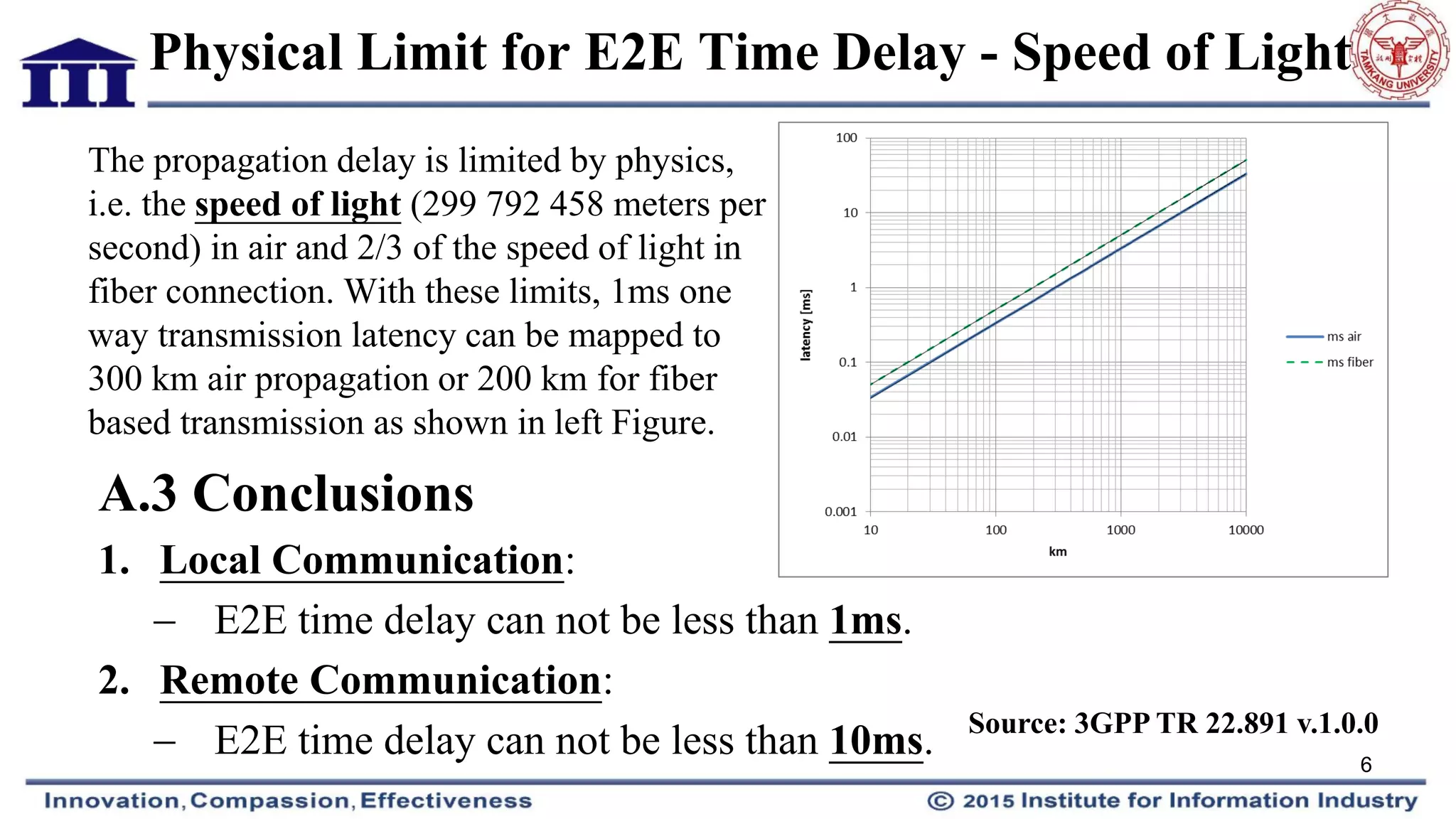
Quantum entanglement and quantum cryptography were discussed as potential technologies to improve communication security and reduce delays. Quantum key distribution uses quantum entanglement to securely generate and distribute encryption keys. However, the speed of light remains a fundamental limit on end-to-end communication delays. Faster-than-light transmission would be required to significantly shorten delays, which currently requires breakthroughs beyond existing physics theories.