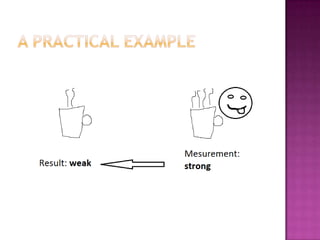
1) Quantum entanglement is a property where quantum states of objects cannot be described independently, even if separated spatially. A practical example involves two cups of hot chocolate where tasting one instantly reveals the other's state.
2) Bra-ket notation is used to describe quantum states as vectors or functionals in a Hilbert space. Operators act on these states to model physical quantities.
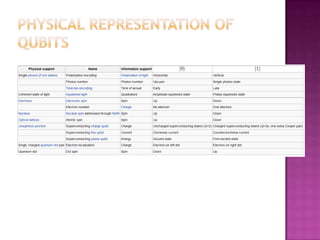
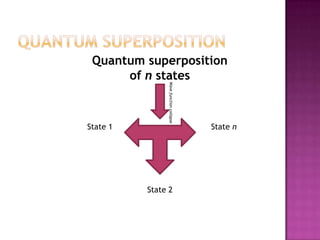
3) A qubit is the quantum analogue of a classical bit, existing in superposition of states |0> and |1>. Quantum computers use entanglement between qubits to perform computations in parallel.









![Bra-ket notationBra-ket notation is a standard notation for describing quantum states in the theory of quantum mechanics composed of angle brackets and vertical bars. It can also be used to denote abstract vectors and linear functionals in mathematics. It is so called because the inner product (or dot product) of two states is denoted by a bracket, , consisting of a left part, , called the bra (pronounced /ˈbrɑː/), and a right part, , called the ket (pronounced /ˈkɛt/). The notation was introduced in 1930 by Paul Dirac,[1] and is also known as Dirac notation.Bra-ket notation is widespread in quantum mechanics: almost every phenomenon that is explained using quantum mechanics—including a large proportion of modern physics—is usually explained with the help of bra-ket notation. The expression is typically interpreted as the probability amplitude for the state to collapse into the state](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumentanglement-110509154038-phpapp01/85/Quantum-entanglement-11-320.jpg)
![Bra-ket – usage in quantum mechanicsIn quantum mechanics, the state of a physical system is identified with a ray in a complexseparableHilbert space, , or, equivalently, by a point in the projective Hilbert space of the system. Each vector in the ray is called a "ket" and written as , which would be read as "ketpsi". (The can be replaced by any symbols, letters, numbers, or even words—whatever serves as a convenient label for the ket.)The ket can be viewed as a column vector and (given a basis for the Hilbert space) written out in coordinates,when the considered Hilbert space is finite-dimensional. In infinite-dimensional spaces there are infinitely many coordinates and the ket may be written in complex function notation, by prepending it with a bra (see below). For example,Every ket has a dualbra, written as . For example, the bra corresponding to the ket above would be the row vectorThis is a continuous linear functional from to the complex numbers , defined by:for all kets , where denotes the inner product defined on the Hilbert space. Here the origin of the bra-ket notation becomes clear: when we drop the parentheses (as is common with linear functionals) and meld the bars together we get , which is common notation for an inner product in a Hilbert space. This combination of a bra with a ket to form a complex number is called a bra-ket or bracket.The bra is simply the conjugate transpose (also called the Hermitian conjugate) of the ket and vice versa. The notation is justified by the Riesz representation theorem, which states that a Hilbert space and its dual space are isometrically conjugate isomorphic. Thus, each bra corresponds to exactly one ket, and vice versa. More precisely, ifis the Riesz isomorphism between and its dual space, thenNote that this only applies to states that are actually vectors in the Hilbert space. Non-normalizable states, such as those whose wavefunctions are Dirac delta functions or infinite plane waves, do not technically belong to the Hilbert space. So if such a state is written as a ket, it will not have a corresponding bra according to the above definition. This problem can be dealt with in either of two ways. First, since all physical quantum states are normalizable, one can carefully avoid non-normalizable states. Alternatively, the underlying theory can be modified and generalized to accommodate such states, as in the Gelfand-Naimark-Segal construction or rigged Hilbert spaces. In fact, physicists routinely use bra-ket notation for non-normalizable states, taking the second approach either implicitly or explicitly.In quantum mechanics the expression (mathematically: the coefficient for the projection of onto ) is typically interpreted as the probability amplitude for the state to collapse into the state The advantage of the bra-ket notation over explicit wave function algebra is the possibility of expressing operations on quantum states independent of a basis. For example the Schrödinger equation is simply expressed asThe operators can be conveniently expressed in different bases (see next section for the operations used in these formulas : action of a linear operator, outer product of a ket and a bra):(For a rigorous definition of basis with a continuous set of indices and consequently for a rigorous definition of position and momentum basis see [2])(For a rigorous statement of the expansion of an S-diagonalizable operator - observable - in its eigenbasis or in another basis see [3])The wave functions in real, momentum or reciprocal space can be retrieved as needed:and all basis conversions can be performed via the relations such as(for a rigorous treatment of the Dirac inner product of non-normalizable states see the definition given by D. Carfì in [4] and [5])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumentanglement-110509154038-phpapp01/85/Quantum-entanglement-12-320.jpg)
![Mathematical formulations of quantum mechanicsThe mathematical formulations of quantum mechanics are those mathematical formalisms that permit a rigorous description of quantum mechanics. Such are distinguished from mathematical formalisms for theories developed prior to the early 1900s by the use of abstract mathematical structures, such as infinite-dimensional Hilbert spaces and operators on these spaces. Many of these structures are drawn from functional analysis, a research area within pure mathematics that was influenced in part by the needs of quantum mechanics. In brief, values of physical observables such as energy and momentum were no longer considered as values of functions on phase space, but as eigenvalues; more precisely: as spectral values (point spectrum plus absolute continuous plus singular continuous spectrum) of linear operators in Hilbert space.[1]These formulations of quantum mechanics continue to be used today. At the heart of the description are ideas of quantum state and quantum observable which are radically different from those used in previous models of physical reality. While the mathematics permits calculation of many quantities that can be measured experimentally, there is a definite theoretical limit to values that can be simultaneously measured. This limitation was first elucidated by Heisenberg through a thought experiment, and is represented mathematically in the new formalism by the non-commutativity of quantum observables.Prior to the emergence of quantum mechanics as a separate theory, the mathematics used in physics consisted mainly of differential geometry and partial differential equations; probability theory was used in statistical mechanics. Geometric intuition clearly played a strong role in the first two and, accordingly, theories of relativity were formulated entirely in terms of geometric concepts. The phenomenology of quantum physics arose roughly between 1895 and 1915, and for the 10 to 15 years before the emergence of quantum theory (around 1925) physicists continued to think of quantum theory within the confines of what is now called classical physics, and in particular within the same mathematical structures. The most sophisticated example of this is the Sommerfeld–Wilson–Ishiwara quantization rule, which was formulated entirely on the classical phase space.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumentanglement-110509154038-phpapp01/85/Quantum-entanglement-13-320.jpg)

![Quantum bitsIn quantum computing, a qubit (/ˈkjuːbɪt/) or quantum bit is a unit of quantum information—the quantum analogue of the classical bit—with additional dimensions associated to the quantum properties of a physical atom. The physical construction of a quantum computer is itself an arrangement of entangled[clarification needed] atoms, and the qubit represents[clarification needed] both the state memory and the state of entanglement in a system. A quantum computation is performed by initializing a system of qubits with a quantum algorithm —"initialization" here referring to some advanced physical process that puts the system into an entangled state.[citation needed]The qubit is described by a quantum state in a two-state quantum-mechanical system, which is formally equivalent to a two-dimensional vector space over the complex numbers. One example of a two-state quantum system is the polarization of a single photon: here the two states are vertical polarisation and horizontal polarisation. In a classical system, a bit would have to be in one state or the other, but quantum mechanics allows the qubit to be in a superposition of both states at the same time, a property which is fundamental to quantum computing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumentanglement-110509154038-phpapp01/85/Quantum-entanglement-15-320.jpg)