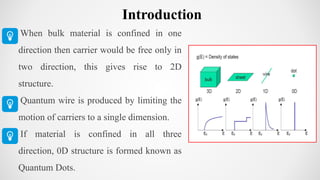
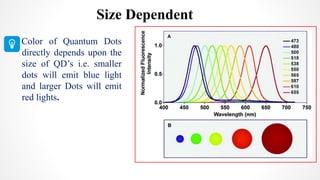
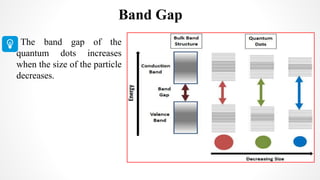
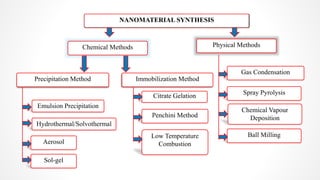
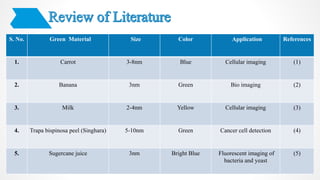
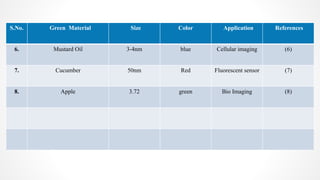
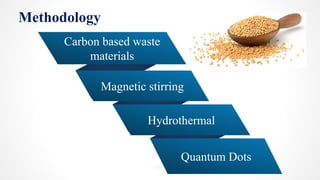
The document discusses the green synthesis of fluorescent carbon quantum dots, detailing their properties, synthesis methods, and various applications in fields like cellular imaging and bioimaging. It emphasizes the significance of size-dependent properties of quantum dots, which can emit different colors based on size, and outlines methodologies for characterizing these quantum dots. The conclusion highlights the innovative potential of quantum dots in multiple industries and future applications.