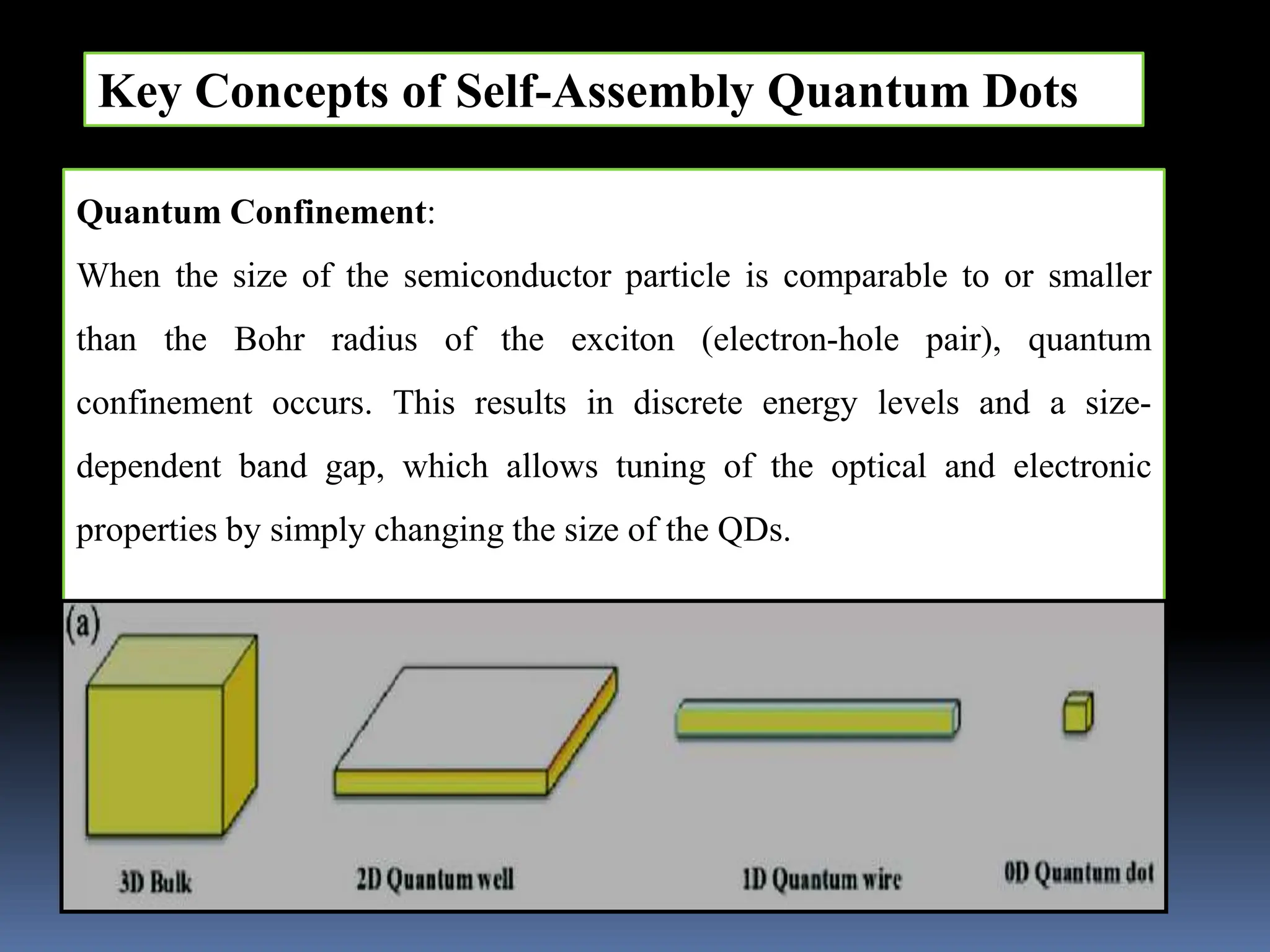
Self-assembled quantum dots (QDs) are nanoscale semiconductor particles with unique optical and electronic behaviors due to their size, enabling applications in optoelectronics, quantum computing, and biomedical imaging. The growth techniques for QDs include molecular beam epitaxy, chemical vapor deposition, and colloidal synthesis, each with specific advantages and challenges related to factors such as temperature and material choice. Ongoing research aims to enhance the efficiency and stability of QDs while addressing their toxicity and reducing production costs.