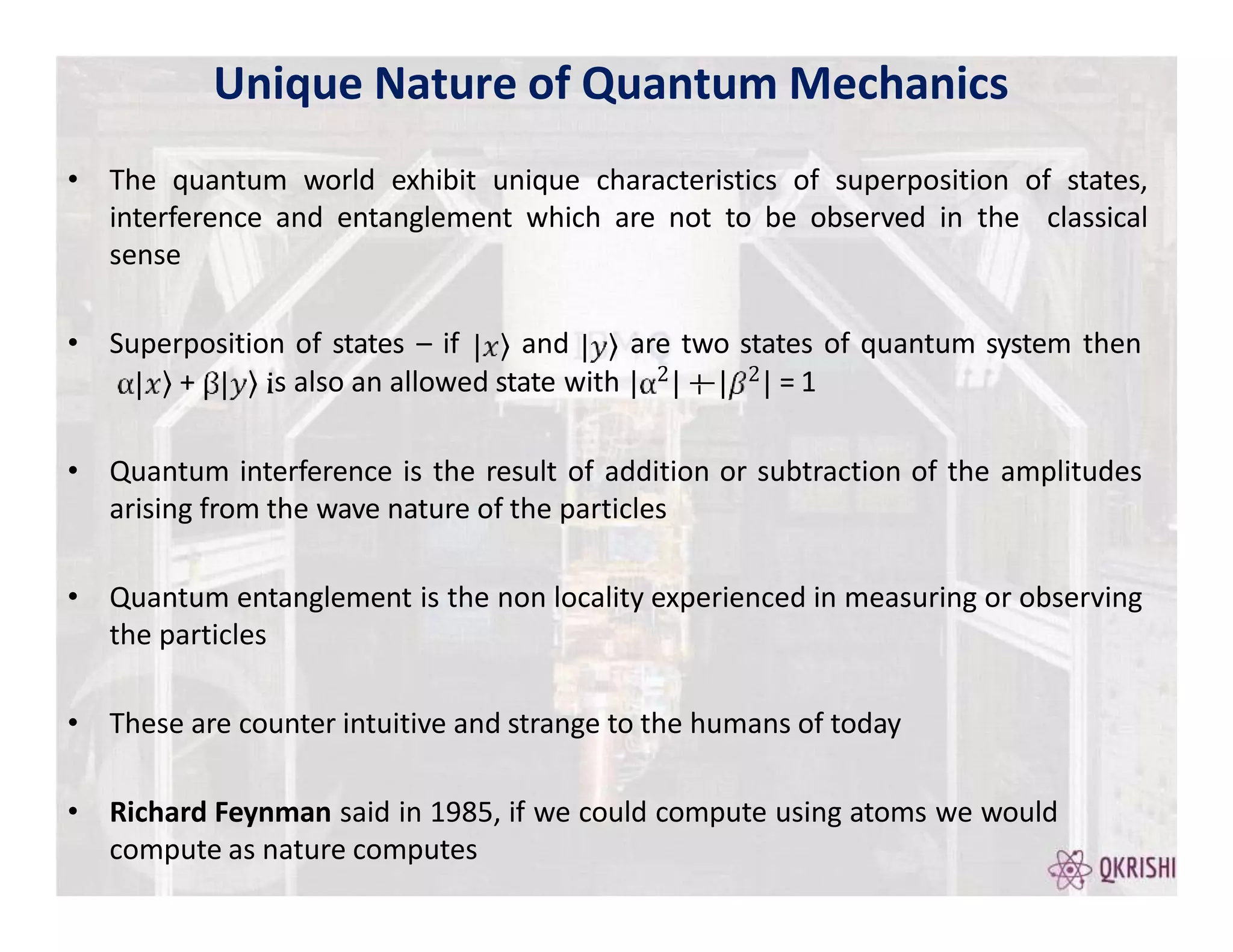
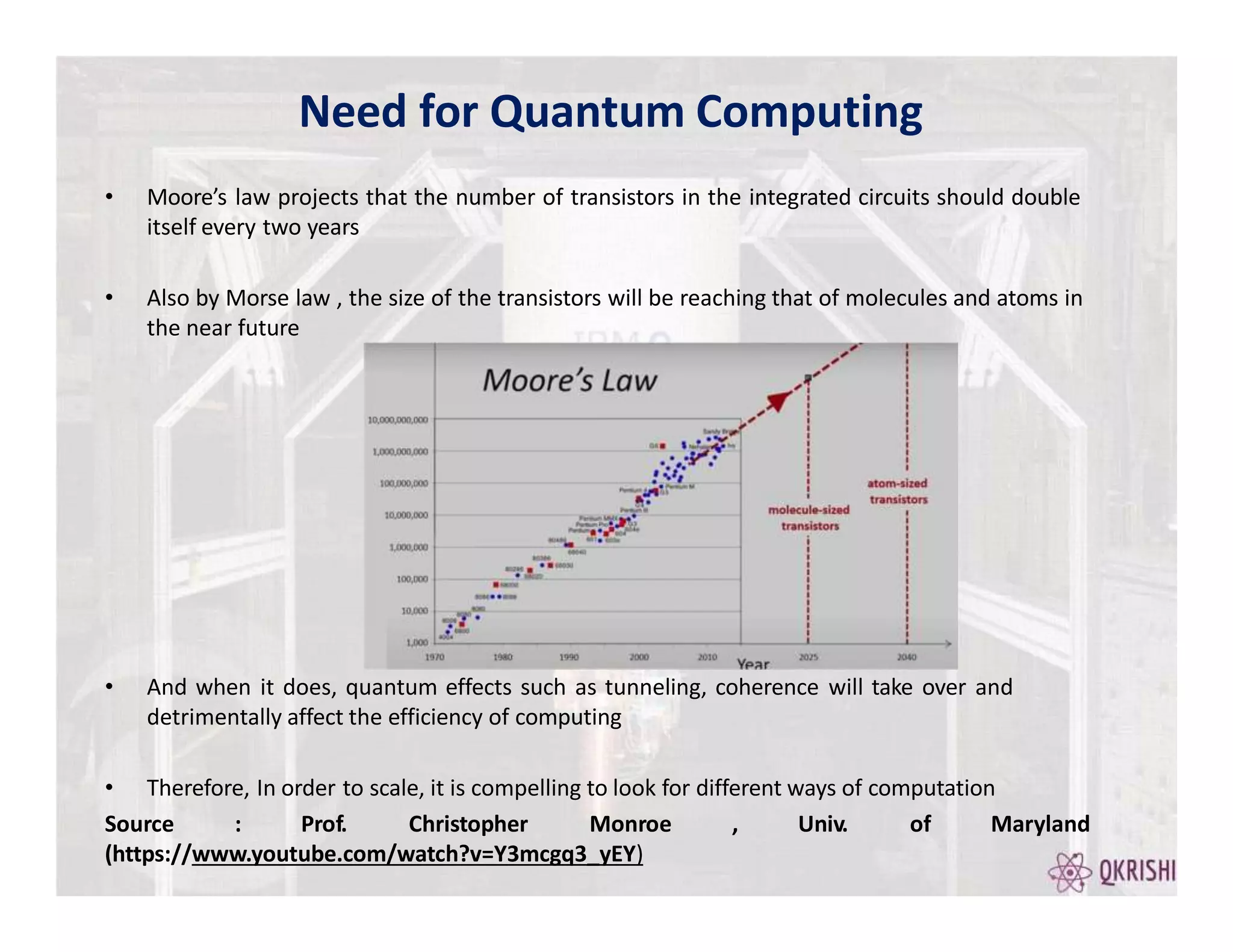
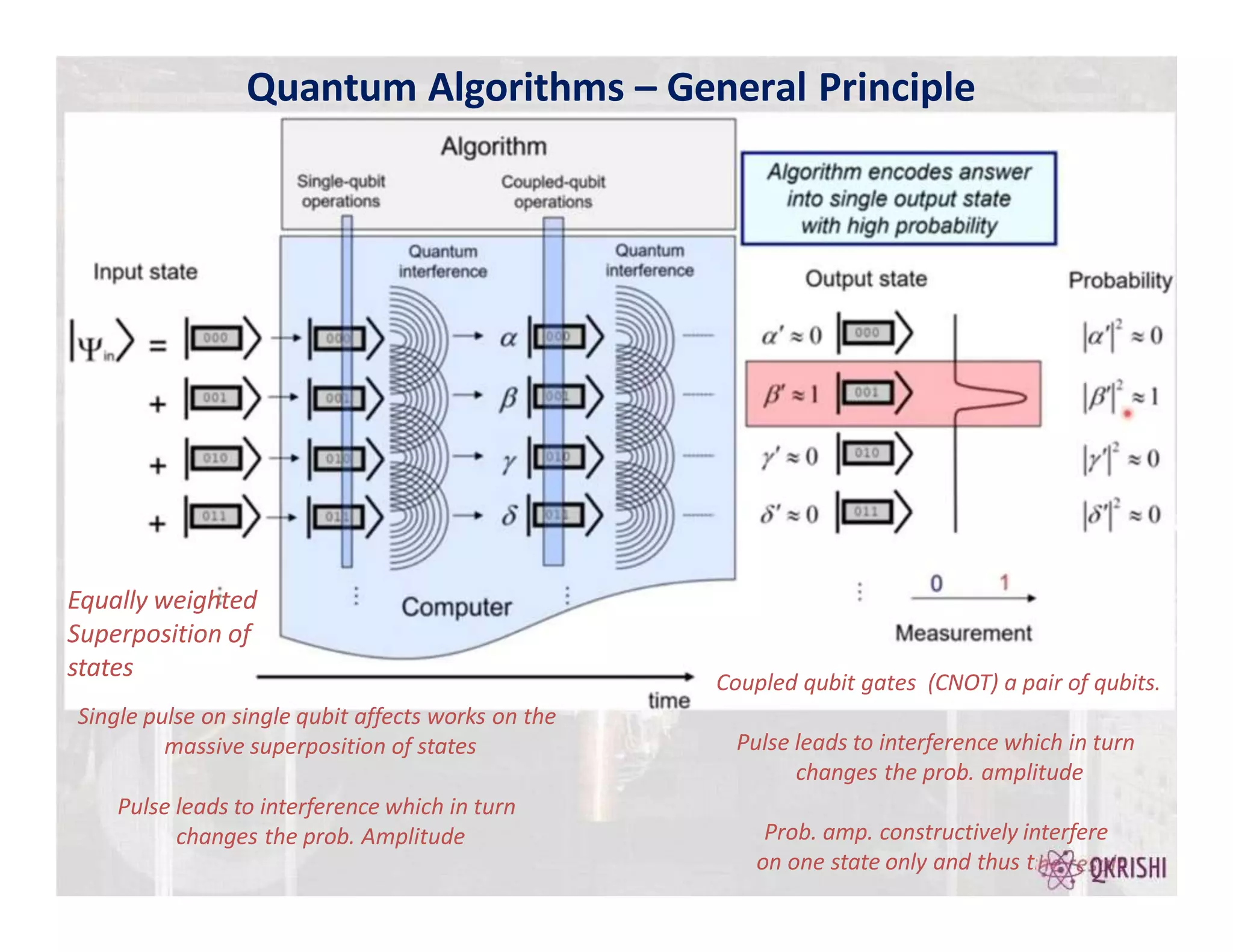
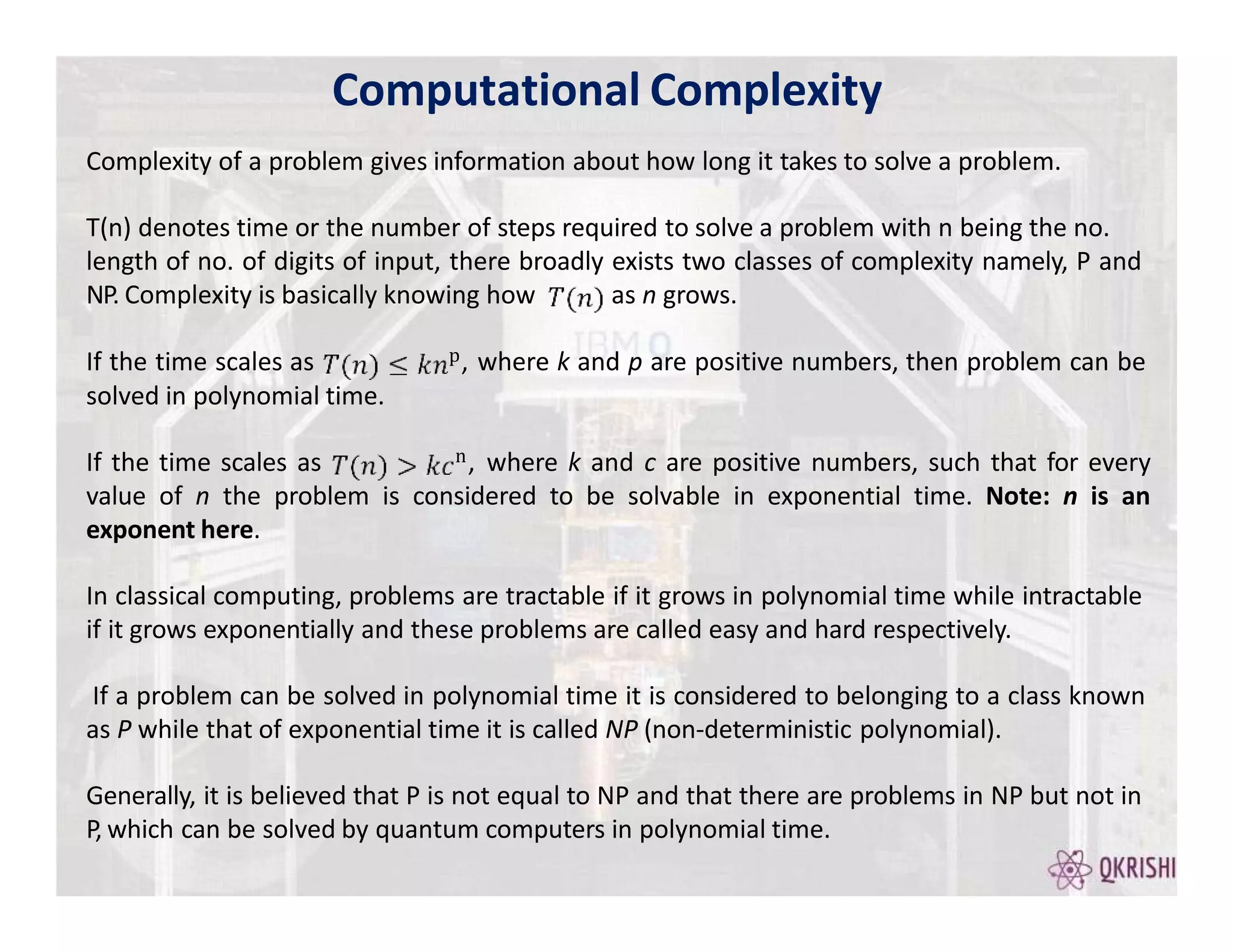
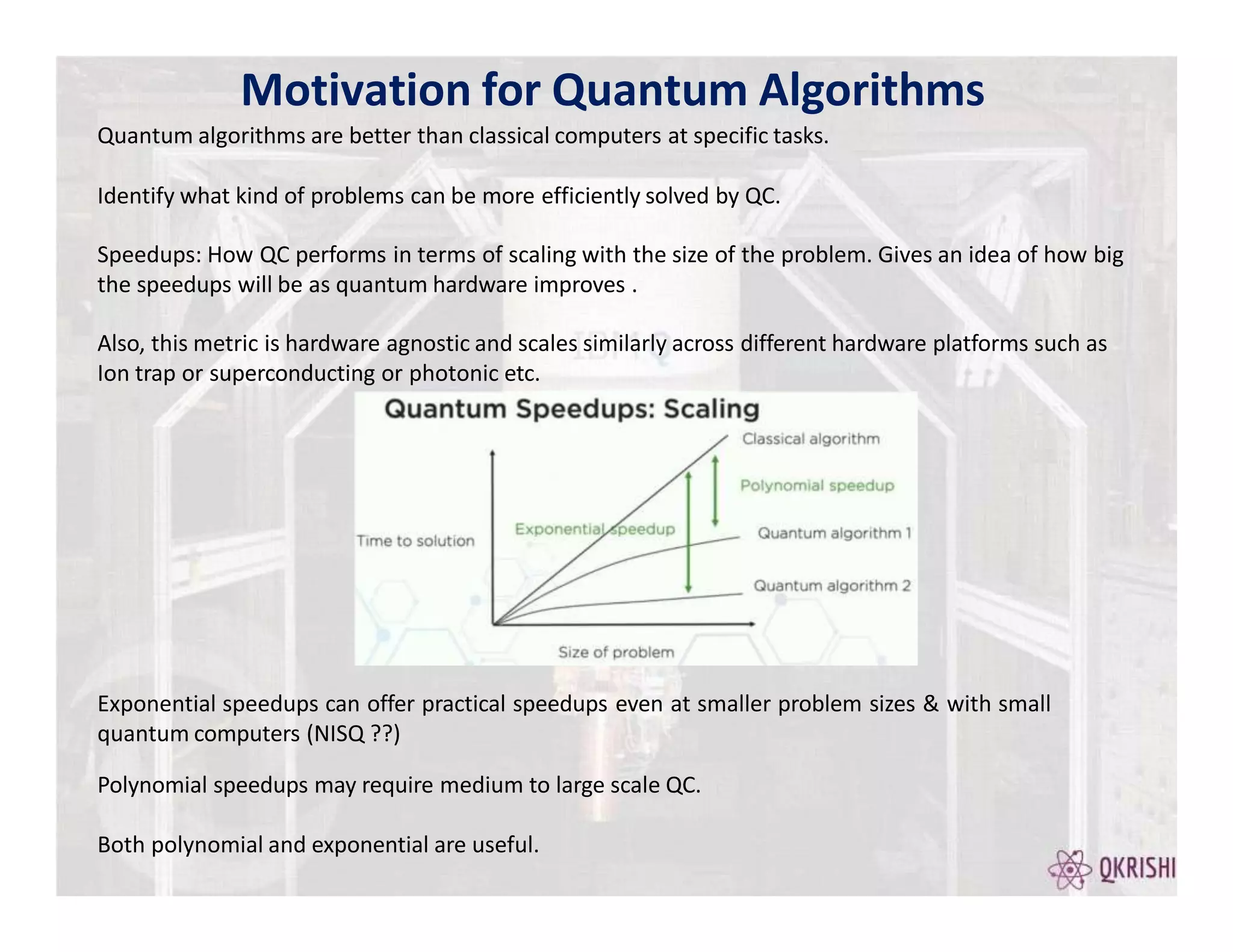
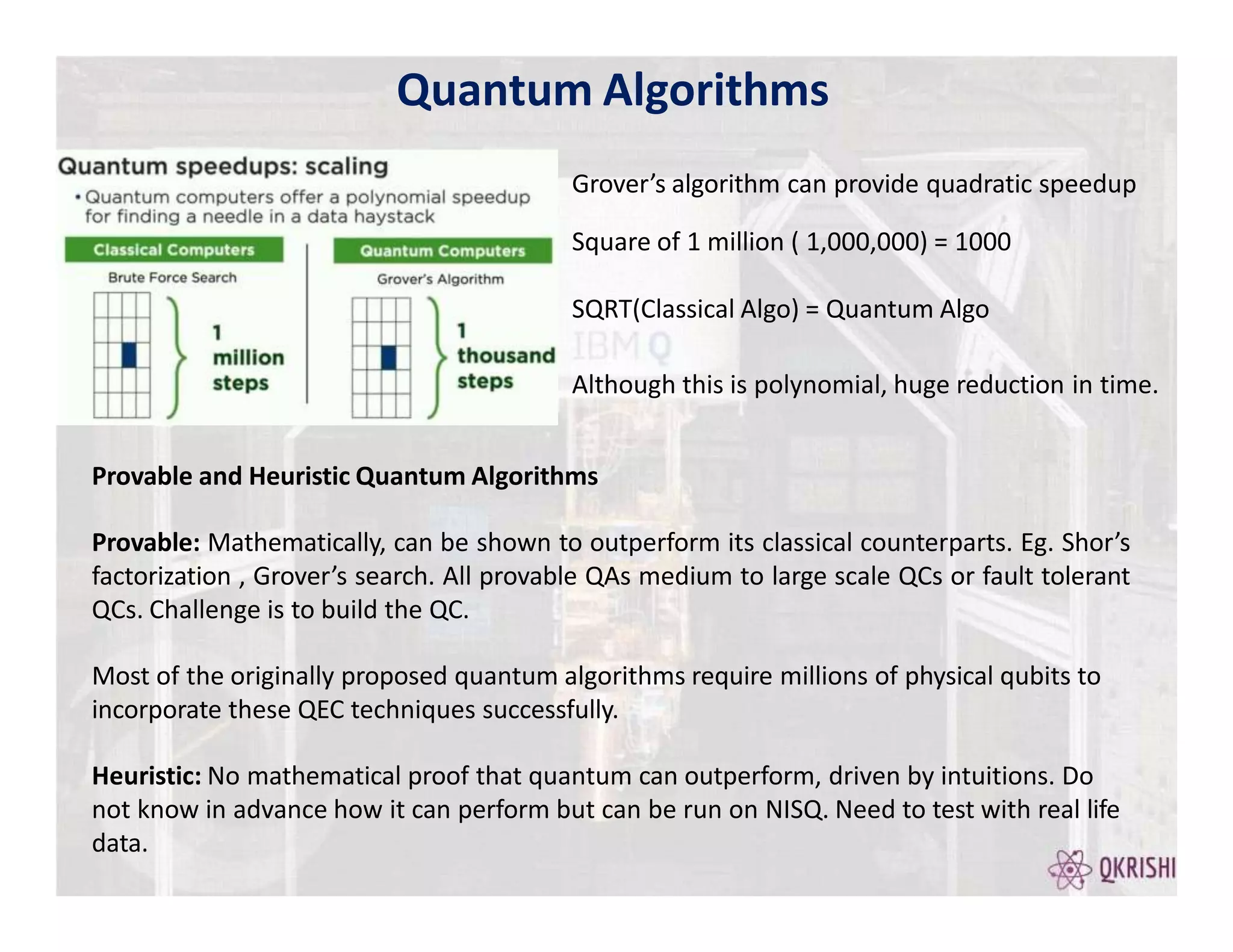
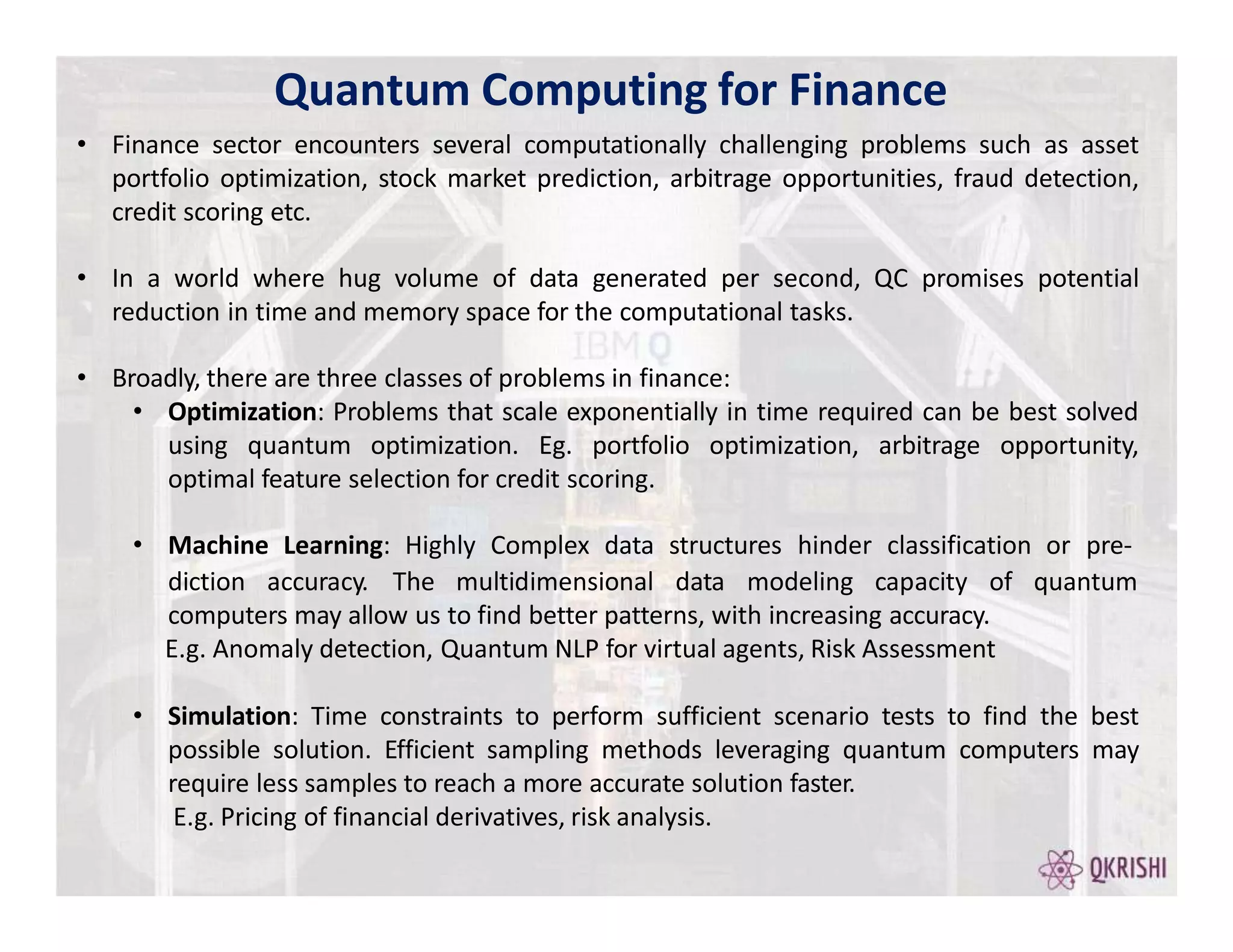
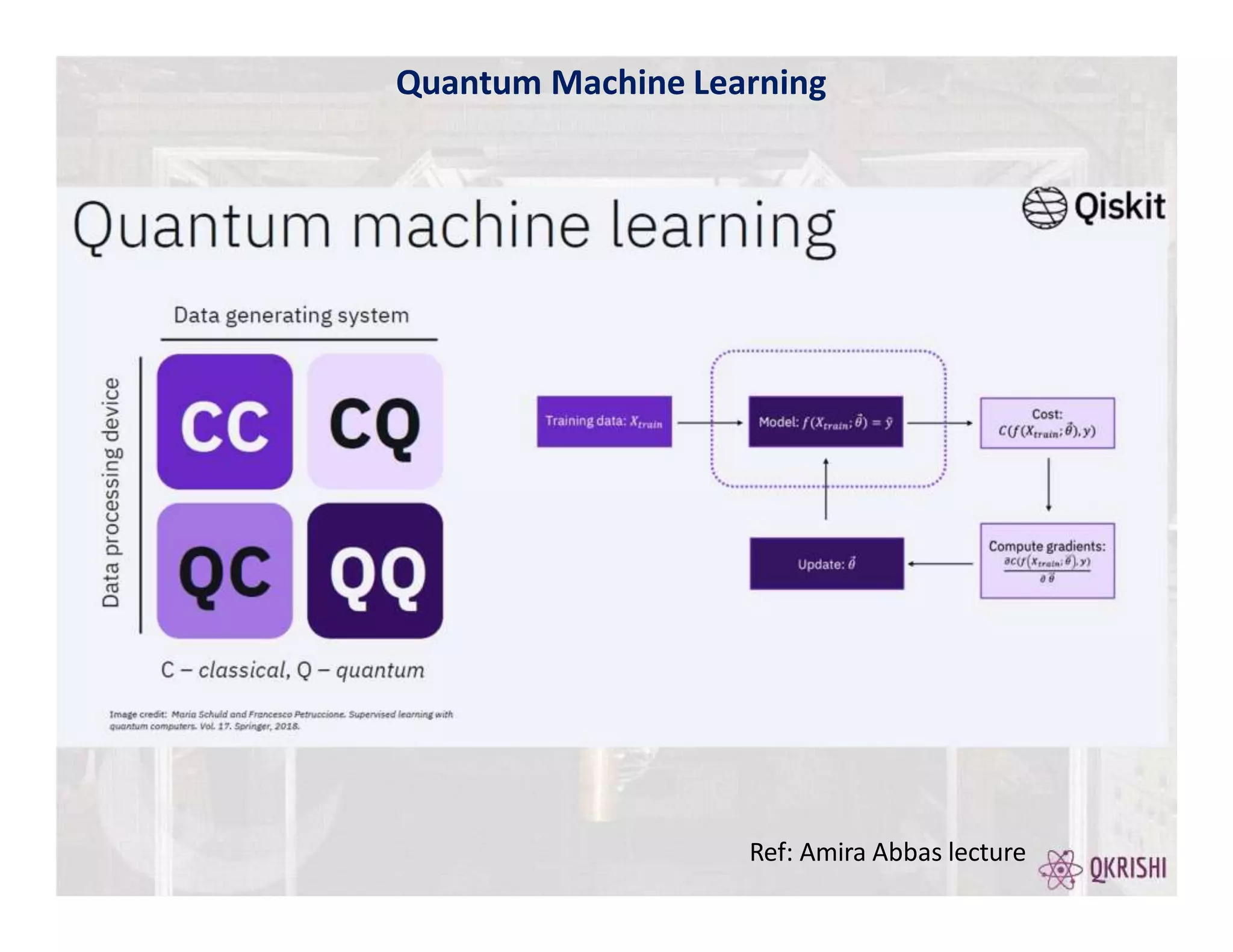
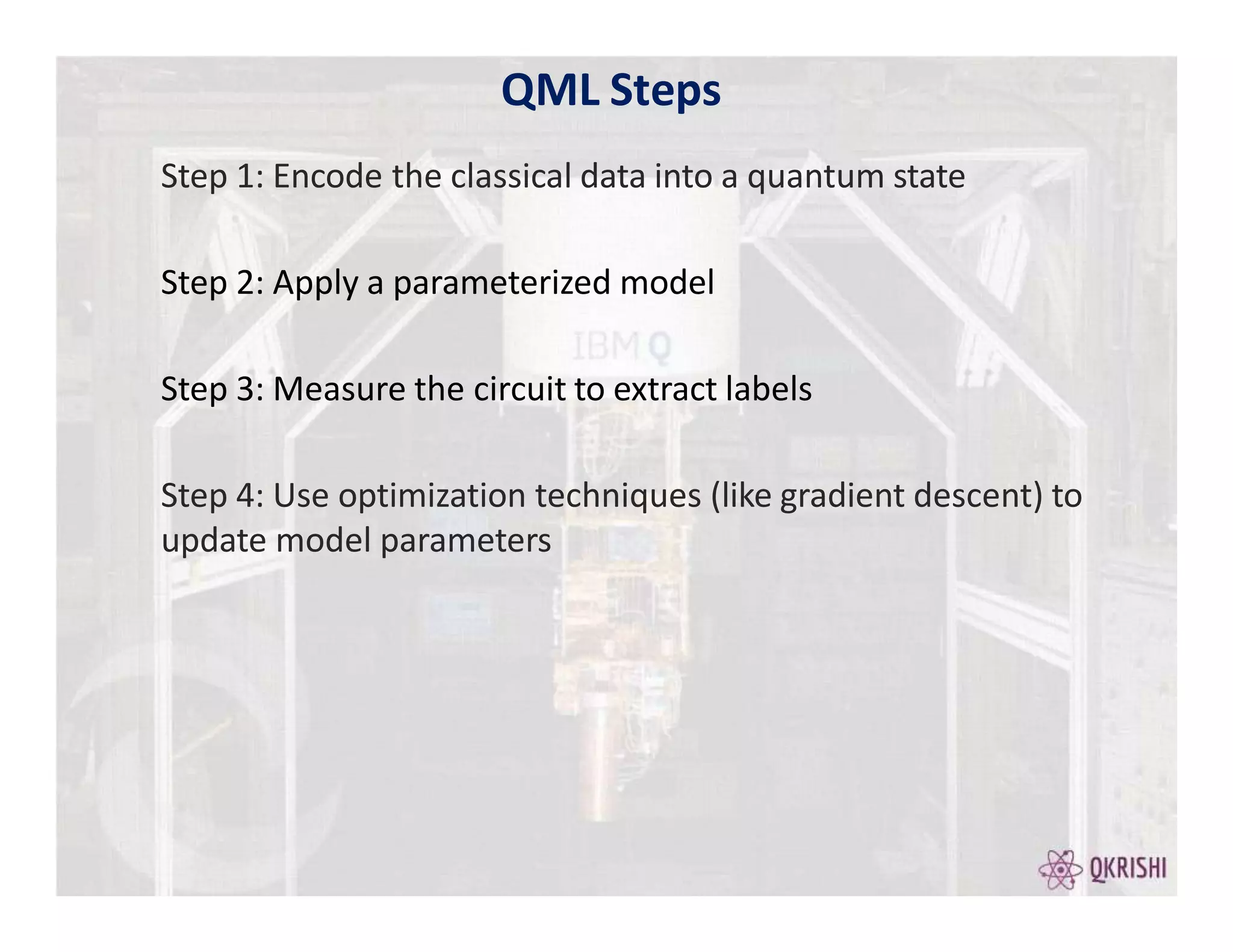
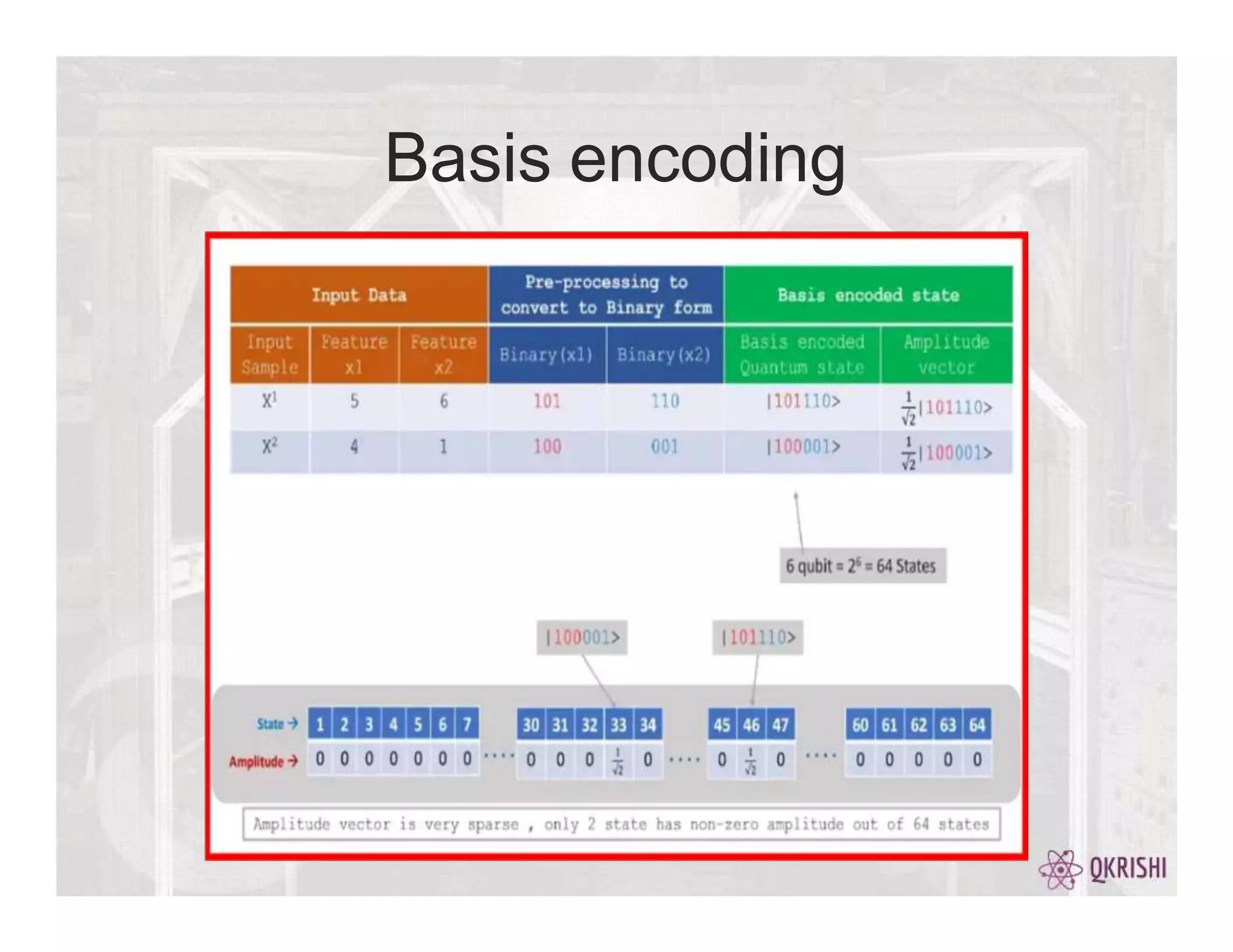
Quantum computing has the potential to solve certain problems exponentially faster than classical computers by exploiting principles like superposition, entanglement, and interference. Current quantum computers with 50-100 qubits operate in the Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) era and use algorithms like the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) that are hybrid quantum-classical and incorporate techniques like quantum error mitigation. Major players in the field include IBM, Google, and Rigetti who are developing quantum hardware and software for applications in optimization, simulation, and machine learning.


















![Unraveling the Effect of COVID-19 on the Selection of Optimal Portfolio Using Hybrid
QuantumAlgorithms
1Shrey Upadhyay, 2Vaidehi Dhande, 1Rupayan Bhattacharjee, 1Ishan NH Mankodi, 1Aaryav Mishra, 2Anindita Banerjee, 1Raghavendra Venkatraman
The unforeseen COVID-19 pandemic delivered a huge blow to the global economy. This
poster elaborates the effect of COVID-19 on the portfolio optimization across different
industrial sectors retail, technology, automotive,oil & gas, airlines & hospitality.
Portfolio Optimization is to select best portfolios with an objective to maximize the return
value and minimize the risk factor. To understand the trend in Portfolio Optimization pre
covid-19 and during covid-19 three time intervals are considered and the results from
different quantum algorithms are compared with classical results. The quantum algorithms
used are Variational Quantum Eigen solver (VQE), Quantum Approximate Optimization
Algorithm (QAOA).
Outline
Covariance Graphs
Abstract
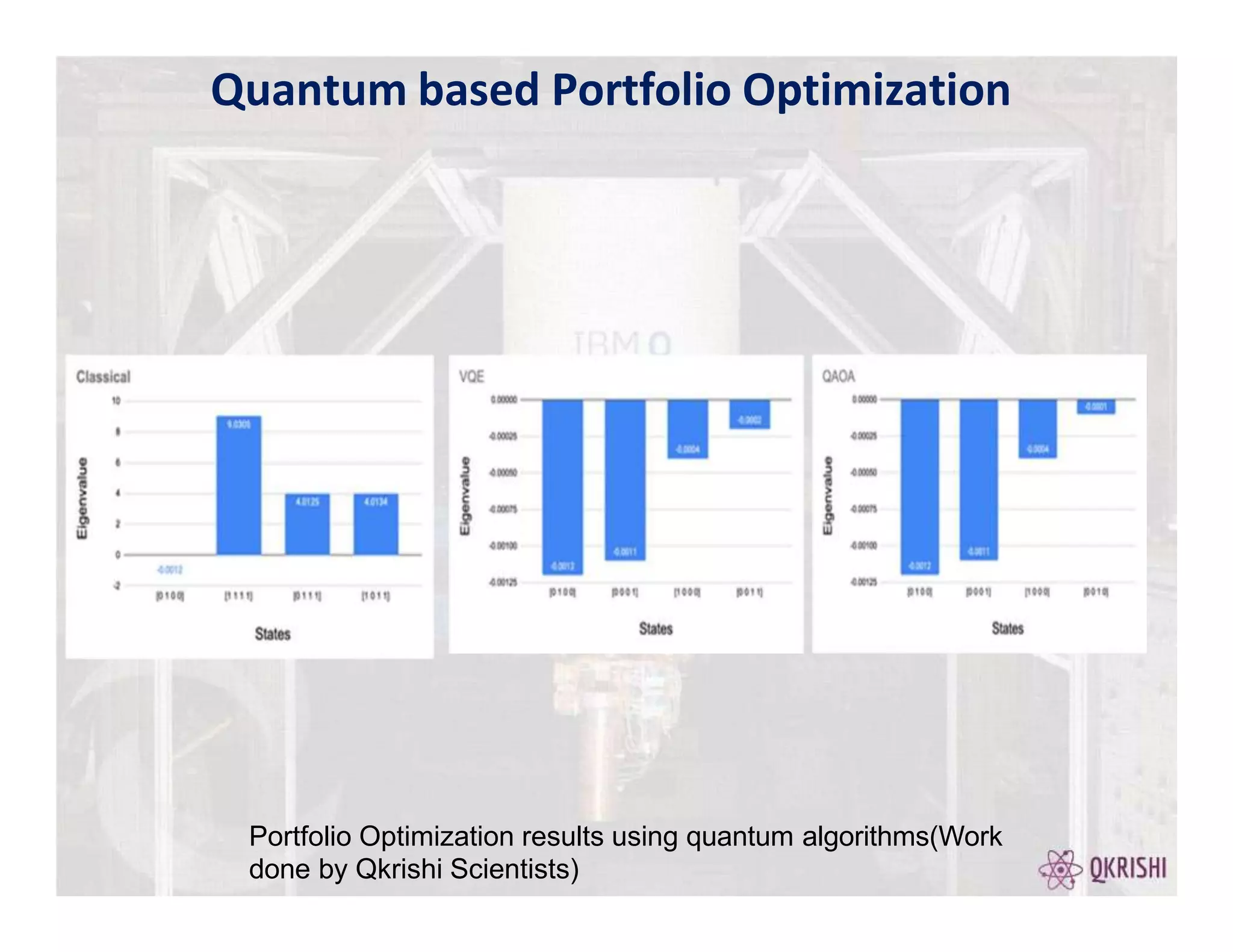
1. Portfolio Optimization- MaximizeReturns and Minimize Risk
2. Classical Algorithms- Markowitz, Numpy EigenSolver
3. QuantumComputing-VQE,QAOA
4. Impactof Covid-19 on portfolio optimization
Pool Non-COVID1
(Jan ‘16-Dec ‘17)
Non-COVID2
(Jan ‘18-Dec ‘19)
COVID
(Jan ‘20-Dec ‘21)
Retail
Technolog
y
Automoti
ve
Oil & Gas
Airlines &
Hospitalit
y
Main objectiveof portfolio optimization is:
1. The investor’s goal is to maximize return for low level of risk
2.Risk can be reduced by diversifying a portfolio through individual, unrelated securities
Initially, the problem of portfolio optimization is translated into the form of variation
circuit called ansatz to enable the quantumcomputer to perform optimization on the
objectivefunction.
VQE is Hybrid Quantum-classical algorithm. VQEwhich is developed on Variational
Principle calculates the lowest energy which corresponds to the optimal portfolio
It aims to find an upper bound of the lowest eigenvalue of a given Hamiltonian.
Methods
0.0015 0.0015 0.0006 0.0006 0.0008 0.0008
1QKrishi, 2C-DAC- India
Methods Cont..
VQE has two fundamental steps:
1. Prepare the quantum state |Ψ(θ)⟩
2. Measure the expectation value ⟨Ψ(θ)|H|Ψ(θ)⟩
3. Optimize the parameter θ on classical computer and generate the updated wavefunction
4. Calculate the expectation value again for the updated wavefunction
5. Iterateuntil convergence criteria is met
QAOA is widely popular methodfor solving combinatorial optimization problems. The VQEalgorithm applies
classical optimization to minimize the energy expectationof an ansatz state to find the ground state energy.
Impact of Covid
Pool
Non-
COVID1
Non-
COVID2
COVID Reason
Results Retail
(Costco,
Amazon, Target,
Walmart)
COST TGT COST
COST & TGT are major
market share holders and as
they open new stores to at
more locations and while
offering the products at
affordable prices, drives the
growthof COST.
Pool
Non-COVID1
(Jan ‘16-Dec ‘17)
Non-COVID2
(Jan ‘18-Dec ‘19)
COVID
(Jan ‘20-Dec ‘21)
Technology
(Google, IBM,
Intel, Microsoft)
GOOG GOOG MSFT
GOOG remains the most
used IT service in the world
in terms of apps and
browsers. MSFT also control
majority of the OS used
worldwide, while launching
its own hardwareproducts.
Retail [0 1 0 0], - [0
0.0012 1 0
0]
[0 1 0 0], - [0 1 0 0],-
[0 0 1 0], - [1 0 0
0.0014 0]
[1 0 0 0], - [0 0 1 0], -
[1 0 0 0], - [1 0 0 0]
0.0014
[1 0 0 0], - [1 0 0 0],-
Automotive
(General
Motors,
Mercedes,
Tesla, Ford )
GM TSLA TSLA
GM owned a large market
cap in automotive around
2016, but as people accept
EV as a better alternative to
gas powered engines, and
look for greener ways of
transport which is also more
technology wise advanced,
TSLA soars after 2017.
Technology
0.0012 0.0012
[0 0 0 1], -0.001 [0 0 0 1]
[0 0 0 1], -0.001 [0 0 0 1] , -
0.0014 0.0014
[0 0 0 1},- [0 0 0 1]
0.0013
[0 0 0 1] , - [0 0 0 1] , -
0.0014 0.0014
[0 0 0 1] , - [0 0 0 1]
0.0015
[0 0 0 1] , - [0 0 0 1] , -
Oil & Gas
(Shell, Conoco
Phillips,
Marathon Oil,
Chevron Corp.)
CVX COP CVX
CVX & COP control majority
of gas and oil extraction in us
and also in some parts of the
world. As they continue to
innovate and expand in the
hydrocarbon fuel markets.
Airlines &
Hospitality
(Marriott Int,
Choice Hotels,
LTC Properties,
Alaska Air)
MAR CHH MAR
MAR and CHH remains
people’s first choice. As they
continue to grown and make
newer and more luxurious
properties. The in them
considerably increases with
time
Automotive
0.001
[0 0 1 0] , - [1 0 0 0]
0.007
[1 0 0 0] , - [0 0 1 0] , -
0.0013 0.0013
[0 0 1 0] , - [0 0 1 0]
0.005
[1 0 0 0] , 0.001 [0 0 1 0] , -
0.0015 0.0015
[0 0 1 0] , - [0 0 1 0]
0.005
[0 0 0 1], , - [0 0 1 0], , -
Conclusions
References
• Egger, D.J., Gambella, C., Marecek, J., McFaddin, S., Mevissen, M.,
Raymond, R., Simonetto, A., Woerner, S. and Yndurain, E. (2020).
QuantumComputing for Finance: State-of-the-Art and Future
Prospects. IEEETransactions on QuantumEngineering, 1, pp.1–24.
doi:10.1109/tqe.2020.3030314.
• Herman, D., Googin, C., Liu, X., Galda, A., Safro, I., Sun, Y., Pistoia,
M., Alexeev, Y. and Chase Bank, J. (2022). A Survey of Quantum
Computingfor Finance. arxiv:2201.02773
Oil & Gas
Classical 0.006 0.007
[1 0 0 0] , - [1 0 0 0]
VQE
0.001 QAOA
[1 0 0 0] , - [1 0 0 0] , -
Classical
0.005
[0 1 0 0] , - [0 1 0 0]
VQE QAOA
0.0004
[0 1 0 0] , - [0 1 0 0] , -
Classical 0.0016 0.005
[0 0 1 0] , - [0 0 1 0]
QAOA
VQE
0.0005
[0 0 1 0] , - [0 0 1 0] , -
Airlines &
Hospitality
Classical 0.001 0.001
[1 0 0 0] , - [1 0 0 0]
VQE QAOA
0.0015
[1 0 0 0] , - [1 0 0 0] , -
Classical 0.0004 0.0004
[0 1 0 0] , -
QAOA
[0 1 0 0]
VQE
0.0006
[0 1 0 0] , - [0 1 0 0] , -
Classical 0.0005 0.0005
VQE
[0 1 0 0] , - QAOA [0 1 0 0]
0.0008
[0 1 0 0] , - [0 1 0 0] , -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumaiinfinanceppt-230106095640-497f2bd4/75/Quantum-AI-in-Finance-32-2048.jpg)